Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
The space technology advances with innovations in defense, exploration, and commercial applications in 2025. Trends like satellite data analytics and space-based quantum communication enhance global connectivity and security. While breakthroughs in propulsion systems and semiconductors are making space travel more efficient and reliable. Further, advancements in space-based solar power and defense security are reshaping space exploration and commercialization.
What are the Top 10 Trends & Innovations in Space Technology in 2025?
- Defense & Space Security
- In-Space Manufacturing
- Satellite Data Analytics
- Space Robotics
- Space-based Solar Power
- Space-based Quantum Communication
- Space Debris Management
- 3D Printed Components
- Propulsion Technologies
- Semiconductors for Space
Methodology: How We Created the Space Technology Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 5M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the space tech industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the space tech innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Space Technology Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Space Technology Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 1400+ global startups & scaleups. The Space Technology Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the space tech industry trends & startups that impact your company.

Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Space Technology Trends
The Tree Map below highlights the top trends in space technology in 2025. Defense and space security, along with space-based quantum communication, are enhancing global security and data encryption. The satellite data analytics transforms Earth observation and remote sensing. Likewise, space robotics and in-space manufacturing enable new capabilities for long-duration missions and orbital infrastructure.
Advancements in propulsion technologies and semiconductors are further improving spacecraft performance, which makes deep-space exploration more feasible. Moreover, sustainability efforts, such as space debris management and 3D-printed components, optimize resource use and reduce costs. Lastly, innovations like space-based solar power are reshaping energy generation beyond Earth to mark a new era in space technology.

Global Startup Heat Map covers 1400+ Space Technology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 1400+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and the United States, followed by India. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.

Want to Explore Space Technology Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Trends in Space Technology [2025 and Beyond]
1. Defense & Space Security
The global aerospace cybersecurity market is set to reach USD 58.9 billion by 2032. It will further grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2022 to 2032.
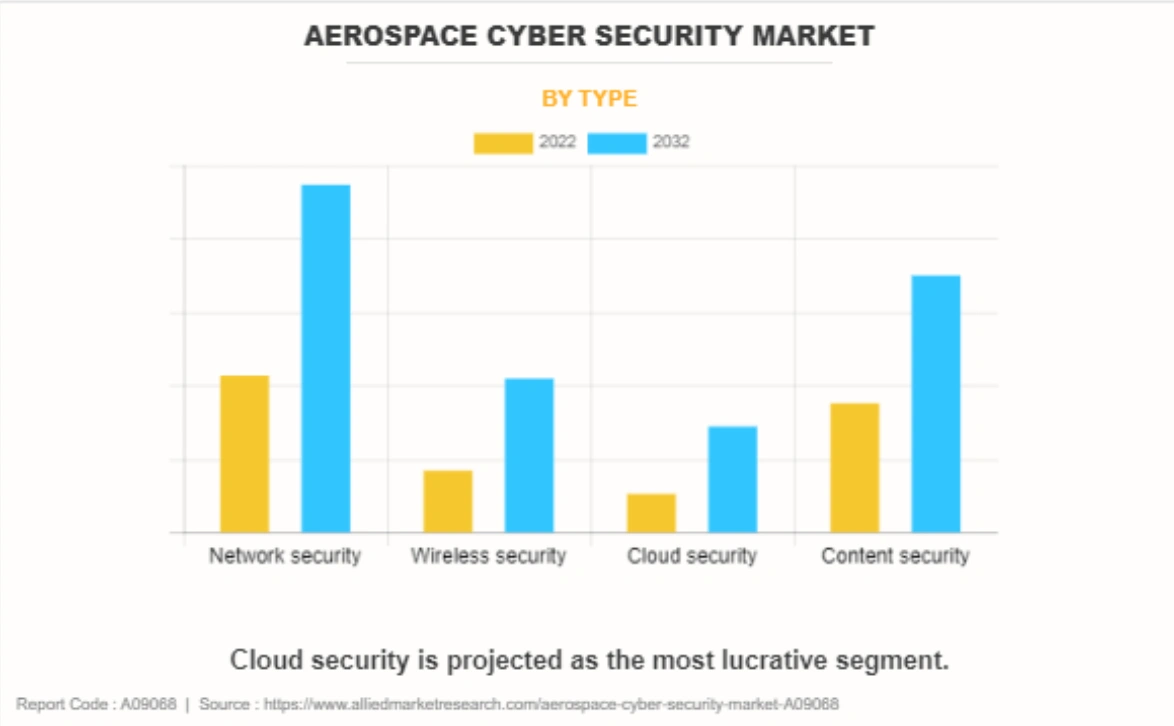
Credit: Allied Market Research
Governments worldwide allocated USD 73 billion to defense-related space programs in 2024. This represents 54% of global government space budgets and reflects the increasing focus on securing aerospace infrastructure.
