Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary: Technology Radar 2026
Macro Influences: Geopolitics, regulation, and sustainability are redrawing the technology map. Export controls on chips, green data center mandates, and compliance frameworks like CSRD and AI Act are reshaping adoption timelines.
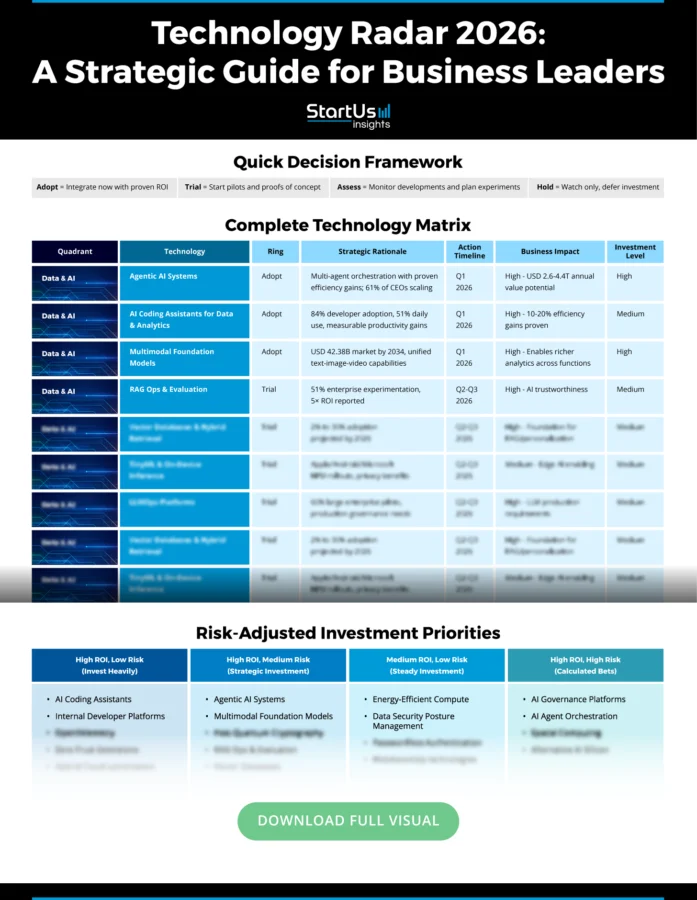
Quadrant 1: Data & AI Priorities: Agentic AI systems, multimodal foundation models, and RAGOps dominate the enterprise agenda. Adoption is high: 79% of firms use AI agents, but only 19% reach scale due to tooling gaps. McKinsey projects AI-driven value at USD 2.6-4.4T annually.
Quadrant 2: Platforms & Infrastructure: Hybrid cloud and distributed edge are now the enterprise baseline. Energy-efficient computing and liquid cooling also reflect sustainability and cost pressures. Vector databases, federated AI, and spatial computing remain trial technologies, while quantum and neuromorphic chips stay on hold.
Quadrant 3: Security & Trust: Zero-trust extensions and confidential computing are becoming non-negotiable in regulated sectors. PQC and DSPM are rising in response to cyber and compliance risks. Disinformation security and AI governance platforms lag in maturity. The EU AI Act, US executive orders, and China’s algorithm laws are setting the global compliance pace.
Quadrant 4: DevEx & Delivery: Developer productivity is being redefined by AI-native coding assistants, internal developer platforms, and OpenTelemetry. Event-driven data meshes, GenAI observability, and SBOM automation are in trial phases. With global skill shortages and rising software complexity, platform engineering and AI-augmented DevEx are strategic levers for competitiveness.
Traditional strategic planning horizons are proving inadequate against the accelerated pace of technological disruption. Therefore, diligent monitoring of the emerging technology radar is a critical step for organizational viability.
The urgency is underscored by 2025 stats like enterprise AI adoption, which has surged to 78% from 55% in the preceding year, while investment in quantum computing increased by 128% year-over-year.
This guide provides decision-makers with a data-driven framework to navigate these complexities and determine which technologies to adopt. It also enables the formulation of resilient strategies essential for maintaining a competitive advantage.
What is a Technology Radar?
A technology radar is a tool that supports organizations in navigating technological change. It categorizes emerging and established technologies based on maturity, relevance, and urgency.
This framework uses concentric rings like “adopt,” “trial,” “assess,” and “hold” to visualize the journey of tech “blips” moving inward over time.
How to Read This Radar
Quadrants: The Four Lenses of Technology Prioritization
The technology radar 2026 is organized into four quadrants that reflect the most critical domains shaping the enterprise technology roadmap:
- Data & AI – It covers next-generation AI systems, machine learning architectures, and data infrastructures.
- Platforms & Infrastructure – It captures distributed compute, advanced chips, cloud-native tooling, and networking innovation.
- Security & Trust – This quadrant spans cryptographic transitions, zero-trust extensions, and security posture management.
- DevEx & Delivery – The fourth quadrant focuses on developer productivity, observability, and continuous delivery.
Rings: The Maturity & Urgency Framework
Within each quadrant, technologies are plotted across four rings that denote their level of maturity and adoption urgency. This ringed structure makes it clear where to invest, experiment, monitor, or defer.
- Adopt – Technologies that have proven ROI, industry adoption, and vendor maturity. Enterprises should incorporate them into their near-term strategy.
- Trial – Technologies mature enough for pilot projects. Early movers can capture a competitive advantage.
- Assess – Technologies that show promise but remain unproven at the enterprise scale. Organizations should track developments and begin internal experimentation.
- Hold – Technologies that are too early, costly, or risky for most enterprises. They may hold long-term potential but should not displace near-term strategic investments.
Blip Movement: Tracking Technology Evolution
Each technology is represented as a “blip” that can move inward or outward across rings over time.
- A blip moving inward (that is, from assess to trial to adopt) signals increasing maturity and enterprise readiness.
- A blip moving outward (eg, adapt to trial) indicates strategic caution, perhaps due to cost escalation, regulatory setbacks, or unproven ROI.
The Technology Radar 2026 Quadrants
Quadrant 1: Data & AI
1. Agentic AI Systems – Adopt
Multi-agent architectures that coordinate planning, memory, and tools to automate workflows beyond copilots.
Why It Matters
Agentic AI extends beyond copilots to manage complex workflows, with McKinsey estimating USD 2.6 – USD 4.4 trillion in annual value potential. It enables embedded AI advisors and predictive maintenance services.
Signals
- Recognition: Named a Top Strategic Tech Trend 2025.
- Adoption: 61% of CEOs scaling AI agents (IBM CEO Study, 2025).
- ROI: 85% expect positive returns by 2027.
- Ecosystem: Frameworks like trust, risk, and security management (TRiSM) emerge to address trust and safety.
