Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Wearable technology refers to electronic devices or clothing that are worn on the body to collect, store, and transmit wearer data, such as physiological parameters and other metrics. Such devices also monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, electrocardiograms (ECG), sleep, and even brain activity. These devices are also increasingly equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities.
They find applications across industries from sports and fashion to healthcare and manufacturing. As a result, wearables provide granular and wearer-specific insights into customers and employees that aid decision-making. In this report, we analyzed 3 428 startups to identify emerging wearable trends. They include head-mounted displays (HMDs), smart clothing, location tracking, and more. Read more to explore how these trends impact your business.
This article was last updated in August 2024.
What are the Top Wearables Trends in 2025?
- Head-mounted Displays
- Beacon Technology
- GPS Trackers
- Wearable Heart Monitors
- Smart Clothing
- Hearables
- 5G
- Artificial Intelligence
- Biosensors
- Big Data & Analytics
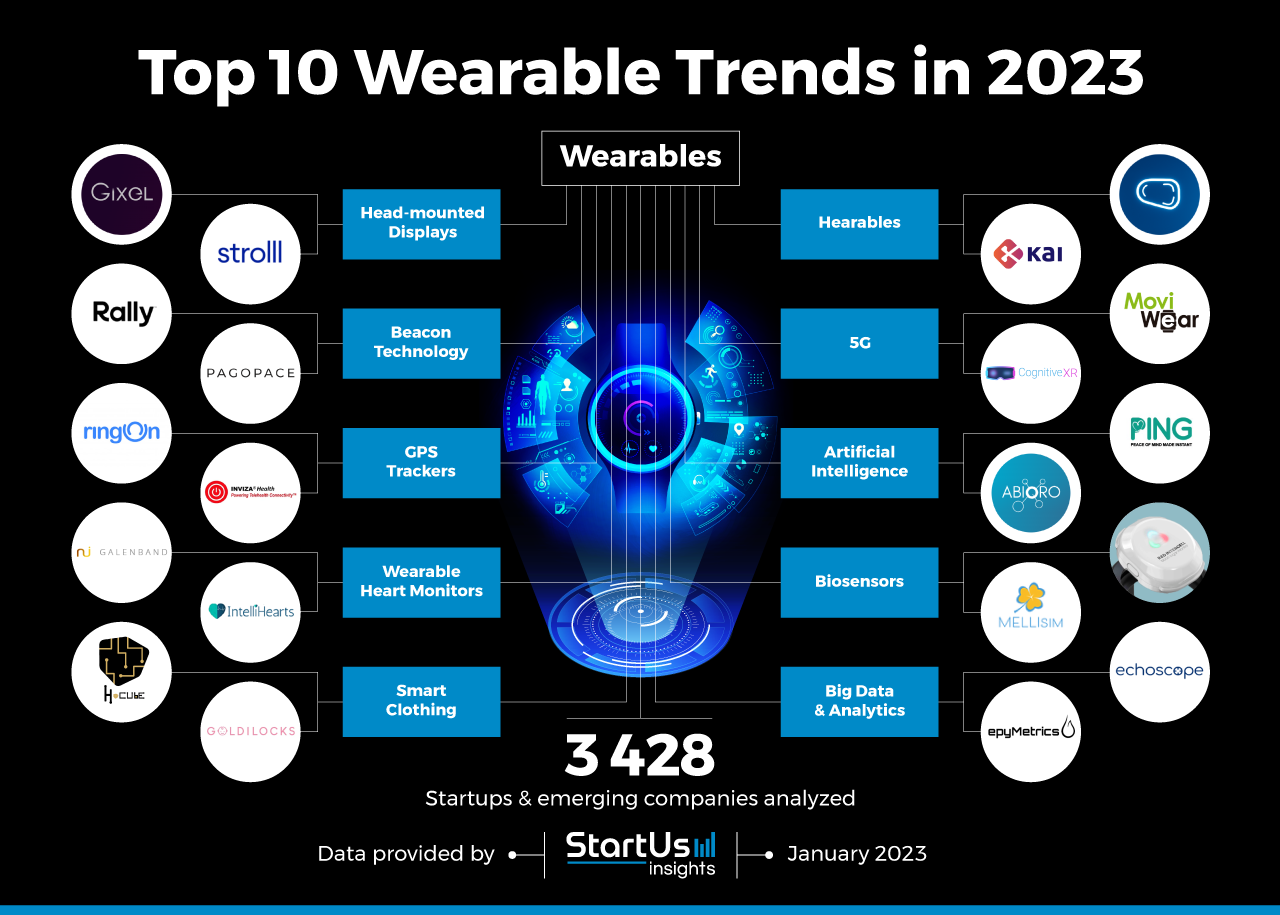
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Wearables Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Wearable Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 3 428 global startups & scaleups. The result of this research is data-driven innovation intelligence that improves strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies & startups in the wearables industry.
