Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary: What are the Top 10 Insurance Industry Trends in 2025?
The insurance industry is undergoing rapid transformation driven by technology, evolving customer expectations, and emerging risks. Top insurance industry trends shaping the sector are:
- Cybersecurity & Cyber Insurance: Ransomware claims spiked over 50% in 2023 versus 2022, with more than 90% of incidents now involving double extortion. Insurers require core cyber hygiene – multi-factor authentication (MFA), encrypted backups, endpoint protection, and incident response plans- or risk non-renewal.
- InsurTech Partnerships: Collaborations with tech startups are reducing insurer losses by 3-8% and value-chain costs by 10-20%. AI-driven claims automation slashes handling costs by roughly 30%, with Generali saving over EUR 80 million through one implementation. Nearly 80% of executives cite co-creation with InsurTechs as their primary innovation source.
- Chatbots & Virtual Agents: A projected loss of 400 000 US insurance workers by 2026 has accelerated bot adoption – consumer chatbot use has nearly doubled since 2020. Today, 67% of insurers deploy generative-AI chatbots, and 77% of executives back rapid AI rollout, with investments rising threefold through 2025 to ensure 24/7 self-service.
- Blockchain & Smart Contracts: Annual insurer-to-insurer subrogation transactions exceed 75 000 via shared ledgers. Parametric smart contracts now automate payouts for events like drought relief – nearly 7000 Kenyan farmers received instant mobile payouts with zero paperwork. Fraud detection using tokenized policies and on-chain marketplaces is also expanding.
- Embedded Insurance: API-first, low/no-code platforms allow e-commerce, mobility, and fintech firms to bundle coverage at checkout without brokers. 63% of insurers partner with non-traditional distributors, and leading embedded startups have closed nine-figure funding rounds to accelerate travel, device, and affinity insurance rollouts.
- Internet of Everything (IoE): Telematics programs have cut fleet collisions by 72% and lowered insurance costs for one in four fleets. Usage-based products enjoy an 87% driver approval rating, and 92% of consumers believe safety data should set rates.
- Customer-Centric Transformation: 71% customers demand personalized experiences, yet only 5% of carriers excel today. Many new buyers begin online, and two-thirds will switch after a bad experience. Leading insurers use AI voice and sentiment tools to enhance claims, driving a gap of 78% versus 15% in automated underwriting.
- Microinsurance & Financial Inclusion: Mobile-money platforms and WhatsApp/SMS enrollment enable micro-policies with instant mobile payouts. Regulatory frameworks now exist in 40 countries (16 more in progress). Gig-economy workers (only 40% insured versus 82% of full-time employees) gain coverage through alternative data underwriting and biometric KYC.
- Omnichannel Experiences: Self-service demand rose by 36% during COVID-19, pushing carriers to integrate FAQs, chat, apps, and advisor channels seamlessly. One in six customers gets no follow-up today, and 40% must repeat issues.
- Climate & Natural Catastrophe Risks: Insurers leverage AI-powered satellite and radar feeds to forecast wildfires and floods. This enables parametric triggers that auto-pay when thresholds are met. Real-time disaster maps and green-bond funding align capital to resilience, while startups deliver sub-hour flood-depth mapping to prioritize claims.
Read on to explore each trend in depth – uncover key drivers, current market stats, cutting-edge innovations, and 20 leading innovators shaping the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the latest trends in the insurance industry?
Leading 2025 insurance trends are AI-driven underwriting and hyper-personalized risk assessment, the surge in parametric and embedded insurance offerings, and expanded use of blockchain smart contracts for fraud reduction.
2. What is the next big thing in insurance?
Parametric insurance: Automatically triggers payouts based on independent data (e.g., rainfall, wind speed) to reduce claims friction and incentivize proactive risk management
3. What is the future of insurance businesses?
Insurance firms are transitioning completely into digital platform ecosystems – integrating API-first distribution, cloud-native cores, and InsurTech partnerships – to deliver on-demand products and services.
Methodology: How We Created the Insurance Industry Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 7M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the insurance industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the insurtech innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Insurance Industry Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Insurance Industry Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 14 090+ global startups & scaleups. The Insurance Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the insurance industry trends & startups that impact your company.

Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Insurance Industry Trends
Insurance continues to evolve as new technologies and customer demands shape its delivery. Cyber insurance and digital security have become central offerings as online threats grow. Further, chatbots and virtual agents improve service efficiency, while blockchain enhances contract automation and fraud detection.