Moreover, AI’s role in defense operations is expanding, with autonomous systems, decision-making enhancements, and military strategy optimization expected to dominate by 2025.
Not only that, laser communication systems are improving data transfer speeds and resilience. This will benefit defense and commercial aerospace applications.
Digital twin technology aids battlefield simulations and equipment maintenance and is projected to grow significantly in defense.
Industry investments are accelerating, with NATO’s EUR 1 billion Innovation Fund—the first multinational defense-focused VC initiative—announcing its first deep-tech investments in June 2024.
BitRezus secures Satellites Operations
Greek startup BitRezus develops Astropledge, a cybersecurity platform that protects space assets and operations. Astropledge integrates embedded hardware and blockchain to create a tamper-proof layer, which ensures real-time consensus among untrusted partners for secure mission operations.
The platform works with any satellite type or manufacturer to provide flexibility across various systems. BitRezus uses smart contracts and advanced cryptography to offer a zero-trust environment that protects space and terrestrial infrastructures.
Muon Space makes LEO Satellite Constellations
US-based startup Muon Space develops an integrated technology stack Muon Halo for low Earth orbit satellite constellations in Earth intelligence missions. It includes a digital twin simulation platform MuSim that optimizes mission design and operations. Also, its middleware MuOS connects space, ground, and cloud systems through an IP-based software-defined network.
Moreover, the startup offers MuCore, which is a software-defined instrument core that supports adaptable sensors and efficient data processing. The configurable spacecraft MuSat with a modular design enables rapid and scalable mission configurations. Further, it provides MuDash, a cloud-based platform that supports communications, command, and control. The startup’s approach ensures faster deployment, better performance, and reliable data capture across various space missions.
In addition, Muon Space secured USD 56 million in Series B funding and surpassed USD 100 million in customer contracts in 2024. This also included a landmark agreement with SNC.
2. In-Space Manufacturing
The in-space manufacturing (ISM) market is projected to grow from USD 1.33 billion in 2024 to USD 10.67 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 29.78%.
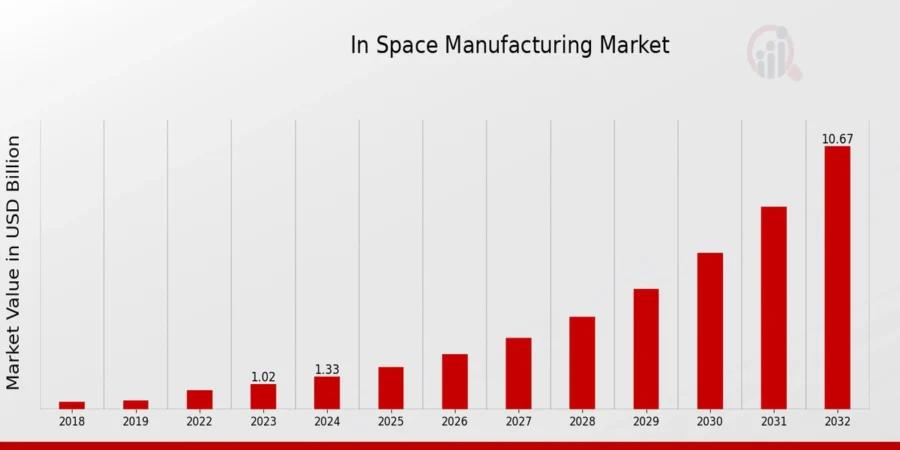
Credit: Market Research Future
The advancements in 3D printing, microgravity casting, and robotics drive ISM’s rapid expansion. These technologies enable the production of high-quality materials like ZBLAN fiber optics and pharmaceuticals, which are challenging to manufacture under Earth’s gravity.
The increasing number of satellites, from approximately 6718 in 2022 to over 9241 by early 2024, further fuels demand for ISM capabilities, especially for satellite assembly and repair in orbit.
ISM’s key applications include manufacturing components for satellites, spacecraft, and space habitats which support long-term space exploration and commercial activities.
Besides, North America accounted for about 34% of the ISM market share in 2023. This is due to strong government support, private-sector innovation, and leadership in advanced manufacturing technologies like additive manufacturing.
A-SpaX advances Space Manufacturing & Experiments
Dutch startup A-SpaX develops the Climate Box to facilitate high-power production in space that controls the environment within commercial space stations. The Climate Box maintains temperature limits using heat architecture to ensure optimal manufacturing conditions.
The startup’s solution’s dimensions are 420x420x900mm, and it integrates with express racks, which makes it suitable for fiber optic production. This controlled environment enables A-SpaX to create superior materials in space, like optical fibers that transmit signals over longer distances than those produced on Earth.