In the Innovation Map below, you get an overview of the Top 10 Wearable Trends & Innovations that impact 3 428 companies worldwide. Moreover, the Wearables Innovation Map reveals 20 hand-picked startups, all working on emerging technologies that advance their field.
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 4.7M+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
Want to explore all Wearable Technology innovations & trends?
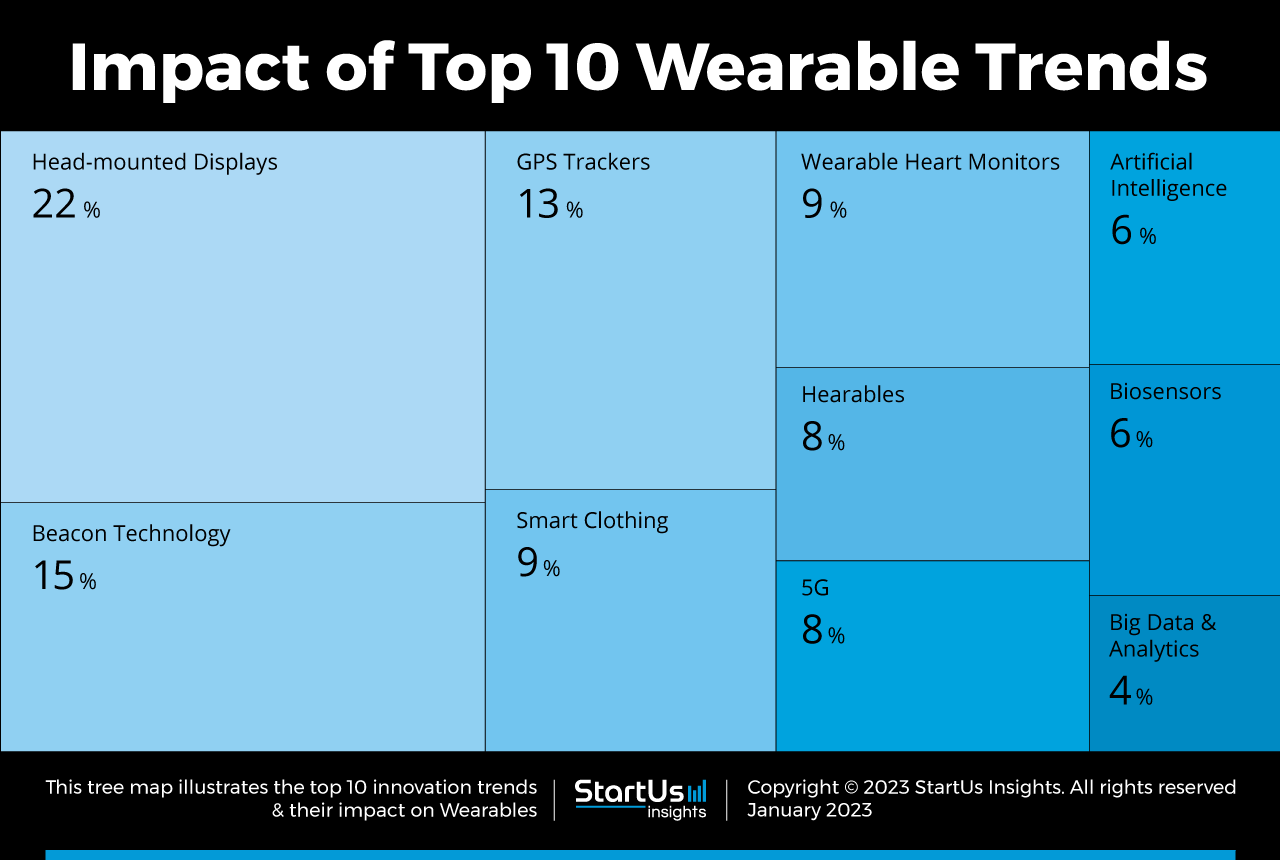
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Wearable Technology Trends
Based on the Wearable Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 10 Wearable Trends in 2025. Startups and scaleups are developing lightweight and compact HMDs. Advances in display technology, such as higher resolution and a wider field of view (FOV), provide a more immersive experience. Additionally, beacon and global positioning systems (GPS) technologies are commonly integrated into wearable devices, particularly in fitness trackers and smartwatches.
Businesses are also developing flexible and stretchable electronics that find use in clothing, allowing for greater comfort and ease of movement. AI-powered wearables analyze data from wearable sensors and other devices to make predictions about the wearer’s health. Further, wearable manufacturers utilize big data to provide population-level insights into fitness and activity patterns. This allows the identification of trends and patterns in large groups of people for research and development.
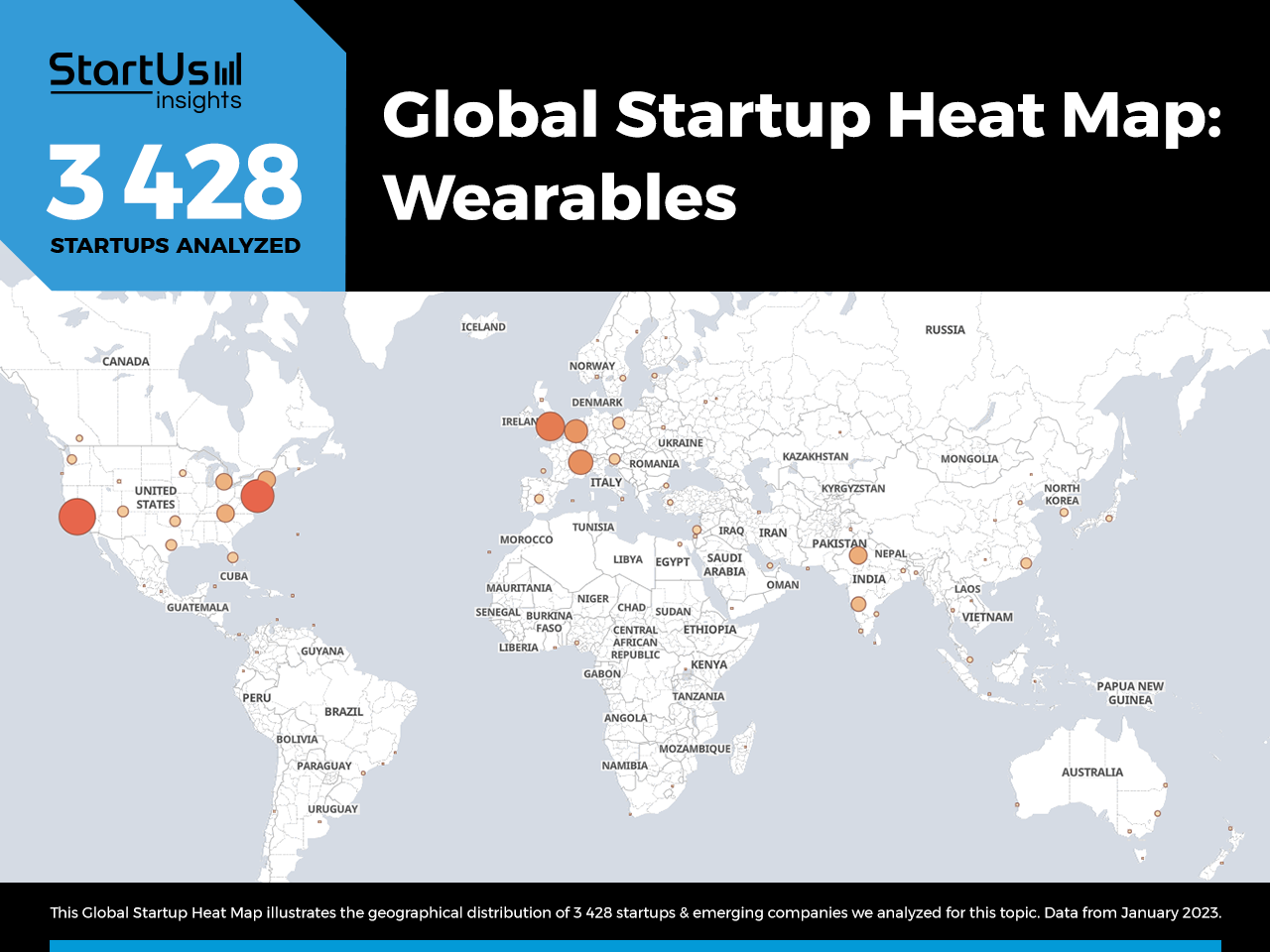