Trajectory
Moved from Trial (2024) to Adopt (2026). Governance maturity will determine the pace of scaling.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Efficiency gains, new service models, and enterprise integration.
- Risks: Compliance gaps and autonomy risks without safeguards (eg, advanced threat framework for autonomous AI agents (ATFAA) and a complementary defense framework (SHIELD)).
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation Ops & Evaluation – Trial
Frameworks that connect AI models to external knowledge sources and add evaluation layers to ensure factual accuracy and reduce hallucinations.
Why It Matters
Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) enhances trustworthiness in GenAI outputs and improves efficiency. Early adopters such as Duolingo report 5x ROI and save 500+ hours monthly using Glean’s AI-powered knowledge tools.
Signals
- Adoption: 51% of enterprises experimenting with AI use RAG, and 70% of engineers building AI tools report integrating it.
- Governance: Lifecycle standards for evaluation and governance are still under development.
- Ecosystem: Vendors like Glean, Pinecone, and Weaviate are embedding retrieval and evaluation modules, but fully enterprise-ready ops systems are nascent.
Trajectory
Advanced from Assess (2024) to Trial (2026). Likely to move into Adopt within 12-18 months as evaluation standards mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Reduce costs and hallucinations while strengthening compliance.
- Risks: Immature tooling, manual evaluation burdens, and data drift challenges.
3. AI Governance Platforms – Assess
Platforms that centralize oversight of AI by embedding policy, compliance, and risk controls into a unified “control plane.”
Why It Matters
Rising global regulations (the EU AI Act and China’s GenAI laws) make governance unavoidable. Forrester highlights its evolution into a control plane for trust at enterprise scale. The market is projected to reach USD 1.4 billion by 2030 at a 35.7% CAGR.
Signals
- Adoption: Enterprises acknowledge the need, but few have mature governance models in place.
- Ecosystem: Solutions like IBM watsonx.governance exists, though standards and integrations remain fragmented.
- Regulation: Divergent regimes and “shadow AI” usage create compliance risks that push firms to develop in-house safeguards.
Trajectory
Remains in Assess (2026). Movement to trial depends on the convergence of regulatory frameworks and vendor maturity.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Reduces bias, increases transparency, and avoids regulatory penalties.
- Risks: Immature tooling, inconsistent regulations, and high integration complexity slow rollout.
4. Neuromorphic AI Chips – Hold
Brain-inspired chips that use spiking neural networks for ultra-low-power, event-driven AI at the edge.
Why It Matters
R&D momentum is strong as Intel’s Loihi 2 Hala Point achieved 1.15 billion neurons, IBM’s NorthPole showed GPU-beating efficiency in lab tests, and TU Dresden’s SpiNNaker2 chip runs 5+ million cores for sustainable architectures.
Yet adoption remains niche compared to graphics processing units/neural processing units (GPUs/NPUs).
Signals
- Immaturity: Programming frameworks remain academic, and developer tools are sparse.
- R&D Bias: Most performance claims are prototype-based, not from production.
- ROI Uncertainty: Competes with rapidly advancing GPUs/NPUs already embedded in enterprise stacks.
Trajectory
Stays on hold. Movement to Assess or Trial depends on the developer ecosystem maturity post-2028.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Potential order-of-magnitude energy savings in edge AI.
- Risks: Developer scarcity, vendor lock-in, unclear ROI in enterprise deployments.
5. TinyML & On-Device Inference – Trial
Runs machine learning (ML) models directly on microcontrollers and neural processing units (NPUs) to enable low-latency, private inference without cloud dependency.
Why It Matters
There’s a rising momentum of technology. For instance, Apple launched on-device foundation models in 2025, Android rolled out Gemini Nano, and Microsoft’s Copilot+ PCs now require NPUs exceeding 40+ trillion operations per second (TOPS). NVIDIA’s Jetson Orin Nano delivers 67 TOPS at 7 to 25 watts for real-time edge AI.
Signals
- Adoption: Demonstrated privacy and latency benefits validated in consumer and industrial pilots.
- Ecosystem: Major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) ship hardware and tooling, but enterprise fleet management and on-device machine learning operations (MLOps) remain immature.
- Maturity Gap: Hardware advances outpace fragmented software toolchains for model compression, OTA updates, and offline evaluation.
Trajectory
Advanced from Assess (2024) to Trial (2026). Likely to move toward adoption by 2027 as MLOps tooling matures.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Privacy-preserving inference, reduced cloud costs, edge intelligence.
- Risks: Fragmented tooling, model quantization complexity, and device variability.
6. AI Coding Assistants for Data & Analytics – Adopt
AI-powered assistants embedded into integrated development environments (IDEs) and notebooks that automate code and queries to accelerate developer productivity.
Why It Matters
Adoption among developers is rising, as shown in the Stack Overflow survey report. 84% of respondents in 2025 are using AI tools, with 51% of professional developers using them daily.
Gartner forecasts 75% enterprise adoption by 2028, while JPMorgan Chase engineers achieved 10-20% efficiency gains, which translated to USD 1 to 1.5 billion annual value.
Signals
- Adoption: Widespread, with strong daily developer use.
- ROI: Quantified efficiency gains across finance and open-source ecosystems.
- Maturity: Tools like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Claude, and Tabnine are deeply integrated into workflows.
Trajectory
Moved from Trial (2024) to Adopt (2026). Now considered a baseline productivity layer for enterprises.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Accelerates development, boosts upskilling, improves enterprise efficiency.
- Risks: Uneven adoption, code quality concerns without governance.
7. Vector Databases & Hybrid Retrieval – Trial
Databases (DBs) that store high-dimensional embeddings to power semantic search and hybrid retrieval are critical for RAG and personalization.
Why It Matters
Adoption is accelerating, as only 2% of enterprises used vector DBs in 2023, but adoption is projected to reach 30% by 2026. Analysts now describe them as “core to AI architectures.”
Vendors like Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant, Milvus, and Chroma are driving strong ecosystem growth.
Signals
- Adoption: Rapid growth trajectory, but still in early mainstream trials.
- Ecosystem: Expanding vendor landscape, with hyperscalers embedding native vector search.
- Role: Foundational to trustworthy GenAI and copilots, but lifecycle management is resource-intensive.
Trajectory
Advanced from niche usage (2023) to trial (2026). Likely to move into Adopt by 2027 as standards and ops practices mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Enables semantic apps, RAG reliability, and enterprise-ready copilots.
- Risks: High indexing costs, fragmented tooling, and complex lifecycle management.
8. Multimodal Foundation Models – Adopt
Models that unify text, images, audio, video, and code to enable contextual reasoning and generation across multiple formats.
Why It Matters
The market is projected at USD 2.51 billion in 2025 and expected to surge to USD 42.38 billion by 2034. Pilots show faster processing, improved analytics, and higher customer satisfaction.