Embedded insurance covers everyday purchases, expanding access through streamlined channels. In parallel, InsurTech collaborations advance product innovation and market reach.
Moreover, internet of everything (IoE) technologies now enable real-time risk monitoring. Meanwhile, climate and catastrophe modeling influence pricing strategies and underwriting decisions. These developments make insurance distribution more efficient, inclusive, and quick.

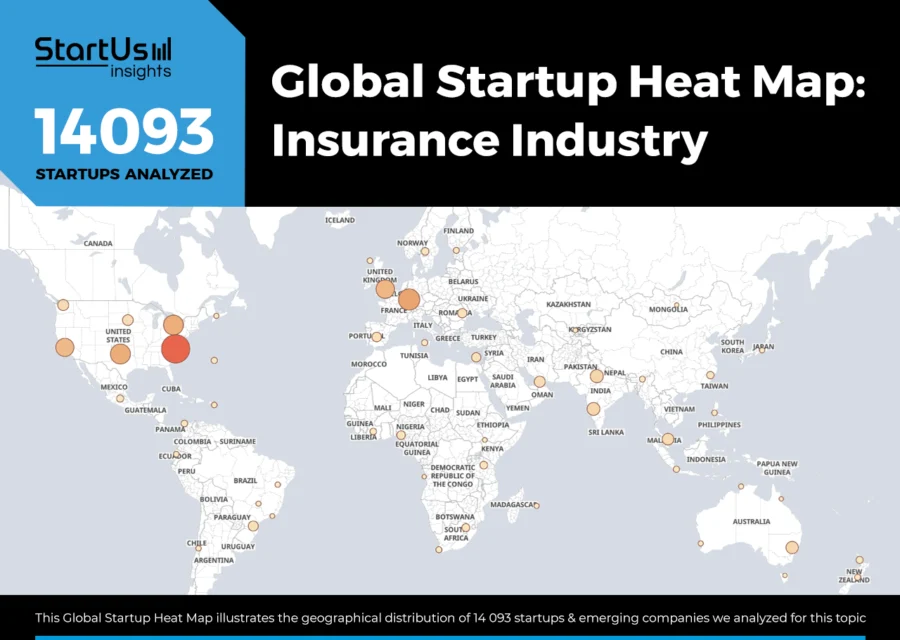
Global Startup Heat Map covers 14 090+ Insurance Industry Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 14 090+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in the USA and the UK, followed by India. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Want to Explore Insurance Industry Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Insurance Industry Trends [2025 and Beyond]
1. Cybersecurity & Cyber Insurance: Premiums to Reach USD 16.3 B in 2025
The rise in ransomware and other cyber attacks during 2023–2024 led to a sharp increase in cyber insurance claims and payouts.
Allianz observed that ransomware incidents in 2023 pushed claims frequency more than 50% above 2022 levels. Attack methods also became more destructive. By late 2023, over 90% of ransomware cases involved double extortion, where hackers encrypted data and stole sensitive files for extortion.
The USA accounted for 59% of global cyber insurance premiums in 2023. Europe followed with roughly 21% of projected 2024 premiums, with about 26% CAGR in recent years as awareness spreads.
Insurers continue to enforce underwriting discipline and emphasize stronger cyber hygiene. Underwriters expect companies to adopt core security practices. These include multi-factor authentication, encrypted data backups, endpoint protection, and incident response plans.
Meanwhile, insurers grew cautious about catastrophic cyber events. A severe cyber hurricane could cause USD 20-46 billion in losses by affecting many insured clients simultaneously.
To limit exposure, insurers tighten policy language. For example, Lloyd’s of London required all standalone cyber policies to exclude coverage for nation-state cyber war events. This clause targets risks from government-backed attacks, which could impact multiple companies at once.
In late 2023, Beazley launched the sector’s first cyber catastrophe bond program. It secured USD 140 million in coverage from capital markets to cover extreme scenarios.
Further, generative AI introduced new challenges such as deepfake fraud and AI-generated attacks. It also raised liability concerns. While most insurers are still evaluating these risks, some are starting to adapt.
For instance, Coalition updated its cyber policy language to reflect this shift. It now explicitly includes AI-driven events in its definition of covered security failures. Additionally, it recognizes deepfake-related fraud under its crime and fraud coverage.
Looking ahead, the global cyber insurance market could reach USD 90.6 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 22.3% from 2024 to 2033.
