Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Synthetic biology faces several hurdles from concerns around reproducibility and scalability to the unpredictable behavior of engineered organisms when moved from a controlled lab environment. Emerging trends in synthetic biology span CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, automated DNA synthesis and assembly, and computational design tools, among others, are addressing these challenges.
For example, these solutions foster the development of novel solutions across various sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, and bio-manufacturing. The benefits of these innovations are manifold, offering accelerated drug discovery, sustainable agricultural practices, and the creation of novel materials and chemicals with minimal environmental footprint.
What are the Top 10 Synthetic Biology Trends in 2025?
- Gene and Cell Therapy
- Gene Editing
- Next-Gen Sequencing (NGS)
- Alternative Proteins
- Synthetic Vaccines
- Cellular Agriculture
- Biocomputing
- Microbiome Engineering
- Epigenetics
- Gene Library
Methodology: How We Created the Synthetic Biology Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 5M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the synthetic biology industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the synthetic biology innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Trends in Synthetic Biology & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Synthetic Biology Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 700+ global startups & scaleups. The Synthetic Biology Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the synthetic biology industry trends & startups that impact your company.
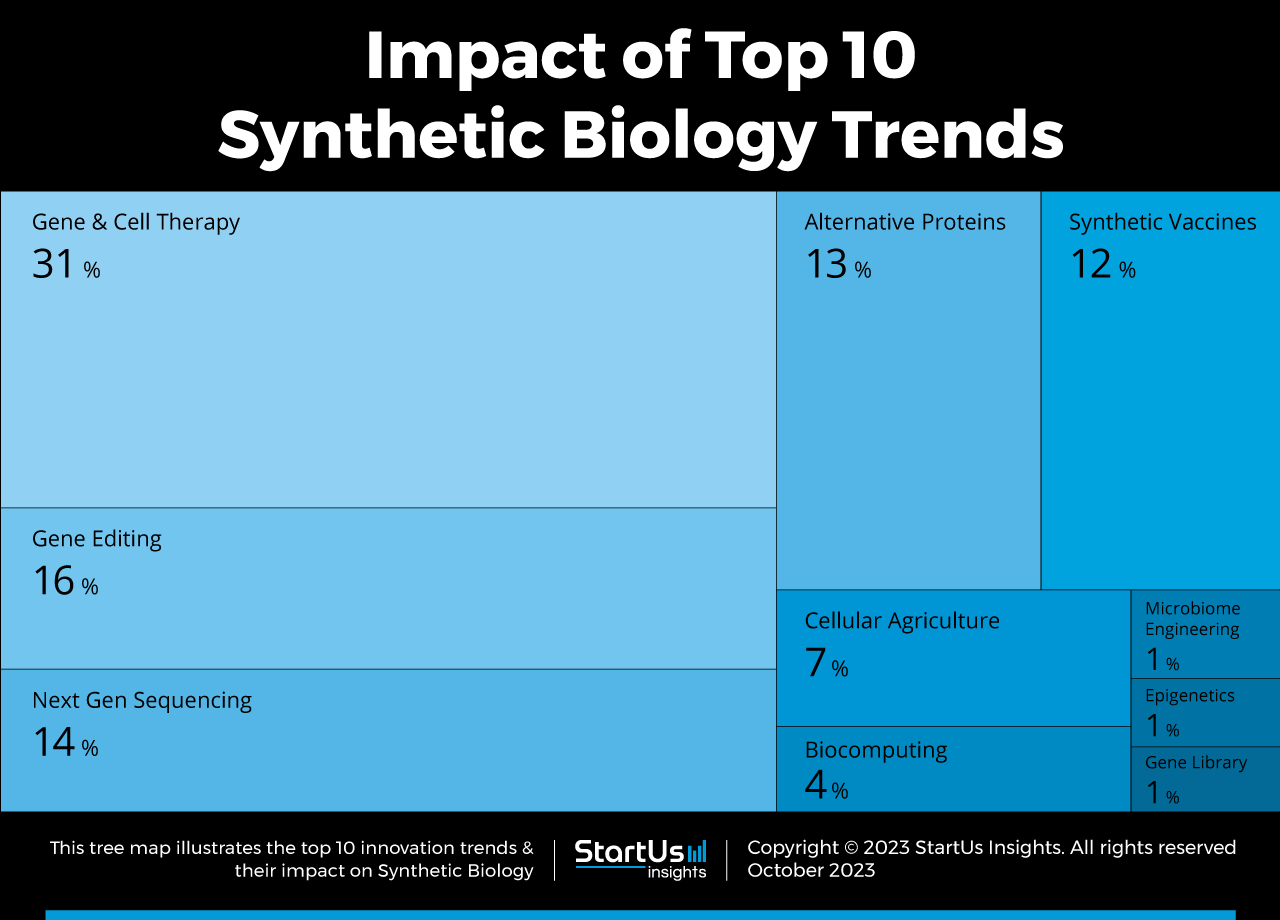
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Synthetic Biology Trends in 2025
Based on the Synthetic Biology Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 10 Synthetic Biology Trends in 2025. Gene and cell therapy are at the forefront of synthetic biology, with techniques like CAR-T cell therapy creating better cancer treatments, among others. CRISPR-Cas9 is enabling precise genomic modifications, with potential cures for genetic disorders.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 718 Synthetic Biology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 700+ synthetic biology exemplary startups and scale-ups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Silicon Valley (USA), followed by the UK and Europe. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Want to Explore Synthetic Biology Innovations and Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Synthetic Biology Trends [2025 and Beyond]