ArcSpace builds Orbital Testbed Operations Platform
French startup ArcSpace offers the Orbital Testbed Operations Platform, a semi-autonomous orbital testbed for low Earth orbit (LEO). It is equipped with robotic arms, tools, processes, and instruments, and supports in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing (ISAM) technology demonstrations.
The startup’s platform also enables on-orbit hardware qualification and validation of robotics and attitude and orbit control systems (AOCS) algorithms in real space conditions. Its key features include a 12-month contract-to-flight timeline for hardware and a 1-month timeline for software to facilitate rapid iterative design for space products.
3. Satellite Data Analytics
The global satellite data services market will grow at a CAGR of 16.0% from 2024 to 2030 due to increased investments and advancements in data processing technologies.
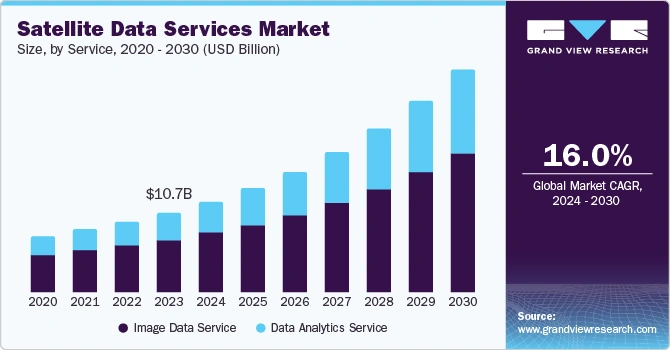
Credit: Grand View Research
In 2024, Earth Observation (EO) investments reached USD 1.7 billion, with over USD 1 billion going to downstream firms using satellite data for commercial applications.
Satellite data is crucial for tracking climate change, monitoring deforestation, and managing disasters. Real-time geospatial data enhances rapid response to events like wildfires and floods to improve emergency management and mitigation strategies.
What’s more, the market for EO satellites is growing quickly. There were over 900 active EO satellites in orbit in 2024, which is expected to exceed, 2300 by 2032.
The integration of AI and machine learning (ML) into satellite analytics enables predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and faster data processing. Companies like Planet Labs are working with NVIDIA to integrate AI edge processing into next-generation Pelican satellites.
Edge computing on satellites is also emerging as it allows near-real-time data processing and reduces reliance on ground stations.
Space-Eyes provides AI Space-based Market Prediction
US-based startup Space-Eyes builds AI-driven predictive analytics for space domain awareness, maritime intelligence, wildfire detection, carbon emissions tracking, and financial risk analysis. It uses satellite, airborne, and non-spatial data to provide real-time insights for decision-making across industries.
The startup’s SeaWatch system enhances maritime navigation and security with AI analytics, real-time support, and sustainable optimization of fuel and emissions. FireWatch predicts wildfires, assesses risks and improves disaster response with sensors and AI. Further, CarbonWatch monitors carbon emissions and biomass changes via satellite geospatial analysis to support carbon credit verification and environmental sustainability.
Moreover, its FinancialWatch delivers predictive market insights for commodities and global financial risk assessment by combining data from various intelligence platforms. Space-Eyes optimizes operations, enhances security, and promotes sustainability in aerospace, defense, and environmental sectors through AI-powered space-based market prediction and disaster management.
Zaitra makes Space Qualified Data Processing Unit
Czech Republic-based startup Zaitra develops onboard data processing solutions to lower satellite data transmission costs. It advances spacecraft autonomy and filters noise from data using AI. SKAISEN, its AI-powered onboard cloud detection solution, identifies and flags cloudy pixels in Earth observation imagery that enables operators to minimize unnecessary data transmission.
Further, the startup’s SKAIDOCK, is a space-qualified data processing unit that supports the Xiphos Q8 computational module. It features a CubeSat-compatible PC104 form factor and versatile interface options. Zaitra’s solutions optimize limited downlink capacity and reduce latency in satellite communications.
4. Space Robotics
The global space robotics market was valued at USD 5.41 billion in 2024. It is projected to grow from USD 5.69 billion in 2025 to USD 8.47 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 5.1% during the forecast period.
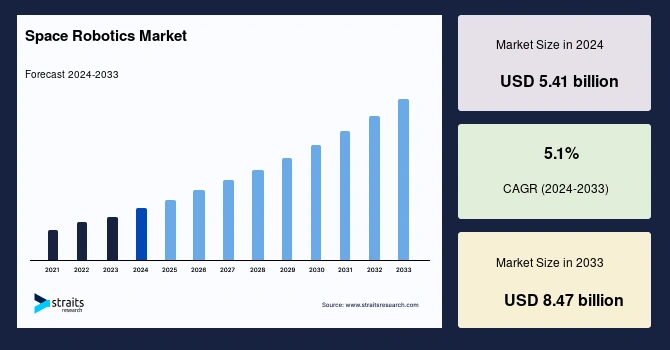
Credit: Straits Research
The increasing demand for satellite deployment, maintenance, and repair drives the adoption of robotic systems for cost-effective and efficient space missions. Robotics also plays a critical role in planetary exploration, space colonization, and space debris removal.