Baidu’s Ernie 4.5 Turbo and AI infra provider Fal’s USD 125 million raise highlight strong ecosystem momentum.
Signals
- Adoption: Already embedded in retail, healthcare, and media workloads.
- ROI: Documented performance gains validate enterprise readiness.
- Ecosystem: Backed by VC funding, cloud APIs, and major vendor integration.
Trajectory
Progressed from Trial (2024) to Adopt (2026). Expected to become a core capability across industries.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Enables video summarization, multimodal analytics, and personalized product recommendations.
- Risks: High compute/storage costs, complex data annotation requirements.
9. Federated AI Platforms – Trial
Platforms that enable collaborative model training across decentralized nodes without sharing raw data, which is critical for privacy-preserving AI.
Why It Matters
The federated AI market is projected to reach USD 9.8 billion by 2034. Pilots in healthcare, financial fraud detection, and IoT show clear value in regulated environments where data cannot move.
Signals
- Adoption: Active pilots in healthcare and finance, but limited enterprise scale.
- Ecosystem: Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Owkin are building platforms; interoperability is nascent.
- Revenue Reality: Still early, with low commercial revenues.
Trajectory
In the trial phase. Likely to progress slowly, with adoption tied to regulatory clarity and interoperability standards.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Enables privacy-preserving AI collaboration across silos.
- Risks: Technical complexity in aggregation, regulatory ambiguity on model ownership.
10. LLMOps Platforms – Trial
Operational platforms providing observability, evaluation, and lifecycle governance for large language model (LLM) applications in production.
Why It Matters
Vendors are rising, for instance, Google Vertex AI Evals, Databricks Mosaic AI Agent Eval, and Snowflake Cortex AI Observability are live. Datadog launched LLM monitoring, and OpenTelemetry is drafting semantic conventions for LLMs/agents.
Signals
- Adoption: 60% of large enterprises with active LLM deployments (such as Bank of America clients) have initiated large language model operations (LLMOps) pilots.
- Ecosystem: Rich open source software (OSS) and vendor activity, but standards are still forming.
- Maturity: Interoperability challenges keep deployments at the trial stage.
Trajectory
Moved from Assess (2024) to Trial (2026). Positioned to move toward adoption as telemetry and evaluation standards solidify.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Improves reliability, cost governance, and compliance for production LLMs.
- Risks: Fragmented metrics, blind spots in safety, lack of standardized telemetry.
11. Synthetic Data Generation – Assess
Platforms that create privacy-preserving datasets to augment scarce or sensitive data.
Why It Matters
The market is projected to reach USD 1.7 billion by 2030 at a 35.3% CAGR. By 2030, synthetic data is expected to make up 95% of AI training data for images and videos. However, risks such as model collapse from recursive training remain a major concern.
Signals
- Potential: Demonstrated value for privacy, data augmentation, and rare-event coverage.
- Gaps: Fidelity, bias transfer, and recursion risks limit large-scale enterprise adoption.
- Regulation: The EU AI Act mandates training-data disclosure by 2025-26, pressuring vendors to improve transparency.
Trajectory
Stays in assess (2026). Movement to trial depends on advances in fidelity and compliance-ready provenance controls.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Cuts costs, enables collaboration, expands data access for AI development.
- Risks: Model collapse, compliance exposure, bias transfer without provenance safeguards.
12. AI Agent Orchestration – Assess
Frameworks that coordinate multi-agent workflows across planning, tool use, and task hand-offs.
Why It Matters
Vendors are emerging, for instance, AWS Bedrock AgentCore, Google Agentspace, LangChain’s LangGraph, and OpenAI/Anthropic’s model context protocol (MCP). MCP standardizes agent-to-tool connectivity, though adoption is still experimental.
Signals
- Adoption: Mostly vertical pilots (eg, IT ops, finance); generalized management is immature.
- Standards: MCP is promising but still forming.
- Potential: Early traction, but safety, cost, and interoperability challenges remain.
Trajectory
Positioned in assess. Expected to progress toward trial by 2027 as standards mature and domain-specific use cases expand.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Scales complex multi-step workflows with human-in-the-loop reliability.
- Risks: Uncontrolled autonomy, vendor lock-in, and fragmented frameworks.
Quadrant 2: Platforms & Infrastructure
13. Hybrid/Distributed Cloud & Edge – Adopt
Architectures that integrate public clouds, private data centers, and edge nodes into orchestrated platforms to enable flexible workload placement.
Why It Matters
Hybrid cloud has become the default strategy, as 89% of enterprises pursue multi-cloud usage and 94% already run hybrid models.
Moreover, the hybrid cloud market is projected to reach USD 311.75 billion by 2030. This approach balances performance, cost, sovereignty, and real-time analytics.
Signals
- Adoption: Standard enterprise strategy across industries.
- ROI: Proven benefits in cost reduction, compliance, and performance optimization.
- Ecosystem: Platforms like F5 Volterra and EdgeConnex are widely adopted. BMW uses hybrid edge workloads for connected vehicle analytics.
Trajectory
Firmly in Adopt. Expected to remain foundational for enterprise IT through 2030.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Low-latency edge innovation, resilience, sovereignty control.
- Risks: Orchestration complexity, multi-cloud security management.
14. Energy-Efficient Compute (Liquid Cooling & Advanced Chips) – Trial
Energy-efficient compute combines liquid cooling (direct-to-chip, immersion) with optimized GPUs/NPUs to reduce power, thermal, and environmental impacts of dense AI workloads.
Why It Matters
The global data center liquid cooling market is projected to reach USD 27.72 billion by 2033 (22.8% CAGR). Hyperscalers operate AI racks at 20-135kW density, driving immersion and direct-to-chip cooling adoption.
NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs halve cooling energy use that delivering 25x energy efficiency and 300x water efficiency over air-cooling.
Signals
- Adoption: Strong hyperscaler pilots; limited enterprise rollout.
- ROI: Clear OPEX savings; retrofit costs remain high. Microsoft announced a USD 80 billion investment in liquid-cooled AI data centers by 2030.
- Ecosystem: Vendors are active, but operational best practices are immature.
Trajectory
In the trial phase. Expected to expand beyond hyperscalers as retrofit economics improve.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Lower OPEX, sustainability gains, and energy efficiency.
- Risks: High upfront investment, complex maintenance requirements.
15. Spatial Computing Toolchains – Assess
Integrated augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MR), AI, and internet of things (IoT) toolchains that enable immersive collaboration, simulation, and training across industries.
Why It Matters
The spatial computing market is projected to reach USD 1.06 trillion by 2034. Pilots are increasing for eg. Hadean integrated with Google Cloud Gemini; Apple Vision Pro and HoloLens 3 are driving momentum.
Sharp HealthCare launched a Spatial Computing Center of Excellence in 2024 using Apple Vision Pro + Epic for clinical training and workflow collaboration.