1. Gene and Cell Therapy
Therapies that focus on genes and cells often struggle due to off-target effects, where engineered organisms might interact with unintended targets, potentially leading to unforeseen consequences. Additionally, the scalability of synthetic constructs in real-world environments is a concern, as lab conditions often differ from natural ecosystems.
To address these issues, advanced gene editing tools, like CRISPR-Cas systems, are being refined to enhance precision and reduce off-target interactions. Cell therapy advancements are also enabling the creation of more controlled and contained environments for synthetic organisms. This ensures their functionality aligns with intended applications while minimizing ecological disruptions.
In Q3 of 2024, there were 35 phase 3 trials and 289 phase 2 trials in cell and gene therapy, indicating significant progress in late-stage development.
The global cell and gene therapy market is expected to reach USD 111.4 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.3% from 2024 to 2033
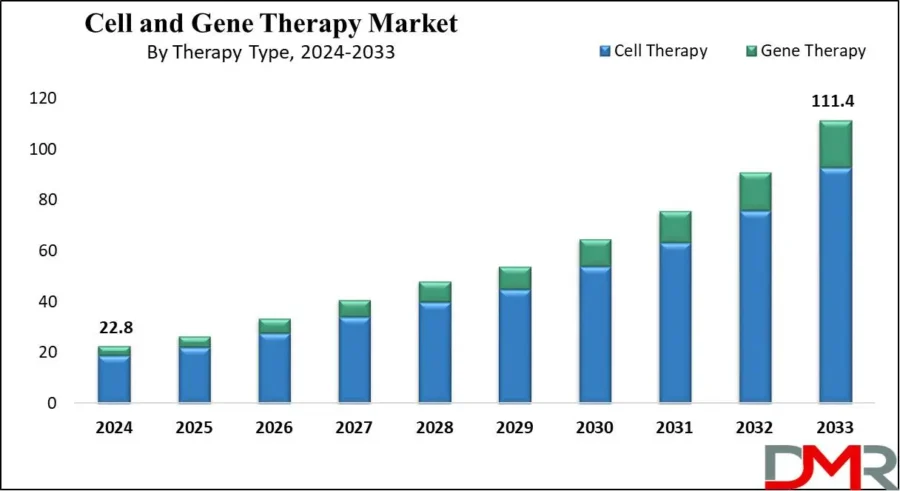
Credit: Dimension Market Research
NewBiologix develops Engineered Cell Line Technology
Swiss startup New Biologix offers advanced technologies and therapies, particularly in gene and cell therapy. Its therapies combat rare and previously incurable diseases by restoring normal gene or cell activity. The startup uses recombinant adeno-associated viruses (rAAVs) to serve as delivery mechanisms for engineered genetic materials to diseased cells.
Moreover, New Biologic’s gene therapy solution features growth in suspension to high cell density and inducible gene expression to overcome cellular toxicities. The startup’s approach involves stably engineered HEK cells, optimized for rAAV production, highlighting its adaptability for various therapeutic products.
Bloomsbury Genetic Therapies treats Rare Neurological and Metabolic Diseases
Bloomsbury Genetic Therapies is a UK-based startup that provides gene therapy for rare neurological and metabolic diseases. It designs viral vectors with an understanding of target disease biology and well-characterized adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids to focus on therapeutic efficacy, safety, and high manufacturability.