North America leads the space robotics market with over 35% of the market share in 2023. This is driven by NASA’s ambitious missions and private-sector advancements from companies like SpaceX.
Further, venture capital investments have surged, raising over USD 200 million for more than 40 pioneering space robotics firms in the past three years.
In Europe, the European Commission allocated USD 183.5 million for robotics-related projects between 2023 and 2025.
NASA’s Artemis mission invests in autonomous robots for lunar construction to support long-term Moon and Mars exploration.
Moreover, emerging trends in space robotics include autonomous robots capable of real-time decision-making, swarm robotics for coordinated tasks, and modular robotic systems designed for diverse missions.
InspeCity builds Remotely Actuated Motorized Arm
Indian startup InspeCity develops autonomous robotic platforms for in-orbit satellite repairs, upgrades, and life-extension activities to reduce costly replacements and minimize space debris. The startup’s RAMA (Remotely Actuated Motorized Arm) has a multi-degree-of-freedom design and integrated sensors for performing targeted diagnostics and repairs to extend satellite lifespans.
The RIG (Robotically Inserted Guidance System) autonomously docks with satellites and performs critical repairs and upgrades with precision to ensure compatibility with various satellite models. Further, its VEDA (Vehicle for Life Extension and De-orbiting Activities) transports RIG and RAMA to their destinations, and uses GITA, an eco-friendly propulsion system, for satellite maintenance.
Evolunar manufactures Lunar Exploration Autonomous Spacecraft
Italian startup Evolunar builds the LuNaDrone, a small autonomous spacecraft for lunar exploration and post-landing mobility services. It operates independently of external signals with rocket propulsion and a proprietary visual-inertial navigation system.
LuNaDrone flies over challenging lunar terrains like craters, pits, and permanently shadowed regions. Its compact size allows compatibility with various commercial landers and ensures frequent lunar access. The startup’s spacecraft collects high-resolution data, transports payloads with power and communication support, and performs scouting flights to identify resources and potential hazards.
5. Space-based Solar Power
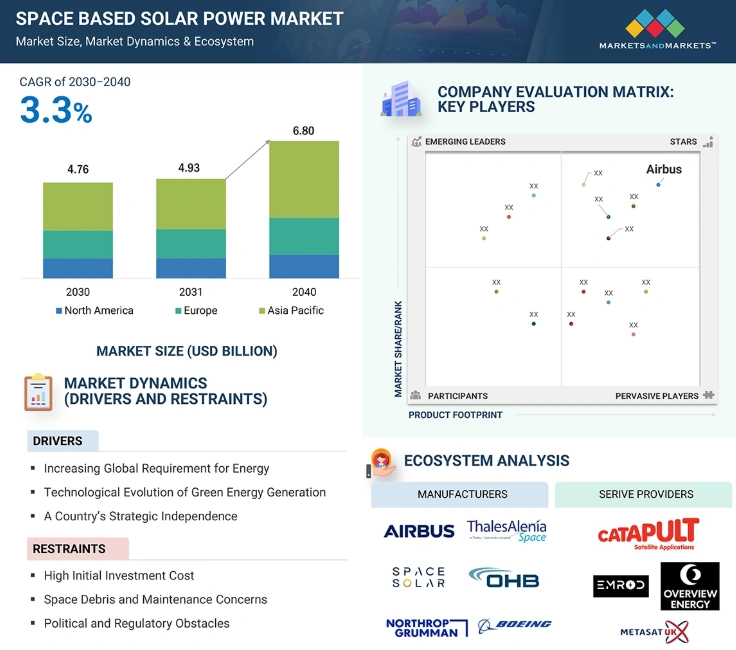
The space-based solar power (SBSP) market will reach USD 4.7 billion in 2030 and grow to USD 6.8 billion by 2040, at a CAGR of 3.3% from 2030 to 2040.
Credit: Markets and Markets
SBSP systems generate 2000 gigawatts of continuous power. They produce 40 times more energy than Earth-based solar panels and eliminate intermittency issues faced by terrestrial renewable sources like wind and solar.
Governments and institutions worldwide are investing in SBSP technology. The European Space Agency (ESA) launched the SOLARIS program to evaluate large-scale SBSP deployment across Europe.
Likewise, China’s Chasing the Sun project aims to generate one megawatt of space-based solar power by 2030 and achieve commercial viability by 2050.
Caltech demonstrated wireless power transmission from space in early 2024, marking a milestone toward commercial SBSP adoption.