Global Startup Heat Map covers 3 428 Wearables Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 3 428 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that US and UK see the most startup activity.
Below, you get to meet 20 out of these 3 428 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These wearable startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 10 Wearable Technology Trends in 2025
1. Head Mounted Displays
With HMDs, wearers receive information directly in front of their eyes, providing a hands-free operation. They also support capturing photos and videos, and controlling other devices. HMDs find applications in training and simulation in fields like aviation, medicine, and military industries. This provides a more realistic and safe training environment. The use of technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in HMDs provides students and employees with immersive learning experiences. This includes virtual field trips, real-life simulations, and interactive educational content. Further, HMDs assist people with auditory and mobility impairments in communication and navigation.
Gixel makes AR-powered Video Call Glasses
German startup Gixel develops AR glasses to enable real-like video calls. The glasses offer a large field of view, delivering the impression of the person being in front of the speaker. They incorporate spatial audio from the speaker’s direction and provide the video call participants an idea of where to look or address. The glasses also resemble ordinary spectacles and maintain individual visual acuity, enabling direct eye contact and facial communication.
Strolll AR Glasses enable Digital Therapeutics
UK-based startup Strolll creates Cue X, digital therapeutics software that supports AR glasses to assist people with Parkinson’s disease. The software provides AR-based movement training and physiotherapy to patients remotely. It also offers real-time analysis of gait, symptoms, and other patient activities. The startup’s other product, Cue Markers, stimulates goal-directed motor programs by guiding the patients. This allows patients to treat symptoms such as slowness, shuffling, or freezing of gait, thus enhancing mobility for people living with neurological disorders.
2. Beacon Technology
Beacon technology utilizes Bluetooth low-energy (BLE) to transmit signals to nearby devices and converge offline and online activities. In the context of wearables, beacon technology enhances the functionality of devices by providing accurate and real-time location of assets. Beacons provide indoor navigation for users, like guiding a user through a shopping mall or a hospital. Beacon sensors also track customer location to deliver targeted and personalized advertising to their mobile devices, increasing the outcomes of proximity marketing. Beacon wearables, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, improve fitness by providing users with real-time information on their physical activity. They track users’ movement, heart rate, and other metrics and deliver feedback on how to improve their fitness.