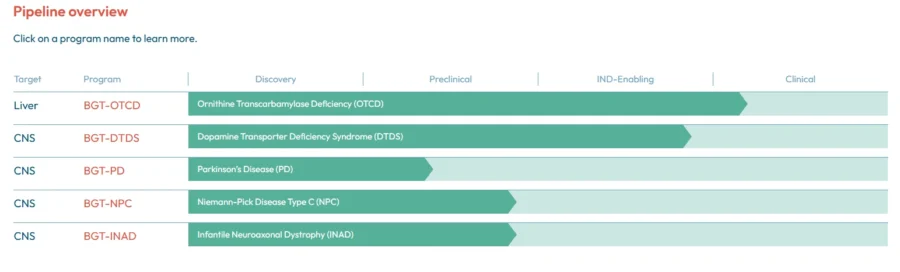
For neurological programs, direct administration to the CNS ensures targeted efficacy and improved safety. Bloomsbury Genetic Therapies’ pipeline includes solutions for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD), and more. Through gene and cell therapies, the startup expedites the delivery of potentially curative medicines.
2. Gene Editing
Modern genetic editing technology faces many challenges including the unpredictable behavior of engineered genetic circuits and horizontal gene transfer. They lead to inconsistent cellular responses and unintentional transfer of engineered genes to non-target organisms in an ecosystem. Innovations in gene editing are addressing these problems, particularly with tools like CRISPR-Cas9.
For example, enhanced accuracy in gene editing allows for the fine-tuning of gene structures, ensuring more predictable cellular behaviors. Additionally, startups are developing gene drives to control the spread of edited genes and mitigate the risks associated with horizontal gene transfer. These innovations contribute significantly to the emerging synthetic biology trends.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam successfully used CRISPR to cut out HIV from infected cells, marking a world first in potential HIV treatment. By 2025, it’s predicted that gene editing technologies will enable rapid precision DNA editing at multiple locations simultaneously.
The global gene editing market size is estimated at USD 9.30 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 40.10 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.73% from 2024 to 2034.
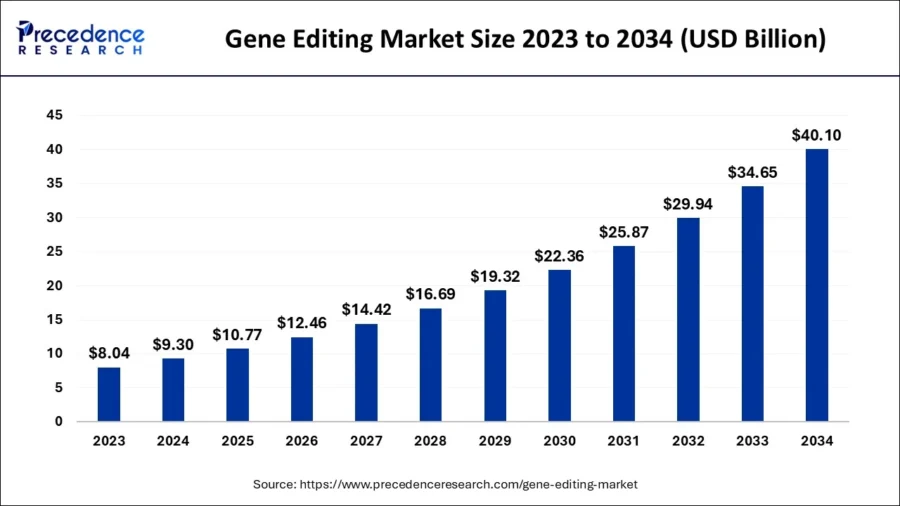
Credit: Precedence Research
Graphite Bio advances Precise DNA Repair
US-based startup Graphite Bio develops a platform to utilize the full potential of gene editing for precise DNA repair. Its UltraHDR platform builds on CRISPR technology, focusing on precise DNA repair known as homology-directed repair (HDR). The platform utilizes the cell’s natural DNA repair processes to restore function to mutated genes causing diseases.
The startup’s approach is similar to the find-and-replace method for gene editing. First, the startup identifies the genetic mutation, then uses proprietary HiFi Cas9 to precisely cut the incorrect DNA sequence. It also introduces the correct DNA sequence to restore the gene’s function. Graphite Bio’s precise DNA repair technology advances the potential for synthetic biology to cure genetic diseases.