Moreover, global investment in SBSP reached USD 370 million in 2024 and is projected to rise to USD 1.9 billion by 2029.
Wematics advances Solar Power Forecasting
Austrian startup Wematics develops AI-driven fisheye sky cameras to improve solar power forecasting. Its SkyAI system uses deep learning and edge AI to monitor and predict solar energy output to reduce uncertainties and enhance grid efficiency.
The startup’s SkyTwin creates a digital twin of the sky through volumetric cloud rendering and shadow projection to generate real-time irradiance maps for better performance.
Source manufactures Space Energy Products
US-based startup Source develops spacecraft power solutions such as space-grade solar modules, small solar arrays, and large deployable solar arrays. The solar modules range from 15.9W to 65W and provide reliable energy for space applications. Small solar arrays offer 130W to 1kW and support body-mounted and deployable configurations for flexible satellite power needs.
Further, large deployable solar arrays generate 1.7kW to 10kW to deliver high-output energy for space stations, deep-space missions, and high-power satellites. Source’s products feature high specific power, full electrical redundancy, and fault tolerance against micrometeorites and shading.

6. Space-based Quantum Communication
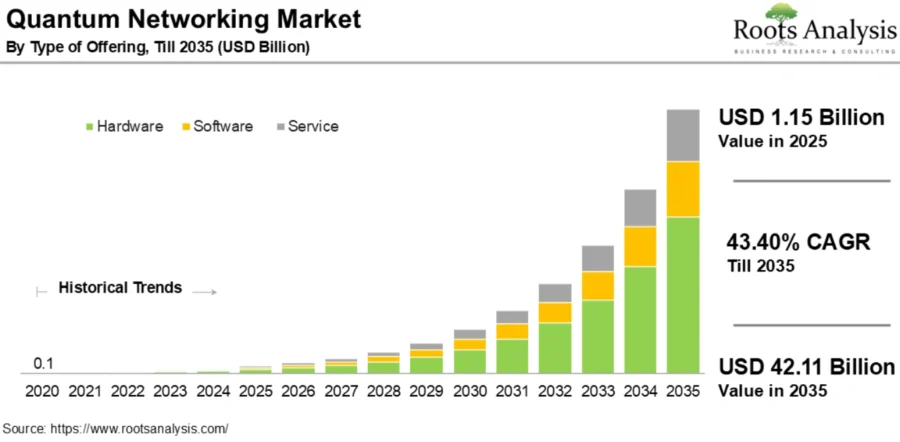
The global space-based quantum computing market will reach USD 7.5 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 22.5% during the forecast period.
The increasing adoption of quantum communication technologies is driving advancements in aerospace, cybersecurity, national defense, and telecommunications. Quantum key distribution (QKD) emerges as a critical solution against cyber threats.
The integration of quantum systems with existing telecommunication networks accelerates commercialization efforts. Hybrid networks combining classical and quantum systems become more scalable and accessible, expanding practical applications.
By 2035, the broader quantum networking market will grow from USD 1.15 billion in 2025 to USD 42.11 billion, at a CAGR of 43.4%.
Credit: Root Analysis
In January 2025, WISeSat.Space achieved a breakthrough in post-quantum transactions from space by integrating blockchain and quantum technologies.
Further, the SEAQUE experiment launched aboard SpaceX’s CRS-31 mission in November 2024 tested quantum entanglement for secure long-distance space communications and reinforced the viability of quantum networks.
Adamant Quanta builds Chip-scale Quantum Sensors
Swedish startup Adamant Quanta makes chip-scale quantum sensors for measurements, communication, and navigation on land, sea, and space. Its DiCE.X (Diamond Integrated Crystal Electrode) uses a metalized, synthetically grown diamond to generate a dense nitrogen-vacancy defect ensemble, which facilitates flexible integration and testing for various sensing and signal-generating architectures.
The startup’s QDiAC.X (Quantum Diamond Atomic Clock) utilizes a dense ensemble of electron spin transitions to generate a stable reference signal. It comes in a rugged, surface-mount form factor, outputting fixed frequencies between 10–25 MHz as square or sine wave references, and a square pulse-per-second signal.
SPACEOPTIX makes Quantum Communication Mirrors and Telescopes
German startup SPACEOPTIX develops mirrors and telescopes for free-space communication and includes laser and quantum communication applications. The startup contributes to the CubEniK project, which advances satellite-based QKD. It provides specialized telescopes and optical components essential for transmitting entangled photons between ground stations.
This facilitates secure quantum communication over long distances. SPACEOPTIX also develops the TLX80, a modular all-aluminum mirror telescope for optical free-space communication and quantum technologies.