Signals
- Adoption: Active pilots across healthcare, training, and design; ROI is still early.
- Barriers: costs, interoperability, and training requirements.
- Momentum: Positioned as essential for next-gen immersive innovation.
Trajectory
In Assess. Could progress to Trial by 2027 as enterprise ROI evidence strengthens.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Immersive training, digital twins, collaboration enhancements.
- Risks: High total cost of ownership (TCO), lack of interoperability standards, and security vulnerabilities.
16. Quantum-Enhanced Hardware – Hold
Superconducting, photonic, and ion-trap chips designed for advanced computation, optimization, and secure communication.
Why It Matters
Quantum hardware research is advancing quickly, with Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, and IBM pushing improvements in qubits and error correction. Despite this momentum, most systems still operate with fewer than 200 logical qubits.
Investment remains strong in supercomputing, photonic, and ion-trap architectures, with companies such as Terra Quantum validating error-correction methods and PsiQuantum leading in photonic chip development.
Signals
- Adoption: Mostly limited to proofs of concept, demonstrations, and national research programs; enterprise adoption remains rare.
- Barriers: High costs, scarce quantum engineering skills, and a lack of standards.
- Readiness: Full fault tolerance and robust quantum error correction are not yet enterprise-ready.
Trajectory
In Hold. Enterprise-scale adoption is unlikely until qubit reliability and error correction significantly improve.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Potential breakthroughs in defense, pharmaceuticals, logistics, and cryptography.
- Risks: ROI uncertainty, vendor concentration, and “harvest now, decrypt later” data security threats.
17. WebAssembly at the Edge – Trial
A portable binary format enabling near-native, sandboxed execution at the edge for secure and low-latency workloads.
Why It Matters
Pilots such as wasmCloud show superior performance and lower latency compared to containers. WebAssembly system interface (WASI) 0.3 adds async and portability, while research demonstrates up to 99.5% reduction in cold-start latency for WASM edge functions versus container deployments.
Signals
- Adoption: Stable in pilots; not yet mainstream.
- Standards: WASI is evolving, improving portability and async support.
- Workforce: Limited expertise relative to container ecosystems.
- Barriers: Orchestration and monitoring tools are still immature.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to expand with maturing standards and tooling, potentially moving to Adopt within 5 years.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Modular, low-cost edge services, improved security via sandboxing.
- Risks: Fragmented standards, immature tooling, and debugging complexity.
18. eBPF-Powered Networking & Observability – Adopt
eBPF enables safe, programmable hooks in the Linux kernel for observability, networking, and security without custom kernel modules.
Why It Matters
93% of organizations are using, piloting, or evaluating Kubernetes, and 80% already run it in production. eBPF boosts packet throughput and reduces observability overhead. Tools like Cilium, Hubble, Pixie, and Parca are now standard in the cloud-native stack.
Signals
- Adoption: Standard in Kubernetes and OpenShift networking stacks.
- ROI: Faster troubleshooting, reduced downtime, improved resilience.
- Ecosystem: Backed by vendors and the open-source community.
Trajectory
In Adopt. Will remain foundational in Kubernetes-driven environments.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Fine-grained observability, programmable security, and performance boosts.
- Risks: Kernel-level programming complexity, potential misuse risks.
19. Next-Gen AI Accelerators – Adopt
GPUs, NPUs, and custom chips optimized for GenAI, multimodal models, and edge workloads, delivering higher performance-per-watt and bandwidth.
Why It Matters
Wall Street analysts project USD 3 – USD 4 trillion in AI infrastructure investments over the next five years. NVIDIA’s Blackwell GPUs are in high demand, powering high-performance AI infrastructure. Foxconn is deploying Blackwell for AI factories and digital twins, demonstrating ROI in industrial settings.
Signals
- Adoption: Rapid uptake by hyperscalers and enterprises.
- Ecosystem: Broad support across PyTorch, TensorFlow, ONNX, and CUDA/ROCm ensures production readiness.
- ROI: Proven in industrial deployments with faster cycles and cost reduction.
Trajectory
Solidly in Adopt. Will remain a key pillar of enterprise AI infrastructure.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Enables real-time AI, green computing, and multimodal workloads.
- Risks: Procurement volatility, rapid product cycles, vendor fragmentation.
20. Confidential Computing – Adopt
Safeguards data in use by running workloads inside hardware-rooted trusted execution environments (TEEs) or secure enclaves that complement encryption at rest and in transit.
Why It Matters
The market is projected to grow from USD 12.28 billion in 2025 to USD 41.17 billion by 2029 (35% CAGR). Microsoft migrated its Windows licensing service to handle billions of secure transactions to Azure’s confidential computing platform. Use cases include AI model protection, federated healthcare analytics, fraud detection, and cross-border data processing.
Signals
- Adoption: In production across hyperscalers and regulated industries.
- Standards: Supported by the Confidential Computing Consortium (CCC).
- ROI: Strengthens compliance controls and enables secure collaboration in sensitive environments.
Trajectory
Firmly in Adopt. Expected to expand as compliance regulations tighten and AI workloads move into regulated domains.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Safe AI adoption in finance, healthcare, and cross-border collaboration.
- Risks: Migration complexity, enclave performance overhead, vendor lock-in.
21. Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) 1.0 – Trial
An enhanced Ethernet standard for AI/HPC, delivering microsecond latency, RDMA-level throughput, and multi-vendor interoperability.
Why It Matters
The UEC 1.0 spec was released in June 2025, with 45+ members (including hyperscalers and the Open Compute Project (OCP) foundation joining the consortium. It promises congestion control, multipath transport, and performance tuned for clustered AI workloads.
Signals
- Adoption: Currently in hyperscaler pilots, not yet at production scale.
- Ecosystem: Broad industry backing with compliance and interoperability programs in development.
- Readiness: Product support is expected in late 2025 as vendors align with the spec.
Trajectory
In Trial. Likely to move toward adoption by 2027 as deployments stabilize and interoperability matures.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Low-latency GPU networking, reduced vendor lock-in, multi-vendor ecosystem.
- Risks: Integration challenges with legacy infrastructure, protocol instability in early rollouts.
22. Liquid & Advanced Cooling – Trial
Cooling solutions, including direct-to-chip, immersion, and two-phase systems that address AI’s escalating thermal demands while improving energy efficiency and rack density.
Why It Matters
The direct-to-chip segment alone is forecasted to grow from USD 2.53 billion in 2025 to USD 12.76 billion by 2034 (19.7% CAGR). Microsoft has deployed two-phase immersion cooling in production.
Also, Google rolled out liquid-cooled tensor processing unit (TPU) pods, achieving 99.999% uptime and halving rack footprints.
Signals
- Adoption: Proven in hyperscaler pilots; limited enterprise uptake due to retrofit costs.