SeQure Dx offers Predictive Off-Target Assessments
SeQure Dx is a US-based startup that advances gene editing with its predictive off-target assessment platform. Its approach involves nominating all possible off-target sites using a diverse genomic database to ensure a comprehensive understanding of potential risks. Confirmation of these off-target edits takes place in various environments, correlating results to pathogenic, oncogenic, and biological impact data.
The startup offers NoteSeQ, powered by ONE-seq assay technology, which profiles off-target sites using high-throughput DNA synthesis technology. This platform, in combination with bioinformatics and a non-homology-based orthogonal assay, offers a scalable and editor-agnostic suite of tools. SeQure Dx also offers ScopeSeQ to confirm candidate off-target edits for individual patient genomes, targeted populations, or allogeneic cell lines.
3. Next-Gen Sequencing
The intricacies of comprehensive characterization and understanding of complex synthetic constructs and their interactions within host organisms cause unexpected phenotypic outcomes or metabolic imbalances. To avoid this, startups are advancing NGS to rapidly sequence vast amounts of DNA that allow researchers to dissect and analyze the behavior of synthetic constructs at high resolution.
Innovations such as sequencing by synthesis, pyrosequencing, and sequencing by ligation facilitate the identification of potential issues in synthetic designs, enabling iterative refinement. Further, metagenomic studies powered by NGS offer insights into how synthetic organisms interact with native microbial communities. This ensures safe and effective deployment in diverse environments.
The year 2025 is expected to see a shift towards in situ sequencing of cells in tissue, expanding the capabilities of current spatial biology methods. The global DNA sequencing market size is expected to reach around USD 51.31 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 14.90% from 2025 to 2034.
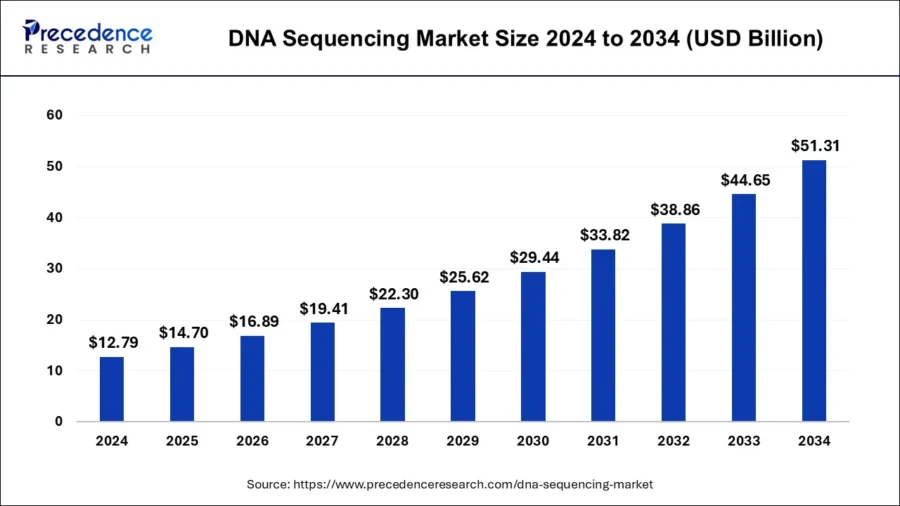
Credit: Precedence Research
Deep Biotech provides Whole RNA Sequencing
Hungarian startup Deep Biotech Solutions specializes in personalized next-generation sequencing and molecular biology services. The startup offers whole transcriptome sequencing services, diving deep into RNA sequencing and de-risks experiments through advanced filtering and AI support.
Besides, it delivers tailored analysis to enhance research focus with ready-to-use in-depth analysis, supporting documentation, and more. Deep Biotech Solutions also provides differential gene expression, novel transcript identification, and splice variant analysis. Moreover, its single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing provides customizable analysis with the detection of structural variations, complex genomic regions analysis, and more to accelerate genomic research.
Lost Arrow Bio makes Automated Sequencing Library Prep Workflows
US-based startup Lost Arrow Bio specializes in next-generation sequencing sample preparation. It provides a system that automates nearly any NGS library prep workflow without altering protocols. Its patented single-use injection molded cassettes and durables efficiently control fluidic movement, temperature, and magnetic separation.