7. Space Debris Management
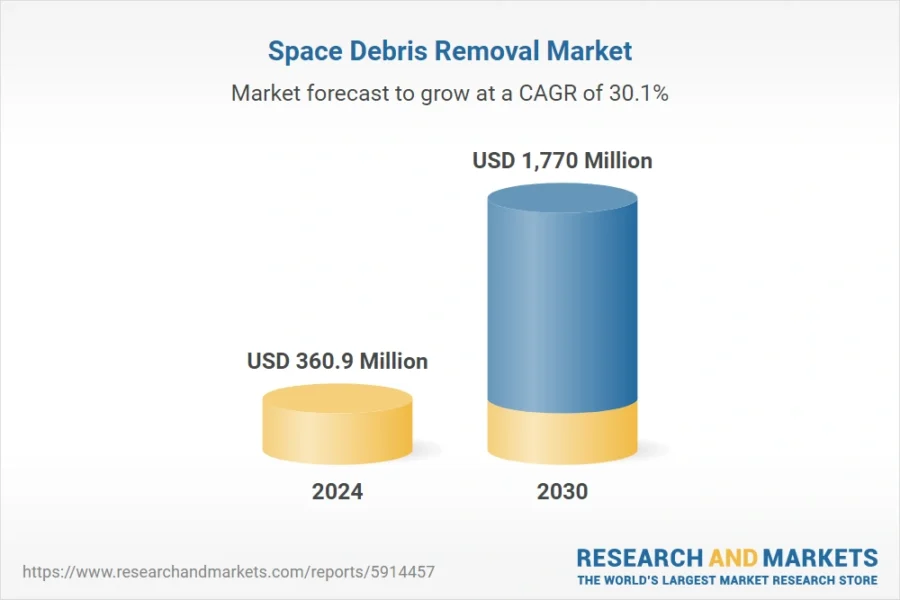
The space debris removal market was valued at USD 360.90 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 30.10%, reaching USD 1.77 billion by 2030.
This market growth is driven by increasing regulatory pressures, international agreements, and technological advancements to mitigate the threat of orbital debris.
Credit: Research and Markets
Statistical models estimate there are approximately 40 500 space debris objects larger than 10 cm, 1.1 million objects measuring between 1 cm and 10 cm, and 130 million smaller fragments between 1 mm and 1 cm.
Likewise, nearly 37000 objects are actively tracked and cataloged, including defunct satellites, spent rocket bodies, and collision fragments. These pose significant risks to active space missions and future operations.
Governments and agencies are intensifying debris management efforts. The European Space Agency (ESA) in 2024 awarded a EUR 86 million (USD 93.4 million) contract to ClearSpace SA for an active debris removal mission.
Meanwhile, NASA is conducting studies on cost-effective debris management strategies to emphasize economic feasibility for mitigation and remediation.
Active debris removal technologies are also evolving rapidly, with solutions such as robotic systems, lasers, and deorbiting devices gaining traction.
Andraste Group makes Debris Acquisition Satellite
UK-based startup Andraste Group develops the DARES (Debris Acquisition and Retrieval Satellite) to address space debris in low Earth orbit. DARES approaches larger defunct satellites and debris and attaches to them.
It either transports them to the Orbital Asset Recovery Unit (OARU) for preservation or guides them into a controlled deorbit to burn up in the atmosphere. The startup’s method ensures the safe removal or retrieval of space objects.
Delta Infinite enables Orbital Debris Remediation
US-based startup Delta Infinite builds Object Capture technology to capture and dock with objects in space, including asteroids and orbital debris. The system enables secure docking regardless of an object’s size, material, or spin rate, which allows for resource extraction and space debris removal.
The capture mechanism addresses one of the most pressing challenges in modern space operations by reclaiming and clearing orbital pathways. Delta Infinite offers solutions for asteroid resource utilization and debris remediation to enhance space sustainability and ensure the long-term viability of shared orbital space.
8. 3D Printed Components
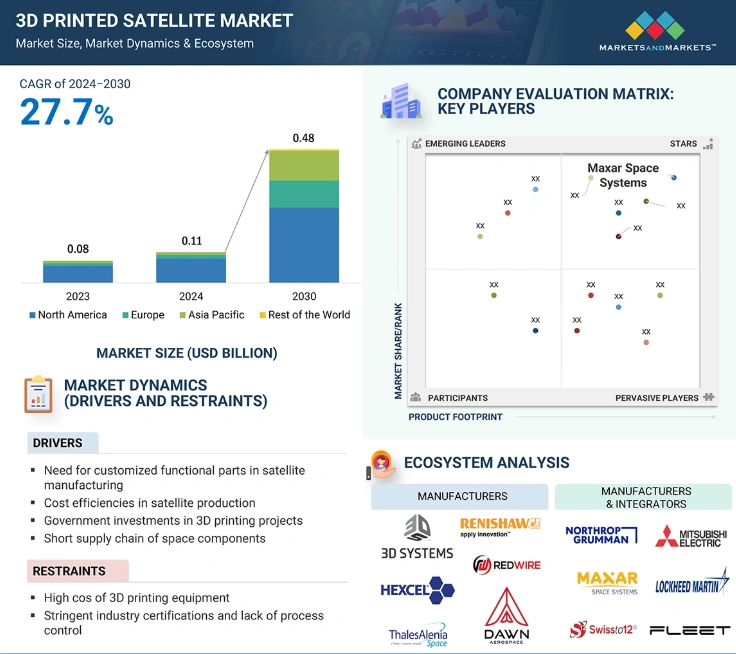
The 3D-printed satellite market will grow from USD 112 million in 2024 to USD 487 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 27.7%.