Rally Safety improves Personal Safety
US-based startup Rally Safety offers a wearable Bluetooth beacon for personal safety. The startup’s wearable button attaches to the user’s smartphone and sends alerts to other people and emergency professionals when the user foresees danger. Additionally, its companion app connects wearers with other members on the app who are willing to help in times of danger. Upon emergency situations, other users receive a GPS alert for faster response, ensuring on-demand safety for individuals.
PAGOPACE facilitates Wearable Payments
German startup PAGOPACE makes smart rings for contactless payments. The ring works without a battery and connects to the user’s bank account. This facilitates the convenience of payment. Moreover, the ring is not directly recognizable and makes payments only in certain positions and proximities, increasing transaction security. Being hypoallergenic, it enhances durability and user comfort while preventing allergic reactions.
3. GPS Trackers
Wearable devices integrate GPS trackers to monitor the location of wearers and provide location-based services. For instance, wearable GPS trackers simplify physical activity tracking. Many fitness wearables also utilize GPS sensors to track the distance covered, speed, and route during workouts. GPS trackers also allow users to navigate through unknown terrain, which assists in case of an emergency or military operations. Additionally, GPS trackers ensure the safety and security of people and assets, which is why parents use them to monitor the location of their children.
RingOn offers a Smart Ring
US-based startup RingOn makes a ring-shaped GPS tracker to improve child safety. The wearable ring uses Internet-of-things (IoT) to monitor the whereabouts of children. It also incorporates a panic button that allows children to alert their parents in real-time in case of any dangerous situation. Additionally, the ring sends the location information as well as a live audio stream to designated recipients. This allows differentiating between actual and fake alarms.
Inviza creates Remote Patient Monitoring Insoles
US-based startup Inviza creates tracking insoles for remote patient monitoring. They integrate into footwear and automatically connect to smartphones. The insoles offer fitness and location biometric analytics in real-time as wearers walk, skip, or run. This allows them to monitor the distance, duration, heart rate, calories burned, and more. Moreover, the startup’s insoles are self-chargeable and generate power from footsteps. This provides more convenience to users as they need not charge the wearable frequently.
4. Wearable Heart Monitors
Wearable heart monitors continuously track a person’s heart rate, allowing them to monitor their cardiovascular health and fitness level. They detect early signs of cardiovascular issues, such as abnormal heart rhythms or high blood pressure, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. Innovations in these wearables include the incorporation of improved sensors and AI algorithms. The devices are now smaller and more comfortable to wear, making them more practical for everyday use. Such devices remotely monitor electrocardiograms (ECGs) and detect abnormalities, thereby eliminating the need for frequent doctor’s visits. Some wearable heart monitors also track wearers’ sleep patterns, duration, and quality as well as include fall detection to alert their emergency contacts if they fall.
Galenband enables Rhythm Monitoring
Irish startup Galenband develops a wearable wristband for continuous heart rhythm monitoring. The device is equipped with sensors that collect biometric data about the patient, such as heart cycle interval, heart rate variability, inferred respiratory rate, sleep quality, and more. It then leverages AI to analyze gathered data to identify potential indications of silent atrial fibrillation. This allows clinicians to take corrective steps at an early stage.
ABIORO designs an ECG Monitoring Patch
Brazilian startup ABIORO develops wearable devices for heart monitoring. The ABIORO RX Patch, an adhesive patch, offers passive ECG monitoring for up to 14 days. ABIORO’s AI-driven platform employs convolutional neural network (CNN) models to analyze ECG waveforms. The startup provides enhanced cardiac monitoring with a user-friendly design that can be worn during exercise, showers, and sleep, surpassing traditional Holter monitors, which are restricted by limited monitoring hours and lack of water resistance.
5. Smart Clothing
Smart clothing or electronic textiles embed sensor, electronic, and connectivity technologies to provide additional functionality beyond their traditional counterparts. This makes it more convenient and portable for wearers as it mitigates separate devices. Smart clothing finds application in monitoring vital signs such as heart rate and breathing patterns. It also sends this data to healthcare professionals. In the industrial context, smart clothing tracks the movement of workers, monitors their safety, and provides them with relevant on-site information. Further, some smart clothing also alerts emergency contacts in case of accidents or sends out distress signals.