Additionally, the cassettes automate any NGS library prep workflow with any commercially available reagent kit. By containing samples and reagents within the cassette, it minimizes waste, errors, and contamination. Besides this, Lost Arrow Bio’s Jeannie System allows the processing of up to eight samples identically, eliminating the need for batching.
4. Alternative Proteins
Global food production systems are struggling to sustainably rely on traditional protein sources, which are resource-intensive and cause environmental pollution. Innovations in alternative proteins are addressing this challenge by engineering non-traditional protein sources, such as plant-based proteins, algae-derived proteins, and lab-grown meat.
Additionally, the integration of fermentation technologies and the utilization of mycoproteins offer alternative avenues for protein production. These alternative proteins reduce the environmental footprint and also enhance the efficiency and versatility of synthetic constructs. This paves the way for more sustainable and wide-ranging foodstuffs in the future.
The global alternative protein market size is expected to reach around USD 36.37 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 8.23% from 2024 to 2034.
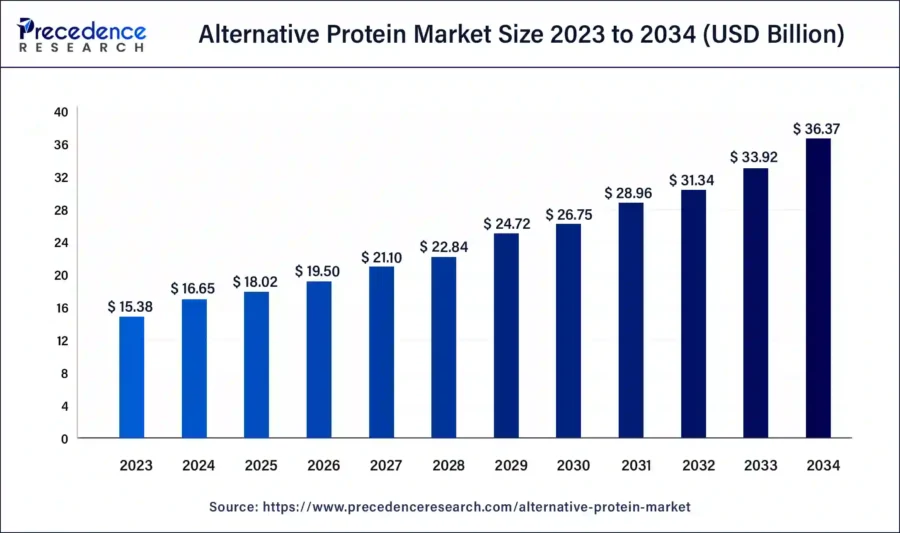
Credit: Precedence Research
Basecamp Research simplifies Protein Data Contextualization
UK-based startup Basecamp Research develops a knowledge graph with a comprehensive view of genetic data found in natural environments and labels genetic sequences with geological, environmental, and chemical tags. This provides a unique, contextualized data source, with a significant portion of the proteins in their graph being entirely new.
By mapping the planet’s microbial bio-diversity, Basecamp Research expands the known protein count and showcases unseen relationships between proteins. It then predicts protein function using environmental and genomic contextual data. This method identifies sequences with varying identities but identical functions and structures. Such contextualized protein data is pivotal in optimizing performance and reducing lab testing in the R&D of protein-based solutions.
MarraBio creates Bacterial Protein Polymers
MarraBio is a UK-based startup that constructs bacterial protein polymers essential for cellular growth, division, and proper cell behavior. The startup offers a multi-functional solution encapsulated in a single, highly functional material that supports combining multiple bioactive signals. This enables industrial-scale cell growth for diverse applications like research, agriculture, or therapy.
Its Caf1 polymer utilizes a unique protein technology that enables the creation of proteins mimicking conventional protein functions but at a lower cost and improved performance. Through high-yield bacterial fermentation, it ensures low-cost production while retaining quality. Additionally, the materials are highly functionalized and house multiple bioactive signals in one material, enhancing rapid, flexible, and scalable production to meet market demands.
5. Synthetic Vaccines
Traditional vaccine development is time-consuming and struggles with rapid and effective response to emerging fast-evolving pathogens like COVID-19. Addressing this slow pace, innovations in vaccine development leverage synthetic DNA and RNA platforms to design and produce vaccines in a short time.
This accelerates vaccine development while ensuring safety, as researchers are not exposed to the live virus. Further, the modularity of synthetic vaccine platforms allows for swift adjustments in response to viral mutations, ensuring that the vaccines remain effective against evolving strains.