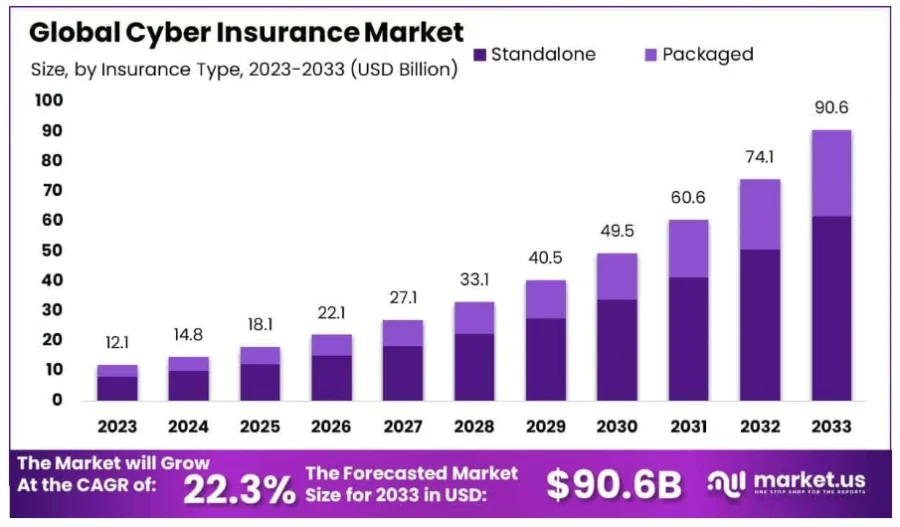
Credit: market.us
Insiber.com facilitates Cybersecurity and Cyber Insurance Management
Dutch startup Insiber offers CyberControl, a platform for cybersecurity and cyber insurance management. It enables businesses to monitor digital assets, apply protective measures, and assess insurance eligibility.
The startup’s platform gathers data on critical systems and links them to applicable security controls. It also features a real-time dashboard for managing security posture and insurance requirements.
CyberControl supports asset inventory and task tracking. It also gives access to cybersecurity tools that match insurance coverage criteria.
Additionally, users receive step-by-step guidance through an onboarding wizard. They can consult with experts and explore a knowledge hub for regulatory updates and policy alignment.
Nothreat builds Self-Learning AI Cyber Defense
UK-based startup Nothreat creates an AI-powered platform for cybersecurity automation. It supports threat prevention and response across enterprise systems, edge devices, and cloud infrastructure.
The platform uses tools such as CyberEcho, AIoT Defender, ThreatShield, and AI Analyzer. These tools detect threats, analyze behavior, and deliver real-time countermeasures.
CyberEcho sets undetectable clone traps to study attackers without exposing production systems. ThreatShield upgrades existing firewalls using AI-powered threat feeds for agile defense.
Further, AIoT Defender installs self-learning firewalls on edge and internet of things (IoT) devices. It operates independently and requires no external hardware. Meanwhile, AI Analyzer turns technical threat data into practical insights for teams and leadership.
Nothreat supports banking, fintech, and insurance companies and provides tailored protection for services that depend on compliance and digital stability.
2. InsurTech Partnerships: Q3 2024 Funding Tops USD 1.38 B
Regulators established open insurance programs and fintech sandboxes globally to reduce obstacles to innovation.
InsurTech collaborations produced quantifiable cost and efficiency gains. Insurers may reduce losses by 3-8% and save 10-20% on costs throughout the value chain by utilizing data analytics and automation.
Many insurers are now tech-ready after years of investing in modernizing their core systems. Insurers integrate InsurTech solutions by leveraging application programming interface (APIs) and cloud-based cores.
In fact, AI-driven automation in claims administration alone reduces handling costs by roughly 30%.
McKinsey states that working with InsurTechs, particularly in analytics, increases an insurer’s loss ratio by 3-5% by preventing claims more effectively and settling them more quickly. These efficiency improvements result in substantial cost savings. For instance, by partnering with a tech company to implement an AI-enabled claims system, international insurer Generali saved over EUR 80 million.
Further, according to a PwC poll, almost 80% of insurance executives now state that their company’s main source of innovation comes from co-creating with InsurTech firms through partnerships, joint ventures, or acquisitions.
Allianz, a global insurer, selected Singapore-based InsurTech bolttech as its partner. It integrates bolttech’s API-driven platform to sell device protection and other coverages through non-insurance channels.
Also, Farm Bureau Insurance of Idaho teamed up with AI pricing startup Akur8 to incorporate a machine-learning (ML) platform into its rating process in the USA.