SPA2099 makes Smart Clothing for Health Monitoring
Dutch startup SPA2099 creates advanced fabrics for continuous health monitoring. Its smart clothing integrates sensors to gather ECG data and various body metrics, facilitating the tracking of heart health, physical activity, and stress levels. It includes a panic button and geolocation capabilities, enabling swift emergency responses by alerting security services or colleagues.
Additionally, SPA2099 offers HealthBox, a standalone device that collects, stores, encrypts, and transmits data using a safe protocol, ensuring data protection across networks. Its analytics platform delivers real-time insights into heart health and potential risks through continuous health monitoring – making this smart clothing advantageous for remote workers, drivers, pilots, and those in high-risk professions.
Goldilocks Suit offers a Wearable Suit for Baby Monitoring
Australian startup Goldilocks Suit offers a wearable suit to provide real-time information about newborns. It tracks the baby’s vital information such as sleep, breathing, feeding, and core temperature patterns. The suit’s companion app then offers personalized insights and alerts about the baby’s well-being. Moreover, the startup’s solution provides an economical alternative to buying several devices to monitor different parameters.
6. Hearables
Hearables are worn in or around the ear and typically take the form of earbuds or headphones. They often feature advanced noise-cancellation and equalizer (EQ) adjustments. Many hearables have built-in fitness-tracking capabilities, such as heart rate monitoring and step tracking. This provides users with the convenience of hands-free functionality. Moreover, hearables in healthcare function as hearing aids for people with hearing impairments, allowing them to better communicate with others. Some hearables also translate speech in real time, which is useful for travelers or employees working in multilingual environments.
Ohmic Biometric improves Headphone Biometric Sensing
Canadian startup Ohmic improves headphone biometric sensing without additional sensors. The startup’s solution allows users to monitor their heart rate variability and other vitals. It enhances biofeedback and interfacing capabilities such as wear detection, tapping or sliding detection, and user identification in headphones. This provides an economical alternative as it introduces new features to the existing hardware without massive redesign.
Elonic designs Wearable Medical Equipment
US-based startup Elonic provides Kai, a hearable for hands-free voice interactions. Using bone-conduction technology, Kai delivers important notifications from the user’s phone into the ear. This improves wearer’s convenience while removing the need to physically interact with devices. Kai also incorporates an integrated voice assistant to further enhance user experience and convenience.
7. 5G
5G technology enhances the capabilities of wearables by enabling faster data transfer speeds and allowing for more data-intensive applications such as streaming high-definition video. With 5G’s low latency, it offers real-time communication and remote control of devices. 5G networks also use less power and thereby extend the battery life of wearable devices. Since 5G-enhanced wearables transmit large amounts of data in real-time, they prove beneficial for telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
MoviWear advances Remote Patient Monitoring
US-based startup MoviWear develops 4G and 5G-powered medical wearables. These devices power remote patient monitoring, vital signs monitoring, fall detection, GPS tracking, medical reminders, and more. The low latency of 5G connectivity enables prompt data analytics, thus improving patient outcomes. This allows health professionals to deliver real-time care to patients.
Cognitive XR enables Smart City-scale Cognitive Augmentation
Austrian startup Cognitive XR offers a high-bandwidth interface for smart city-scale cognitive augmentation. The startup’s platform, CognitiveXR, combines technologies like AR, edge computing, and AI, to work with wearable devices and process environmental sensor data. This overlay enhances users’ perception of information received from the environment. Interconnecting multiple wearables also opens new avenues for AR applications.
8. Artificial Intelligence
AI algorithms analyze data from wearable devices to provide personalized recommendations and insights, such as personalized fitness plans, personalized ads, and more. By integrating AI into wearable devices, device manufacturers make wearables more efficient and user-friendly. Wearable devices integrated with AI-powered virtual assistants enable users to access information and perform tasks hands-free. This automates tasks like scheduling reminders and providing navigation directions. AI algorithms also analyze data from wearable devices to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail, allowing for preventive or predictive maintenance.