Reports suggest that mRNA technologies within synthetic biotechnology are shifting towards targeted in vivo delivery strategies, particularly for oncology, immunology, and inflammatory indications.
Hexamer Therapeutics creates Vaccine Scaffolds
US-based startup Hexamer Therapeutics focuses on next-generation vaccine technologies. Its vaccine scaffold consists of natural peptides that are adjustable to target specific virus regions or mutations. Additionally, the technology enables stoichiometrically controlled reactions, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of antigens.
Besides, the scaffold self-assembles into higher structures in aqueous solutions, remaining non-immunogenic until antigenic targets are conjugated. In combination with synergistic adjuvants, it induces robust and durable immune responses. Hexamer offers rapid, scalable, and adaptable solutions that address mutating viral strains, ensuring broad-ranging vaccine effectiveness.
AiBIOLOGICS enables AI-powered Antibody Discovery
AiBIOLOGICS is an Irish startup that specializes in AI for antibody discovery, diagnostic development, and vaccine design. Its deep learning algorithms refine and expedite processes that improve antibody discovery, immunogenicity mapping, and more.
The startup’s EpitopePredikt technology provides adaptable, cost-effective, and efficient solutions for diagnostics and antibody discovery. AiBIOLOGICS’ technology designs its algorithms to form an artificial neural network for intelligent biological design solutions. Moreover, the startup validates its AI models in real-world laboratories and improves diagnostics, vaccine designs, and therapeutic evaluations.

6. Cellular Agriculture
The global agricultural industry faces challenges in meeting the growing demand for sustainable food sources without exacerbating environmental degradation or compromising nutritional value. Innovations in cellular agriculture are providing solutions to these issues by cultivating animal cells directly without the need to raise and slaughter whole animals.
Moreover, cellular agriculture offers a method to produce crops with higher yields, build more resistant crops to fight pests and remediate poor soil conditions. This approach drastically reduces the environmental impacts of agriculture while ensuring clean and consistent product quality. Further, cellular agriculture allows for the customization of nutritional profiles, potentially creating healthier and more tailored food options for consumers.
The cellular agriculture market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 12.81% to reach USD 451.44 billion by 2030.
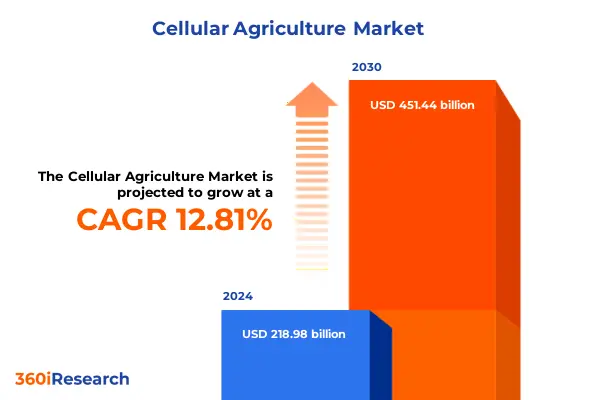
Credit: 360iResearch
Myriameat manufactures Cell Cultured Whole Meat
German startup Myriameat creates tissue-engineered muscle that mimics that mimics the natural meat. The process starts by taking a few cells called the pluripotent stem cells from the animal and creating a cell line with it. The startup copies the natural growth process of the muscle without slaughtering or harming any animals using its patented technology. The process ensures health, animal welfare, sustainability, and scalability.
Real Deal Milk advances Precision Fermentation
Spanish startup Real Deal Milk specializes in the production of milk using precision fermentation, eliminating the need for cows. The startup utilizes cellular agriculture, specifically precision fermentation, to produce milk proteins like casein and whey. It uses yeast cells, equipped with the genetic recipe for the proteins, to act as protein-building machines.
This method reduces CO2 emissions, requires fewer resources, and eliminates the ethical concerns of dairy farming. Real Deal Milk’s technology offers a humane, cost-effective, and healthier dairy alternative, reducing animal suffering, lowering production costs, and providing a guilt-free dairy experience for consumers.
7. Biocomputing
The process of modifying biological systems entails highly intricate design and optimization, and here, manual trial-and-error approaches are labor-intensive and lack precision. Moreover, the complexity of biological interactions requires intensive computational tools for accurate predictions and designs. Startups are creating biocomputing technology to address this through advanced algorithms, machine-learning models, and simulation platforms.