InsurTechs also form direct partnerships with reinsurers. Munich Re, Swiss Re, and others established venture funds and incubators. These organizations frequently collaborate to develop solutions in fields such as digital distribution and IoT risk mitigation.
Moreover, Gallagher Re saw an increase in reinsurance firms investing in mid-stage InsurTechs in the last year as strategic investors.
According to IMARC Group’s forecast, the market would grow at a CAGR of 31.51% from 2025 to 2033, reaching USD 152.9 billion.
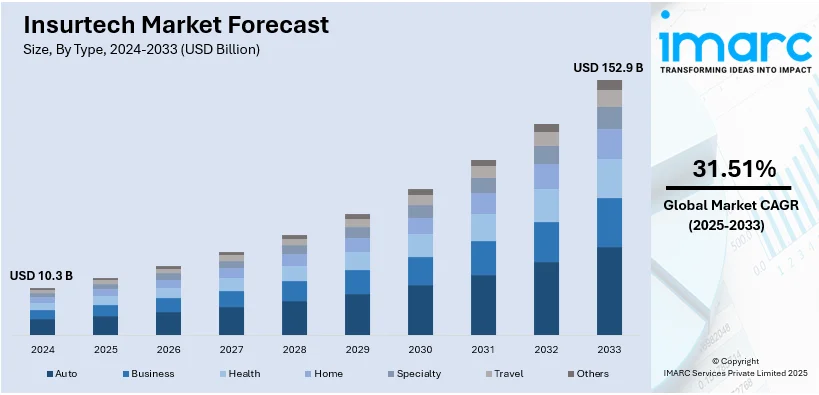
Credit: IMARC Group
Herald develops Unified Commercial Insurance API
US-based startup Herald builds a unified API infrastructure for commercial insurance platforms. It allows users to quote, bind, and issue policies from multiple carriers through one integration.
The platform converts carrier APIs into a consistent format. As a result, brokerages, software as a service (SaaS) providers, and embedded platforms access over sixty insurance products. These include general liability, workers’ compensation, business owner policy (BOP), cyber, tech errors and omissions (E&O), and management liability.
Herald offers tools like OpenAPI 3.1 support, interactive documentation, and sandbox environments to support developers. It also provides Slack-based assistance to streamline deployment.
For carriers, the startup’s platform reduces onboarding time and manages partner access. It also delivers performance insights in real time.
This approach removes integration hurdles and shortens go-to-market timelines. Consequently, insurance providers and distributors are able to scale digital operations with ease.
Moreover, Herald announced a USD 12 million Series A funding round. Lightspeed Venture Partners and Brewer Lane Ventures co-led the round with participation from Afore Capital and Underscore Venture Capital.
Lexasure Financial Group creates Reinsurance-as-a-Service (RaaS) Platform
Cayman Islands-based startup Lexasure Financial Group builds a digital platform for insurance and reinsurance. It supports insurers in Southeast and South Asia with risk management, operational scaling, and localized product delivery.
The startup’s LexasureCloud, brings together policy administration, claims processing, and data analytics. It also offers reinsurance-as-a-service in a single web-based interface.
LexasureCloud automates underwriting, pricing, and compliance functions. It applies AI and ML to allow insurers to track risks and improve performance in real time.
The platform includes tools for embedded insurance, custom product design, and automated reinsurance underwriting. These features serve small and mid-sized insurers in underinsured markets.
The startup also enables direct offerings for individuals, such as life investment products. In addition, it supports collaboration with brokers and reinsurers.
3. Chatbots & Virtual Agents: Market at USD 14.1 B by 2030
The insurance industry experiences a talent shortage, especially in customer service and claims. An aging workforce and ongoing retirements reduced the staffing gap. In the USA alone, the sector will lose about 400 000 workers by 2026 due to attrition.