Credit: Markets and Markets
Space-based 3D printing is expanding due to the need for lightweight components and cost-effective manufacturing. In-space production capabilities also reduce reliance on Earth-based supply chains.
North America leads the market, with the United States at the forefront. Significant investments by NASA, Maxar Space Systems, and Northrop Grumman Corporation drive this growth. These investments focus on lightweight designs and cost savings, including additive manufacturing technologies.
Similarly, Asia-Pacific will witness the fastest growth, as China, India, and Japan adopt 3D printing for aerospace applications in their space programs.
Further, advanced materials like metals and polymers are enhancing the development of lightweight spacecraft, satellites, and rover components.
In-space manufacturing using 3D printing reduces dependency on costly resupply missions. It enables on-demand production of housing, tools, spare parts, and large-scale structures such as space stations and solar arrays.
Besides, the integration of AI optimizes design processes and material selection for space environments. Emerging advancements such as using local resources like lunar dust for in-situ construction are creating the way for sustainable long-term space infrastructure.
SpaceLab manufactures Space 3D Printers
Kazakhstan-based startup SpaceLab designs a 3D printer for space tech applications and offers FDM (fused deposition modeling) and SLA (stereolithography) technologies for diverse manufacturing needs. The startup’s SL310 model features a 300×300×300 mm working area and has nozzle sizes ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 mm. The print speed reaches up to 200 mm/s with an accuracy of up to 50 microns.
The startup’s 3D printer supports materials such as PETG, PLA, and thermoplastics up to 280°C to ensure versatility across production processes. The FDM method enables the cost-effective production of complex parts through sequential thermoplastic layering, while SLA printing utilizes liquid photopolymers to achieve high resolution and smooth surfaces. It also minimizes waste and enhances material strength.
ABRA Space makes 3D Rocket Engines
UK-based startup ABRA Space manufactures solid-fuel rocket engines by integrating 3D printing technology. The product lineup includes the ABRA18 Maya, TEO 18, and AURA 24, which feature compact designs with diameters of 18mm to 24mm for small-scale propulsion needs.
The larger models such as the SKYLAB 24, VULCAN 29, ALPHA 29, and KAYRA 38 extend performance capabilities and have lengths ranging from 120mm to 200mm. The startup’s AEGIS 54 measures 400mm in length and 54mm in diameter, and provides robust thrust for more demanding applications. These engines combust a solid fuel and oxidizer mixture to generate thrust and ensure efficient propulsion.
9. Propulsion Technologies
The space propulsion market will grow from USD 216.7 billion in 2025 to USD 322.2 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.25%.
This growth is driven by demand for LEO satellites, space tourism, and satellite-based communication services that advance the development of propulsion technologies.
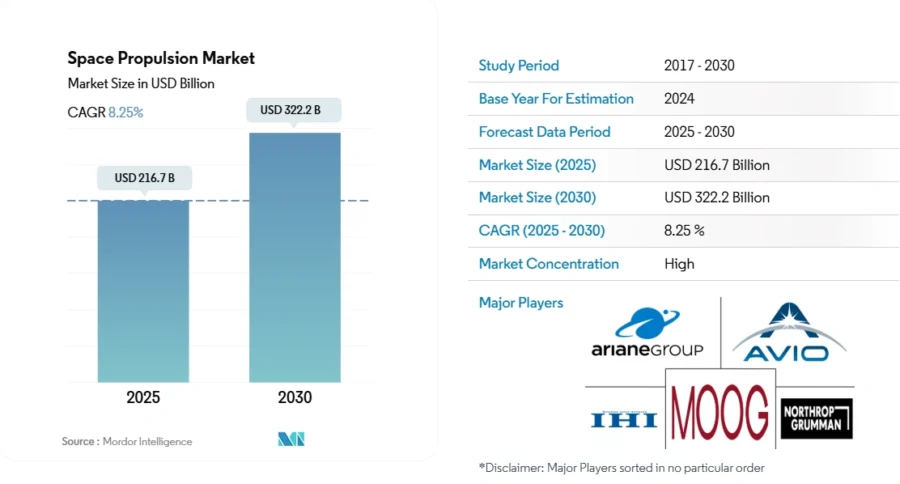
Credit: Mordor Intelligence
Nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) and electric propulsion enable faster and more efficient deep space missions, including future explorations to Mars and beyond.