This approach enables the in silico design and testing of biological circuits and pathways. Consequently, biocomputing allows for rapid iterations, optimization, and validation of synthetic constructs before actual laboratory implementation. The advent of DNA-based computing and storage solutions, as well as utilizing biological substrates, further bridge the gap between biological and digital systems.
Iridia manufactures DNA-based Memory Chips
US-based scaleup Iridia creates a DNA-based data storage solution, utilizing a unique combination of proprietary DNA synthesis chemistry, hardware architecture, and semiconductor fabrication technologies. This enables high-density data storage, ensuring long-term durability and sustainability through decentralized, affordable DNA data storage.
Moreover, the startup’s technology serves as an alternative to current data storage methods, offering high data density, and resistance to data degradation. Iridia’s DNA-based memory chip represents a significant advancement in synthetic biology, providing a practical solution to the growing demand for data storage in enterprises, data centers, and more.
Cortical Labs advances Dishbrain Intelligence
Australian startup Cortical Labs creates a unique dishbrain by merging living brain cells with computing devices. This fusion results in machines possessing biological intelligence that harnesses the power and intricacies of brain cells to enhance computational capabilities.
Its biological intelligence operating system (biOS) performs simulations and transmits information about its environment using positive and negative feedback. Besides, it interfaces with the neurons directly and reacts to impulses. Cortical Labs cultivates the neurons across a silicon chip within a nutrient-rich solution, supplying them with the required nutrients for optimal growth.
8. Microbiome Engineering
Traditional bioengineering methods face difficulties in selectively targeting or enhancing microbial functions without disrupting the complex microbial communities. Therefore, microbiome engineering offers targeted solutions to this by employing advanced genetic tools and delivery systems.
This allows researchers to introduce or modify specific genes within microbes, allowing for the tailored enhancement or suppression of desired functions within a microbiome. Precision microbiome engineering facilitates the development of probiotics with enhanced therapeutic potential, agricultural solutions that promote plant health without chemicals, and environmental interventions that remediate pollutants or restore the ecological balance.
The microbiomes market size is forecast to increase by USD 824.3 million and CAGR of 18.3% between 2024 and 2029.

Credit: Technavio
Ceragen manufactures Microbial Inoculants
Canadian startup Ceragen offers microbial inoculants to enhance plant growth, particularly in hydroponic systems. Its product, ACCelerate, targets hydroponic tomato production, assisting plants in nutrient uptake and resilience against environmental stresses like heat. The microbial inoculant reduces fruit loss from temperature or lighting shifts, minimizes stress symptoms, and increases root growth.
ACCelerate’s liquid formulation further allows for easy application to the plant’s root zone, requiring only a few applications throughout the plant’s life cycle. The startup’s commercial results showcase a yield increase in grape tomatoes and beefsteak tomatoes. By harnessing the power of beneficial microbes, Ceragen offers sustainable and efficient solutions for crop yield enhancement that avoid harmful chemical alternatives.
Endure Biotherapeutics specializes in Native Bacteria Engineering
Endure Biotherapeutics is a US-based startup that engineers therapeutic strains of native bacteria that persist within the body. Its platform focuses on the discovery, development, and commercialization of engraftable live biotherapeutics to treat genetic and chronic diseases. The startup’s approach involves isolating native bacteria from healthy subjects and then genetically engineering them to produce therapeutic proteins.
These bioengineered bacteria are then administered to patients as oral capsules containing freeze-dried bacteria. Early-stage experiments show that these engineered native bacteria can colonize various segments of the gastrointestinal tract and potentially cure various metabolic and inflammatory conditions.
9. Epigenetics
The expression of engineered genes is dictated by DNA sequence as well as by dynamic and complex epigenetics. This inadvertently silences or overactivates synthetic constructs, leading to inconsistent results. That is why startups are developing innovations in epigenetics tools to navigate and manipulate these intricacies.
For example, by understanding and controlling epigenetic markers and modifiers, researchers ensure consistent gene expression, fine-tune synthetic constructs, and design epigenetic switches. This understanding of epigenetic regulation is paving the way for more reliable and sophisticated applications in cancer treatment and DNA modification.
The epigenetics market was valued at 15.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 66 billion by 2032 is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.7% from 2024-2032.