- Innovation: Mixed-phase and high-capacity CDU systems push capacity.
- Maturity: Standards and skilled workforce adoption remain early-stage.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to expand from hyperscalers to enterprises as energy efficiency pressures mount.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Major operating expenditure (OPEX) savings, sustainability gains, reduced space requirements.
- Risks: Integration costs, supply chain dependencies, and coolant regulation concerns.
23. Alternative AI Silicon – Trial
Includes application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), optical interconnects, and neuromorphic accelerators developed to challenge GPU dominance and optimize for edge or domain-specific workloads.
Why It Matters
Graphics processing units (GPUs) still account for 82% of AI datacenter silicon revenue (2024), but alternative silicon is expanding. Geopolitics drive momentum as Chinese firms like Huawei (Ascend), Baidu (Kunlun), and Zhipu AI are building domestic alternatives amid US export restrictions.
Startups such as Ayar Labs, Celestial AI, Axelera AI, and Tenstorrent raised significant rounds in 2025 for optical and ASIC innovation.
Signals
- Adoption: Active pilots among hyperscalers; limited enterprise-scale deployments.
- ROI: Promises energy efficiency and specialization, but benchmarks remain limited.
- Ecosystem: Tooling and developer support are still immature.
Trajectory
In Trial. Could progress toward adoption in niche workloads by 2027 as ecosystems mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Supply chain diversification, domain-specific efficiency boosts.
- Risks: Immature ecosystems, talent shortages, vendor fragmentation.
24. UALink 1.0 (GPU-to-GPU Inside the Rack) – Assess
An open-standard GPU-to-GPU interconnect enabling scalable, low-latency, high-bandwidth communication inside AI pods that are positioned as a multi-vendor alternative to NVIDIA’s NVLink/NVSwitch.
Why It Matters
Ultra Accelerator link (UALink) 1.0 is backed by 85+ members, including AMD, Intel, AWS, Meta, Microsoft, and Cisco. It delivers 200 Gbps per lane and 800 Gbps per port with support for deterministic memory sharing, direct load/store operations, and atomic transactions across up to 1024 accelerators per pod.
Synopsys announced intellectual property (IP) and physical layer (PHY) availability for the second half of 2025, while Lightmatter joined to explore optical interconnect support.
Signals
- Adoption: No large-scale production deployments yet; still under evaluation.
- Ecosystem: Broad consortium support signals durability and openness.
- Readiness: Positioned as a lower-cost, open alternative to NVIDIA’s NVLink, reducing vendor lock-in.
Trajectory
In Assess. Likely to move to trial by 2027 as benchmarks mature and production pilots emerge.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Multi-vendor interoperability, lower-cost GPU fabrics, reduced lock-in.
- Risks: Integration hurdles, early instability, operational tuning challenges.
25. Edge AI Footprint – Assess
Runs inference directly on devices such as cameras, robots, IoT sensors, and industrial controllers to deliver ultra-low-latency, privacy-preserving processing independent of cloud infrastructure.
Why It Matters
The edge AI hardware market is projected to grow from USD 26.14 billion in 2025 to USD 58.9 billion by 2030 (17.6% CAGR). Also, 27% of manufacturing enterprises have deployed edge computing, with 64% planning deployments by 2027.
Microsoft and Qualcomm’s Copilot+ AI PCs illustrate momentum in client-side edge AI workloads.
Signals
- Adoption: Expanding pilots in utilities, oil & gas, and healthcare; standardization is limited.
- ROI: Benefits in latency, privacy, and resilience are offset by infrastructure costs and skills shortages.
- Ecosystem: Tooling remains fragmented across vendors with diverse software development kits (SDKs) and frameworks.
Trajectory
In Assess. Expected to move toward trial by 2027 as enterprise toolchains and skill availability improve.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Efficiency gains, improved privacy, and operational resilience in critical sectors.
- Risks: Endpoint security risks, interoperability challenges, shortage of skilled personnel.
26. Non-Standard, Vendor-Proprietary Fabric Stacks – Hold
Proprietary interconnects such as NVIDIA NVSwitch deliver optimized performance but restrict interoperability, which pushes enterprises toward open standards like UALink and OCP-based fabrics.
Why It Matters
The global data center fabric market is projected to grow at a 34% CAGR (2025-2030). Proprietary systems lock customers in, while industry momentum is shifting to open fabrics.
For example, Arista’s SWAG (Switch Aggregation Group) enables Ethernet-based stacking with unified management to align with OCP initiatives.
Signals
- Adoption: Still used in existing infrastructure but increasingly challenged by open-standard alternatives.
- Ecosystem: Strong shift toward UALink and OCP-backed fabrics.
- Risks: Proprietary fabrics raise TCO, limit flexibility, and create integration hurdles.
Trajectory
On Hold. Enterprises are maintaining current deployments but monitoring open-standard maturity for migration opportunities.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Migration to open fabrics can reduce costs and increase resilience.
- Risks: Proprietary stacks inflate costs, restrict vendor choice, and pose supply chain risks.

Quadrant 3: Security & Trust
27. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) – Trial
Cryptographic standards designed to resist quantum attacks, replacing classical algorithms vulnerable to “store now, decrypt later” threats.
Why It Matters
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) finalized three PQC standards in 2025, such as federal information processing standards (FIPS 203 (CRYSTALS-Kyber), FIPS 204 (CRYSTALS-Dilithium), and FIPS 205 (SPHINCS+)).
A backup Hamming Quasi-Cyclic (HQC) algorithm was also selected. Migration urgency is rising; only 15% of organizations are “quantum-safe champions,” while 50% are conducting pilots. Milestones include awareness/pilots by 2028, critical systems secured by 2031, and full migration by 2035.
Signals
- Adoption: Enterprises performing cryptographic inventories and pilots; full adoption not yet underway.
- Ecosystem: The PQC Coalition released a Migration Roadmap to support staged rollouts.
- ROI: Long-term resilience and regulatory compliance; migration is resource-intensive.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to move toward adoption by 2028-2031 as migration accelerates.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Long-term data protection, regulatory preparedness, resilience against quantum threats.
- Risks: Integration complexity, larger key sizes, latency overhead, skills shortage.
28. Disinformation Security Solutions – Assess
Tools to detect, counter, and mitigate AI-driven misinformation campaigns, deepfakes, and synthetic media threats.
Why It Matters
The World Economic Forum (WEF) Global Risks Report 2025 ranks misinformation as the top global risk in the near term. Fake news drives an estimated USD 39 billion annual stock market loss, with potential global economic damage near USD 78 billion/year.
Phishing/social engineering is also AI-powered, which impacts 57% of organizations daily or weekly.
Signals
- Adoption: Early deployments in AI monitoring, forensics, and blockchain provenance.