Electric propulsion systems are rising due to the growing deployment of satellite constellations. These systems provide low-cost, high-efficiency propulsion solutions for orbital maneuvering and station-keeping.
Moreover, technological advancements in additive manufacturing and advanced materials enhance the production of lighter, more durable, and cost-effective propulsion systems.
On top of that, smart propulsion systems like water-based and iodine-based propulsion offer safety, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for small satellites.
As the space industry expands, the demand for next-generation propulsion systems will rise. These systems will support long-duration space missions, satellite mobility, and sustainable space operations.
ISPTech advances Green In-space Propulsion
German startup ISPTech manufactures green in-space propulsion systems using propellant technologies, HyNOx and HIP_11. HyNOx combines nitrous oxide and ethane, both non-toxic and readily available, which are stored under saturated conditions to leverage their high vapor pressures. This eliminates the need for pressurant gas and simplifies system architecture.
HIP_11 pairs highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide with an ionic liquid fuel. This creates a hypergolic mixture that ignites upon contact and offers performance comparable to traditional hypergolic propellants but with higher density and reduced hazards.
HyNOx suits small, cost-driven spacecraft applications, and provides specific impulses up to 300 seconds. Whereas, HIP_11 caters to larger, performance-driven missions with specific impulses up to 310 seconds.
Besides, ISPTech secured EUR 2 million in pre-seed funding in 2024 to develop green propulsion systems for satellites and spacecraft.
Cosmo Bee builds Spacecraft Electric Propulsion System
Chinese startup Cosmo Bee develops electric propulsion solutions for space missions. It integrates hall thrusters, cathodes, propellant management units (PMUs), and power processing units (PPUs). The hall thrusters generate thrust by accelerating ions through electric and magnetic fields to deliver high specific impulse and fuel efficiency.
The startup categorizes thruster units based on satellite and mission specifications. Its Honeybee (50-150W) suits CubeSats and MicroSats, while Honeybee Plus (100-250W) fits micro and small Satellites. Further, Bumblebee (300-500W) serves mid-sized satellites, whereas Bumblebee Plus (500-1000W) suits larger spacecraft.
10. Semiconductors for Space
The space semiconductor market will grow from USD 3.04 billion in 2025 to USD 5.68 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 7.2%.
Credit: Market Research Future
The increasing demand for satellite constellations in Earth observation, communication, and navigation drives the need for high-performance, radiation-hardened semiconductors in space applications.
North America led the market in 2024 with 45.08% of the global share, approximately USD 0.55 billion. This was driven by strong investments in space exploration, defense applications, and commercial satellite networks.
Innovations in radiation-hardened AI chips enhance autonomous operations and onboard data processing. Advanced materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) enable high-temperature and high-voltage applications in satellites and spacecraft.
Apart from that, developing compact, energy-efficient semiconductors supports satellite constellations and reusable launch vehicles. These developments optimize performance while reducing power consumption.
Advancements in edge computing further enhance real-time data processing onboard satellites, which minimizes communication delays for deep-space missions.
Celtonn advances Millimeter Wave Technology
Irish startup Celtonn develops high-frequency millimeter-wave communication systems. It specializes in W-Band (92-96 GHz) and D-Band (110-170 GHz) solutions for high-speed data transmission. Its W-Band Upconverters and Downconverters operate with an intermediate frequency range of 2-6 GHz, deliver 12-20 dB gain and ensure low-noise signal processing.
The startup’s W-Band Transmitter and Receiver integrate USB-configurable local oscillators for precise frequency control. Its high-power W-Band Amplifiers provide up to 25 dBm output power for enhanced signal strength. Celtonn also offers frequency multipliers and bandpass filters to optimize system performance in 6G networks, aerospace communications, and radar applications.
BPTI RF builds RF & ICs for Space Communication
Lithuanian startup BPTI RF designs wideband RF and millimeter-wave integrated circuits for 5G and space communication applications. Its products cover frequencies from S to Ka band and beyond, using CMOS, SiGe BiCMOS, and GaAs/GaN technologies.
The startup specializes in developing radar receiver and transmitter front-ends and ad hoc implementations. BPTI RF offers commercial off-the-shelf components to provide solutions for advanced communication systems.
Discover all Space Tech Trends, Technologies & Startups
Space technology is advancing through innovations such as satellite data analytics that transform Earth observation and communication, and propulsion technologies that enable deep-space missions. In addition, space debris management is also becoming crucial for long-term orbital sustainability.
The Space Tech Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.