Ping Cares makes an AI-based Healthcare Wearable
US-based startup Ping Cares makes an AI-based wearable watch to monitor the health of the elderly. It measures vital signs such as heart rate and body temperature to instantaneously deliver this data to caregivers and families via cloud servers. This allows for the analysis of current and historical patient data on demand. The startup also designs an app to display measurements captured by the watch for time-series analysis.
ABIORO manufactures a Cardiac Patch
Brazilian startup ABIORO develops Abioro RX Patch, a wearable patch for cardiac event monitoring. The single-piece patch offers an ergonomic alternative to traditional holter monitors. It incorporates biosensing and deep learning to accurately diagnose cardiac arrhythmia, providing doctors with reliable data to monitor patients remotely.
9. Biosensors
Wearable biosensors are devices that monitor various physiological parameters, such as heart rate, body temperature, and blood glucose levels. They find use in fitness tracking, disease management, and medical research. Biosensors also monitor and track mental health, including stress, anxiety, and depression. This data provides wearers and healthcare professionals with a better understanding of wearer mental health and helps them make changes progressively. These devices are relatively low-cost and used to monitor patients remotely, which decreases the need for frequent hospital visits.
LCM Biosensor Technologies supports Preventive Healthcare
US-based startup LCM Biosensor Technologies makes wearable medical devices for self-monitoring of metabolic health. The device uses the osmotic pressure of intercellular substances in living tissues to continuously monitor blood glucose, other molecular biomarkers, calorie intake, and blood pressure. Unlike conventional wearables, it collects molecular-level data for the prevention of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, enabling more accurate self-monitoring.
MELLIsim develops a Glucose Biosensor
French startup MELLIsim makes MELLIsense, a wearable glucose arm patch for diabetic patients. It measures glucose levels and physical activity every few minutes without requesting manual inputs from the user. This biosensor patch thus enables non-invasive glucose measurements for patients. Further, AI-based analysis of procured data offers personalized recommendations to wearers.
10. Big Data & Analytics
The use of big data in wearable technology aids the collection, storage, and analysis of large amounts of data generated by wearable devices. This data includes information on wearers’ physiological parameters, activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health-related metrics. One of the main advantages of using big data in wearable technology is the creation of more accurate and detailed health profiles for individuals. This allows personalization of healthcare for improved effectiveness of treatments. Big data also improves the user experience and design of wearable devices. By analyzing how users interact with wearables, manufacturers implement design changes to improve usability and user engagement.
Echoscope builds a Bladder Monitoring Device
US-based startup Echoscope develops a wearable bladder monitoring device and analytics software to monitor lower urinary tract (LUT) symptoms. The Echoscope sensor automatically tracks the bladder and displays its activity and visual trends on smart devices. The insights are shared with a clinician digitally for the timely management of symptoms. This allows users to better manage their incontinence.
epyMetrics provides Wearable Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Swiss startup epyMetrics creates epySHIELD, wearable personal protective equipment (PPE) for non-desk workers. The startup’s PPE continuously monitors the wearers’ thermoregulation to detect early signs of heat stress in workers. The insights allow safety professionals to set benchmarks and optimize exposure limits. This increases workplace safety and reduces costs due to accidents or mishaps.
Discover all Wearables Trends, Technologies & Startups
Circuit miniaturization, high-performance batteries, high-speed connectivity, and sensor integration drive innovations in wearables. These advanced technologies enable the development of devices such as smart clothing, AR eyewear, fitness trackers, and more. Additionally, there is a growing interest in using wearables for medical and therapeutic purposes like monitoring posture, body temperature, and vital signs.
The Wearable Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Among others, the artificial intelligence of things (AIoT), biosensors, and flexible circuits will transform the sector as we know it today. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage. Get in touch to easily & exhaustively scout startups, technologies & trends that matter to you!