- Ecosystem: Fragmented; includes deepfake detection, forensic tools, and blockchain-based provenance.
- Readiness: Academic proposals (eg, blockchain for authentication) exist; enterprise-grade integration is still unproven.
Trajectory
In Assess. Could move to Trial by 2027 as enterprise demand rises and regulatory drivers mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Protects brand reputation, supports regulatory compliance, and bolsters social stability.
- Risks: Deepfake sophistication, fragmented tools, unclear ROI, and legal ambiguities.
29. Zero-Trust Extensions – Adopt
Expands zero-trust principles that offer least privilege and continuous authentication to AI agents, OT environments, and hybrid cloud workloads.
Why It Matters
Mandates drive adoption, as Executive Order (EO) 14028 directed Zero Trust implementation, the US Office of Management and Budget (OMB) M-22-09 required zero trust (ZT) for agencies, and M-25-04 extended measurement/reporting. Standards include NIST SP 800-207 (conceptual baseline) and SP 1800-35 (operational playbook, June 2025).
Signals
- Adoption: 61% of organizations had partially/fully implemented ZT; another 35% plan adoption within 18 months.
- ROI: Organizations with ZT saw USD 1 million lower average breach costs; a 2025 Zscaler-Marsh study projects up to a 31% reduction in insured cyber losses.
- Ecosystem: Broad alignment, such as Cisco, Microsoft, Google, IBM, Palo Alto, Okta, and Zscaler via NIST reference implementations.
Trajectory
Solidly in Adopt. Expanding to cover AI/machine identities and OT systems through 2027.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Comprehensive defense across cloud, AI, and OT.
- Risks: Complex integration, governance demands, and AI identity management challenges.
30. Data Security Posture Management – Trial
Platforms that unify discovery, classification, and protection of sensitive and shadow data across cloud, SaaS, and hybrid environments.
Why It Matters
The data security posture management (DSPM) market is projected to reach USD 4.15 billion by 2029 (15.1% CAGR). Investment is growing rapidly, as 56% of organizations plan to adopt DSPM within 12 months. Cloud data breaches remain among the most common vectors, underscoring their urgency.
Signals
- Adoption: Fast-growing adoption pipeline; widespread pilots underway.
- Ecosystem: Several vendors have stood out in reviews for their innovations and effectiveness. Although integrations and standards remain fragmented.
- ROI: Demonstrated risk reduction, though scaling and interoperability are challenges.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to move into Adopt by 2027 as standards consolidate and enterprise integrations mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Enhances visibility, compliance, and breach prevention.
- Risks: False positives, fragmented tooling, shortage of skilled practitioners.
31. Spatial Computing Toolchains – Assess
Combines AR/VR hardware with AI and 3D frameworks to enable immersive collaboration, training, and simulation.
Why It Matters
Pilots are accelerating; for instance, Apple’s Vision Pro and Microsoft’s HoloLens 3 catalyze enterprise interest, while Hadean + Google Cloud Gemini integrations expand simulation use cases. Sharp HealthCare launched a Spatial Computing CoE for clinical workflows.
Signals
- Adoption: Active pilots in healthcare, training, and manufacturing; ROI proof cases remain early.
- Barriers: High costs (USD 3499+ per device), limited battery life, and enterprise fit challenges.
- Ecosystem: Growing app/content ecosystem under visionOS; standards not yet stable.
Trajectory
In Assess, there is potential to move to Trial by 2028 as enterprise-grade ROI cases mature.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Immersive training, collaboration, digital twin visualization.
- Risks: Privacy concerns, physical safety issues, fragmented developer tooling, interoperability gaps.
32. Passwordless Auth (Passkeys) – Trial
Replaces passwords with device-bound, phishing-resistant authentication using biometrics or local PINs (FIDO2/WebAuthn).
Why It Matters
Adoption at the consumer scale is massive: Microsoft, Google, Apple, and Amazon rolled out passkeys by default in 2025. Microsoft set passkeys as the default for all new accounts that reporting a 98% success rate vs. 32% for passwords, with nearly 1 million passkeys registered daily. The market hit USD 21.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow to USD 60.3 billion by 2032 (15.8% CAGR).
Signals
- Adoption: Consumer-scale adoption is strong; enterprise-wide rollout (across all apps/IDPs) is still in pilot.
- Readiness: Standards are solid, but recovery flows and legacy app coverage vary.
- Governance: Enterprises testing portability, device loss/recovery, and policy frameworks.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to move to Adopt by 2027 as enterprise adoption catches up with consumer platforms.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Better login UX, lower helpdesk costs, alignment with zero-trust security.
- Risks: Device-targeted attacks, recovery loopholes, uneven support across legacy systems.
33. Model & Software Supply-Chain Security (SBOM, GenAI SSDF) – Assess
Supply chain security uses software bills of materials (SBOMs), model/dataset bills of materials (BOMs), and secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) (secure software development framework (SSDF)) controls to mitigate risks across software and AI pipelines.
Why It Matters
Driven by mandates like US EO 14144 and the European Union Cyber Resilience Center (EU CRA), SBOM adoption is becoming mandatory for critical software and AI. NIST SP 800-218A extends SSDF with foundation model-specific controls. Risk exposure is rising, with 150+ AI/ML supply chain CVEs reported in 2025.
Signals
- Adoption: Broad pilots are underway; production use is uneven, especially for GenAI pipelines.
- Ecosystem: SBOM tooling and lineage tracking are improving; gaps remain in integration and standards harmonization.
- Workforce: Only 23% of organizations report high visibility into their software supply chain; 49% lack a basic understanding.
Trajectory
In Assess. Could move to Trial by 2028 as standards converge and automation improves.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Provenance, faster patching, audit readiness.
- Risks: Standards fragmentation, incomplete model/data lineage, reliance on immature automation.
34. Secure Software Development Attestation (US Federal) – Adopt
Requires vendors to attest to secure-by-design practices from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST SSDF) via CISA/OMB forms stored in the Repository for Software Attestation & Artifacts (RSAA) repository for federal procurement.
Why It Matters
Vendors must file attestations aligning with EO 14028 and OMB memoranda M-22-18 and M-23-16. The process mandates provenance tracking (eg, SBOM), automated scanning, and secure development environments. Adobe and others have submitted attestations.
Signals
- Adoption: Mandatory for federal contracts; compliance already established among major providers.
- Ecosystem: The RSAA repository provides structured workflows for submission/validation.
- Spillover: Adoption spreading to high-assurance commercial markets.
Trajectory
Firmly in Adopt. Will remain essential as federal procurement enforces secure-by-design baselines.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Raises supply chain security baseline, streamlines audits, aligns federal/commercial practices.
- Risks: Non-compliance risks contract loss/legal exposure; rushed implementation may create process gaps.