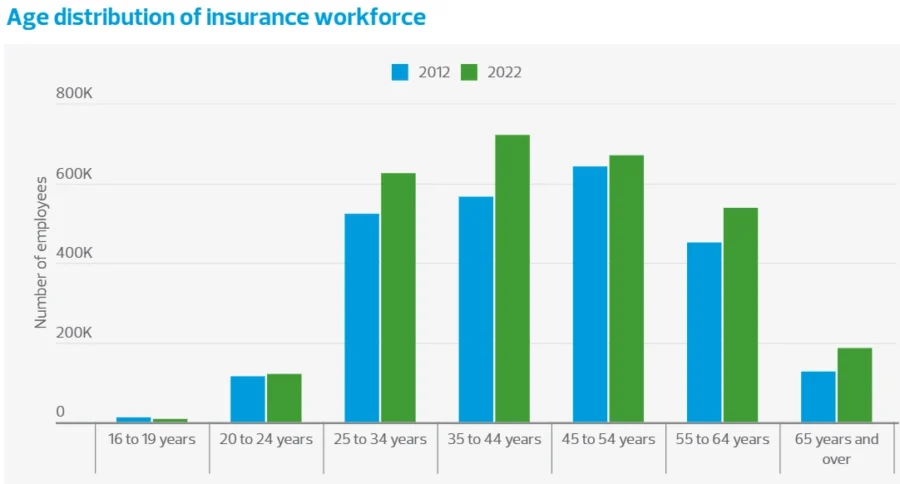
Credit: RSM US
Customers now expect fast, anytime access to insurance services. They want to check policy details or file claims at any hour. This demand led to the rise of chatbots.
Unlike human agents, virtual bots operate 24/7. They provide quick answers and handle simple tasks without delay. This flexibility appeals to global insurers and younger clients who prefer digital tools.
Since 2020, chatbot use among consumers has nearly doubled. Many younger policyholders often choose bots or apps over phone calls for routine support.
According to the Carrier Perspective: 2024 Claims Insights by Gallagher Bassett, 67% of insurers globally adopted generative AI chatbots for customer service.
IBM reports that 77% of insurance executives support faster generative AI adoption to stay competitive. IBM projects a 300% rise in generative AI investment from 2023 to 2025.
As acceptance grows, insurers expand chatbot capabilities. These tools now offer quick self-service functions. For example, customers now update contact details or get a premium quote in minutes.
Besides, advances in large language models expanded chatbot roles. New systems interpret complex questions and summarize documents. This enabled claim advisory bots that analyze incident reports or assistants that support underwriting.
Speech recognition tools have also improved. When combined with natural language processing (NLP), these tools understand regular human language requests and respond accordingly.
Moreover, some insurers and banks replace outdated phone menus with voice bots. These systems offer conversational support instead of numbered prompts. GEICO tested Alexa and Google Assistant features for quotes and basic questions.
The insurance chatbot market is projected to grow significantly. It may reach USD 2.45 billion by 2029, with an expected CAGR of 26.1%.

Credit: The Business Research Company
Inaza creates Insurance-specific AI Agents
Irish startup Inaza offers a usage-based insurance and AI-driven data platform. It supports real-time underwriting, claims automation, and risk assessment for insurers, MGAs, brokers, and reinsurers.
The platform gathers data from sources like telematics, emails, web forms, and call logs. It uses AI agents to analyze inputs, detect fraud, and automate claims processing.
Inaza connects directly with existing systems without retraining. It standardizes diverse data and returns real-time insights through a centralized warehouse.
It offers features such as dynamic pricing, AI-led first notice of loss (FNOL), document checks, quote automation, and loss run reporting for removing manual tasks and reducing premium leakage.
Chatzy AI provides a Conversational Engagement Platform
Indian startup Chatzy AI builds an AI-driven communication platform for insurance providers. It automates customer support, policy management, underwriting, and claims processing.
The platform uses domain-specific language models to engage customers through email, chat, and voice. It collects data, answers questions, and executes backend tasks such as claims intake and policy updates.
It also analyzes user preferences and risk profiles to offer personalized coverage. Alongside, it flags possible fraud by spotting irregularities in submitted claims.
The startup supports 24/7 customer assistance for routine inquiries. It sends automated reminders and shares educational content to improve insurance literacy.
4. Blockchain for Smart Contracts & Fraud Reduction: Cuts Fraud by 80%
Insurance fraud is a serious and expanding issue. The Coalition Against Insurance Fraud claims that insurance fraud costs the USA USD 308.6 billion a year, which eventually increases consumer premiums.
A surge in fraudulent claims forces several insurers worldwide to look for better ways to handle the problem. For instance, Allianz Commercial found claims fraud of GBP 77.4 million in 2023, up from GBP 70.7 million in 2022.
This growing fraud led to the necessity of blockchain’s transparent, immutable ledger to validate claims and exchange data among carriers.
The integration of IoT sensors with blockchain smart contracts enables parametric insurance products. Trusted data oracles validate trigger circumstances, which then initiate claims payouts automatically.