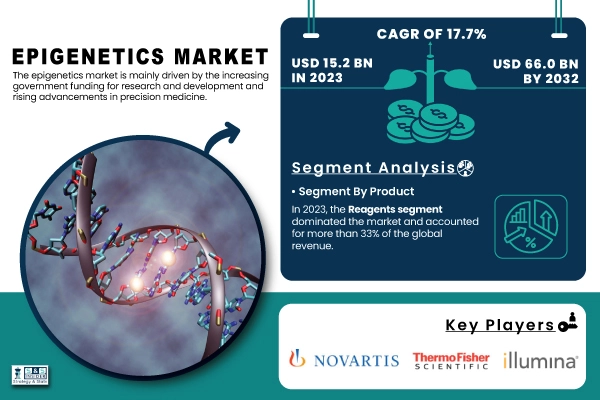
Credit: SnS Insider
Tune Therapeutics offers a Genetic Tuning Platform
US-based startup Tune Therapeutics develops a genetic tuning platform, TEMPO, which controls gene behavior. It performs this in a graded, tunable, and reversible manner, offering a distinct approach compared to traditional gene editing. TEMPO consists of two switchable elements: the DNA-binding domain (DBD) and effectors.
The DBD guides the protein to specific genomic target sites, identifying enhancers and repressors that influence gene activity. Effectors then alter local epigenetic marks, influencing how a gene is accessed and read by a cell’s transcription machinery. By customizing these elements, TEMPO precisely controls gene expression, offering solutions for various therapeutic contexts.
Chroma Medicine creates Programmable Editors
Chroma Medicine is a US-based startup that develops single-dose genomic medicines by leveraging epigenetics for precise and predictable therapies. Its programmable epigenetic editors combine a DNA-binding domain with an epigenetic effector domain, enabling targeted gene silencing or activation.
These editors create specific methylation patterns that determine a gene’s accessibility for transcription, mimicking the cell’s natural gene expression control mechanisms. The startup’s modular platform offers versatility, allowing the development of medicines for various complex diseases. Moreover, unlike traditional gene editing that cuts DNA, Chroma’s editors regulate the genome without producing immunogenic truncated or mutant proteins.
10. Gene Library
The vast combinatorial space of genetic designs that need to be explored for optimal functionality makes the design-build-test cycle a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. This is why startups are creating gene libraries that address this bottleneck with databases that contain vast genetic data. This enables the parallel synthesis of thousands to millions of genetic variants, encompassing a wide array of sequences and functionalities.
Besides this, advanced techniques, such as DNA synthesis platforms and high-throughput screening methods, enable researchers to rapidly assess these variants, identify top performers, and iteratively refine designs. This combinatorial approach, facilitated by gene libraries, accelerates the discovery and optimization process, pushing the capabilities of synthetic biology.
Serengen creates DNA Encoded Libraries (DELs)
Serengen is a German startup that creates DNA Encoded Libraries for efficient and high-quality hit identification. The startup’s advanced DEL technology overcomes the limitations of traditional unbiased screening methods with its druglike tractable hits, synthesizing central scaffolds, and double purification. Serengen’s encoding strategy and DNA-compatible chemistry enable the creation of druglike DELs, covering diverse chemical spaces.
The startup offers customized DEL synthesis, including unbiased, semi-unbiased, structure-enabled, and ligand-enabled designs. Its technology also supports a wide range of molecular and target classes, from small molecules to membrane-bound proteins. Serengen’s DNA-encoded library reduces redundancy, minimizes costs, and accelerates progression in early drug discovery.
Dianox creates In Vitro Validated Aptamers
Danish startup Dianox provides an aptamer library with in vitro validated aptamers that bind specifically to proteins or small molecules. Its collection encompasses aptamers for enzymes, cell surface proteins, intracellular proteins, disease-associated proteins, and immunoglobulins.
These aptamers serve various purposes, from studying enzyme mechanisms to potential therapeutic applications for diseases like cancer. The startup’s unrestricted data access further ensures that researchers freely use the aptamers in their work.
Discover all Current Trends & Technologies in Synthetic Biology
Synthetic genomics is enabling the design and construction of custom DNA sequences, opening doors to numerous applications in medicine, bioenergy, and agriculture. Additionally, the field of biosensors is advancing the development of novel biological sensors capable of detecting and responding to a myriad of environmental signals. Further, the advent of digital-to-biological converters (DBCs) bridges the gap between digital information and biological material, facilitating the direct conversion of digital data into DNA.
The top trends in synthetic biology and innovative startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.