35. Content Provenance/Content Credentials-Trial
Cryptographic standards that embed provenance metadata into media and AI-generated assets to enable verifiable origin and edit history.
Why It Matters
Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) momentum is growing. For instance, Amazon joined the steering committee, alongside OpenAI, Google, Adobe, and Meta. The Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) has expanded to 800+ partners across media, tech, and NGOs. Adoption is visible in hardware (Leica SL3-S and M11-P cameras) and software (Adobe Photoshop, Firefly, and Premiere Pro).
Signals
- Adoption: Strong pilots in news and creative industries; device/app coverage uneven.
- Readiness: Implementation and UX improving; multistakeholder frameworks in development.
- Ecosystem: Broad coalition of vendors, NGOs, and institutions.
Trajectory
In Trial. Likely to move to Adopt as device-level support and policy integration expands by 2027.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Strengthens digital trust, combats deepfakes, aids compliance.
- Risks: Metadata stripping/spoofing, incomplete ecosystem adoption, privacy concerns over edit history.
36. AI Safety & Model Risk Testing – Trial
Benchmarks and tools to continuously test AI models (LLMs/agents) for misuse, adversarial robustness, bias, and operational risks before and after deployment.
Why It Matters
AI safety testing is gaining traction through initiatives like the Future of Life’s AI Safety Index, holistic evaluation of language model (HELM) AIR-Bench with 5694 prompts across 314 risk categories, and the Lakera Model Risk Index.
Regulations, including the EU AI Act and US guidelines, require risk testing for high-impact systems. The AI model risk management market is projected to reach USD 10.5 billion by 2029 (12.9% CAGR).
Signals
- Adoption: Enterprises piloting safety tests, often integrated into SDLC/ML Ops workflows; still experimental.
- Readiness: Tools are improving, but lack full standardization.
- Standardization: Early convergence across frameworks, not yet complete.
Trajectory
In Trial. Likely to move to Adopt by 2028 as regulatory compliance drives enterprise-wide adoption.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Strengthens compliance, resilience, and defensibility.
- Risks: Prompt-injection blind spots, noisy or inconsistent benchmarks, “security theater” if monitoring isn’t continuous.
37. EU AI Act Compliance Toolchains – Assess
Platforms that operationalize EU AI Act obligations risk tiering, documentation, human oversight, transparency, logging, and fundamental rights impact assessment (FRIA) into lifecycle controls and audit artifacts.
Why It Matters
The EU AI Act is in force as general-purpose AI model (GPAI) obligations start in Feb 2025, while high-risk systems must comply by Aug 2026. The draft GPAI Code of Practice and EC guidance are informing phased compliance.
Enterprises are piloting compliance toolchains, but adoption varies. High-risk systems require a quality management system (QMS), conformity assessments, and post-market monitoring.
Signals
- Adoption: Organizations are in planning/pilot phases; few are audit-ready.
- Ecosystem: Fragmented vendor solutions; ongoing integration with governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) platforms.
- Maturity: Standards and supervisory practices not yet finalized.
Trajectory
In Assess. Expected to move to trial by 2027 as obligations harden and supervisory bodies begin audits.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Automates compliance evidence, reduces fine exposure, secures EU market access.
- Risks: High documentation burden, evolving controls, and interoperability gaps, raising costs/delays.
Quadrant 4: Developer Experience (DevEx) & Delivery
38. AI-Native Coding Assistants – Adopt
AI assistants that automate code generation, review, refactoring, testing, and compliance are evolving from autocomplete to autonomous workflows.
Why It Matters
Adoption is mainstream. 84% of developers use or plan to use AI tools, with 51% daily users. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) show 55.8% faster code completion.
Vendors, including GitHub, Anthropic, OpenAI, AWS, and IBM, push offerings like Copilot, Claude, and Gemini. The market is projected to reach USD 1.11 billion by 2028.
Signals
- Adoption: Widely rolled out; now essential in developer workflows.
- Vendor Push: Aggressive competition among hyperscalers and AI leaders.
- ROI: Documented productivity and quality improvements across enterprises.
Trajectory
Firmly in Adopt. Will remain foundational to modern developer tooling.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Accelerates development cycles, boosts productivity, and improves release quality.
- Risks: Code vulnerabilities, skill atrophy, hallucinations, and IP leakage.
39. Event-Driven Data Mesh – Trial
Combines real-time streaming with decentralized data ownership to expose event streams across domains to unify workflows and analytics.
Why It Matters
Vendor support is growing, as seen in AWS’s published reference architecture for event-driven data mesh. Retail deployments show strong use cases in real-time inventory, personalization, and omnichannel operations.
This unifies IoT, point of sale (POS), and backend data. Database Trends and Applications (DBTA) reports that only 19% of organizations use data mesh/fabric architectures today, but 47% plan to invest.
Signals
- Adoption: Early adoption with strong enterprise interest; still maturing.
- Benefit: Breaks down silos, enabling cross-domain agility and operational responsiveness.
- Barriers: Federated governance, complexity, and limited organizational understanding.
Trajectory
In Trial. Likely to mature into Adopt by 2028 as governance frameworks solidify.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Real-time visibility, improved cross-domain analytics.
- Risks: Schema drift, fragmented governance, compliance vulnerabilities.
40. Internal Developer Platforms (IDPs) – Adopt
Self-service platforms provide golden paths that abstract continuous integration (CI) / continuous delivery (CD), infrastructure, and security complexity, empowering developers while maintaining governance.
Why It Matters
Adoption is rising, as 50% of organizations already use IDPs, with 35% planning adoption within a year. Enterprise outcomes include 74% productivity improvement, 77% faster time-to-market, and 85% reporting revenue growth impact. Analysts expect 80% of platform engineering teams to offer IDPs soon.
Signals
- Adoption: Rapid mainstreaming across enterprises.
- Vendor Push: Humanitec, Port, and others enabling self-service CI/CD and infra.
- Strategic Fit: Golden paths are vital for scaling microservices and cloud-native operations.
Trajectory
In Adopt. Expected to become standard for platform engineering by 2027.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Boosts agility, developer satisfaction, and governance.
- Risks: Migration complexity, integration debt, risk of poorly designed IDPs.
41. Continuous Security Testing & SBOM Automation – Assess
Automation of SBOM generation, validation, and scanning within CI/CD pipelines to deliver real-time vulnerability detection, supply chain visibility, and compliance gating.
Why It Matters
Vendors like Anchore and Cybeats enable SBOM automation, while OWASP CycloneDX integrates into secure pipelines. Benefits include faster remediation (eg, Log4j), cost reduction, and stronger supply chain transparency.
The EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) mandates SBOMs in digital products by Dec 2027, and the information sharing and analysis center (Auto-ISAC) SBOM report shows OEM adoption in automotive.
Signals
- Adoption: Broad pilots, expected to accelerate as compliance deadlines approach.
- Ecosystem: Vendor tools are active, but format fragmentation persists.
- Challenges: A 2025 review highlights tooling gaps, SBOM maintenance overhead, and validation risks.
Trajectory
In Assess. Likely to move to Trial by 2027 as CRA and sector-specific mandates force adoption.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Improves transparency, accelerates remediation, and strengthens compliance posture.
- Risks: Format competition, SBOM accuracy over time, extra workload for teams.
42. OpenTelemetry (Traces/Metrics/Logs + Profiling) – Adopt
A vendor-neutral observability standard unifying logs, metrics, traces, and profiling across distributed systems.
Why It Matters
Backed by 60 vendors, OpenTelemetry is now the 2nd most active cloud native computing foundation (CNCF) project (after Kubernetes). There’s an increase in adoption, as 48.5% of IT orgs already use OpenTelemetry (OTel), with another 25.3% planning adoption; 81% view it as mature.
Benefits include a 40 to 60% mean time to resolution (MTTR) reduction, cost savings from tool consolidation, and improved resolution speed.
Signals
- Adoption: Broad enterprise usage; maturity well established.
- Performance: The OTel-Arrow protocol improves compression 10x and efficiency 40% over the OpenTelemetry protocol with Zstandard compression (OTLP+ZSTD). This optimizes the performance and efficiency of observability data transfer.
- Ecosystem: Supported by Dynatrace, Grafana, and most major observability vendors.
Trajectory
Firmly in Adopt. Will remain the default observability standard through 2030.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Unified observability, cost savings, faster troubleshooting.
- Risks: Legacy system integration, data volume management, and early-stage AI tracing features.
43. WebAssembly Components / wasmCloud – Trial
Extends WebAssembly beyond browsers into cloud and edge environments and managed via wasmCloud for secure, portable workloads.
Why It Matters
wasmCloud v1.4 integrates with 20+ Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) projects (eg, Kubernetes, OpenTelemetry, and Argo. Enterprise pilots include Adobe, Orange, BMW, and Akamai. Telecom PoCs (Orange/Vodafone, TM Forum Catalyst) show wasmCloud enabling interoperable, edge-native applications. Benefits include sub-ms startup, fault tolerance, and sandbox security.
Signals
- Standards: WebAssembly system interface (WASI) 0.3 will add async to the component model, broadening server-side applicability.
- Maturity: WASI 0.2 and the Component Model are supported in Wasmtime; full spec and ecosystem maturity are still developing.
- Adoption: Early enterprise pilots; strong vendor and telecom interest.
Trajectory
In Trial. Likely to advance as WASI standards stabilize by 2027.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Portable, secure edge runtimes, interoperable workloads.
- Risks: Immature tooling, onboarding complexity, and evolving standards.
44. GenAI Observability/Evals in CI/CD – Trial
Integrates tracing, evaluation, and guardrails into CI/CD pipelines to monitor generative AI reliability, safety, and cost.
Why It Matters
Vendors are pushing new solutions. AWS CloudWatch GenAI Observability (Preview) offers telemetry for latency, errors, and prompt tracing, while Dynatrace tracks compliance, hallucinations, and prompt misuse.
Tools like Coralogix AI Center help monitor personally identifiable information (PII) risks and bias. Enterprises increasingly include hallucination, bias, and prompt-injection checks in GenAI workflows.
Signals
- Adoption: SDKs and custom evaluators (eg, SageMaker + MLflow) dominate; platforms are still early.
- Standards: No formal standards; fragmented practices.
- Governance: Compliance pressures are pushing organizations toward baseline observability.
Trajectory
In Trial. Expected to progress as industry standards converge and vendor tools mature by 2028.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Builds trust, improves AI reliability, and supports compliance.
- Risks: Nondeterminism in models, complex integrations, lack of standard frameworks.
45. AI-Augmented SRE & Incident Automation – Assess
Uses agentic AI runbooks for incident detection, root cause analysis, and remediation to reduce manual toil in IT Ops, site reliability engineering (SRE), and SecOps.
Why It Matters
ServiceNow enables AI-powered playbook automation for faster response, while Torq reduces incident workflows, eg, replacing an 80-step security operations center (SOC) process with a 3-step AI-driven runbook. These tools promise faster MTTR and cost efficiency.
Signals
- Adoption: Pilots are active across IT Ops and SecOps; standard enterprise adoption is still limited.
- Barriers: Legacy system integration, governance constraints, and complex runbook automation.
- Ecosystem: Early vendor momentum, but the maturity of standards remains low.
Trajectory
In Assess. Likely to advance into Trial by 2027 as incident automation gains confidence.
Opportunities & Risks
- Upside: Self-healing systems, reduced MTTR, operational savings.
- Risks: Unsafe automation without human oversight, governance gaps, and legacy integration friction.
Macro Forces Shaping 2026 Technology Radar
AI Scale-Up
- The global AI market is projected to grow at a 35.9% CAGR to USD 1.8 trillion by 2030.
- AI adoption has accelerated sharply, with 78% of organizations now using AI in at least one business function.
- The AI infrastructure market is forecast to rise to USD 499.33 billion by 2034.
- Supporting this, McKinsey estimates that USD 6.7 trillion in global data center investment will be required by 2030, with USD 5.2 trillion dedicated to AI-ready capacity.
Rise of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
- In August 2024, NIST published the first set of post-quantum cryptography standards.
- Current preparedness is limited, as only 52% of organizations measure their quantum-risk exposure, and 30% are taking concrete steps toward PQC adoption.
Sustainability Mandates
- The EU’s corporate sustainability reporting directive (CSRD) affects about 10 000 companies by mandating ESG disclosures with third-party auditing.
- The ICT sector is forecast to account for 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions by 2040, on par with current US emission levels.
- Global e-waste reached 57.4 million metric tons in 2021, with only 17.4% properly recycled.
Geopolitical Forces
- AI chip export controls, licensing tiers, and military maneuvers in the Pacific heighten supply chain risks.
- New AI alliances, such as US-Gulf AI campuses and EU-led regulation, signal a multipolar order. Asia pushes AI safety benchmarks, while Latin America builds digital cooperation.
- Rising Taiwan conflict risks threaten semiconductor lifelines, while Middle East instability impacts energy and cyber infrastructure.
Explore the Latest Innovations & Startups to Stay Ahead
With thousands of emerging technologies and startups, navigating the right investment and partnership opportunities that bring returns quickly is challenging.
With access to over 7 million emerging companies and 20K+ technologies & trends globally, our AI and Big Data-powered Discovery Platform equips you with the actionable insights you need to stay ahead of the curve in your market.
Leverage this powerful tool to spot the next big thing before it goes mainstream. Stay relevant, resilient, and ready for what is next.