The Lemonade Crypto Climate Coalition, a nonprofit organization headed by Lemonade Insurance, introduced a blockchain-based parametric crop insurance policy for Kenyan farmers. Almost 7000 smallholder farmers signed up, and following the growing season, smart contracts initiated immediate payouts to drought-affected farmers. They transferred money to mobile wallets without requiring any claims documentation.
Major property and casualty (P&C) insurers use blockchain to expedite claims and intercompany settlements. State Farm and USAA created a shared blockchain system for auto claim subrogation, or insurer-to-insurer recoveries. Following rigorous testing, it entered production to manage over 75 000 payment transactions annually, resulting in automated carrier-to-carrier claims payments.
Decentralized insurance solutions include programs such as insurance-linked securities and tokenized reinsurance. Here, insurance risks or assets comprise tokens that investors purchase or trade.
Besides, Aon finished a creative pilot project in April 2024 to put insurance on a public blockchain. In collaboration with the regulated on-chain insurance marketplace Nayms, Aon provided policy quotes and even took cryptocurrency commission payments.
By 2035, it is anticipated that the blockchain in the insurance market sector will grow to USD 45 billion at a CAGR of 25.42%.
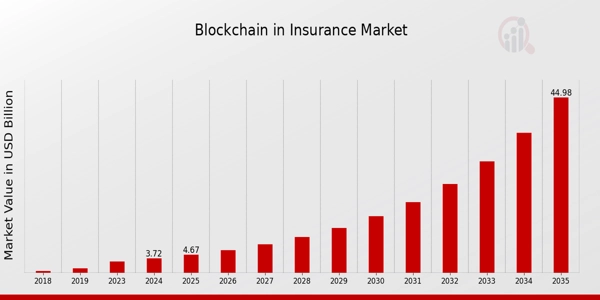
Credit: Market Research Future
SafeOne Chain makes Insurance NFTs
German startup SafeOne Chain builds a blockchain-based insurance platform for the SafeOne ecosystem. It provides tokenized coverage against scams and rug pulls.
The platform uses decentralized ledger technology to manage policies through non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Each NFT represents active coverage and is removed when claims settle or expire. Smart contracts validate incidents and refund users within set limits.
Users mint NFTs using $SAFO or build and build (BNB), where each token links to a specific policy and is exchanged at a reduced rate once expired.
Inkan enables Data Traceability, Fraud Prevention, and Detection
Spanish startup Inkan creates a blockchain-based platform for insurance and warranty services. It digitizes claims, inspections, and post-sale workflows for physical products.
Each product receives a tamper-proof digital identity in the form of an NFT. This identity links ownership, warranty terms, and service history on a secure ledger.
The startup’s platform verifies submitted evidence using AI-based photo and video analysis. It adds geolocation, timestamps, and device checks to detect fraud in real time.
Users collect and process inspection data remotely through customizable forms and automated tasks. This approach reduces the need for manual site visits.
Further, a mobile app converts user-generated content into verifiable proof. It applies cybersecurity protocols and seals records on the blockchain.
5. Embedded Insurance: Market to Reach USD 40.99 B by 2030
Younger buyers often prefer insurance embedded in their purchases instead of managing separate policies. For instance, many millennials and Gen-Z shoppers want auto insurance included with their car purchases.
The growth of digital platforms in retail, travel, finance, and mobility creates space for embedded insurance. As more transactions shift online, non-insurance firms offer protection to enhance loyalty and create new revenue.
Partnering with insurers enables them to improve customer value while insurers reach untapped markets. According to recent reports, 63% of insurers now collaborate with sectors like e-commerce, automotive, and healthcare through embedded channels.
Investment activity supports this trend. For instance, NEXT Insurance, focused on small-business digital coverage, raised USD 265 million from Allstate and Allianz X in late 2023 to scale operations.
In Europe and Asia, B2B2C insurtech platforms drew significant capital. French startup Neat secured EUR 50 million in September 2024 to grow its embedded insurance offerings for retail and travel.
Insurers and insurtechs provide APIs that make insurance easy to integrate into third-party websites and apps. Standardized APIs support real-time data sharing between insurers and distributors.
To simplify deployment, many insurers offer low-code or no-code tools. These enable non-technical partners to launch insurance products using drag-and-drop features or prebuilt templates.
Scalable infrastructure supports delivery at digital scale. Insurers turn to cloud systems to manage large transaction volumes. For example, during events like Black Friday, cloud elasticity enables processing thousands of policies per second without disruption.
Moreover, the embedded insurance market reached USD 10.45 billion in 2025. It is expected to grow to USD 40.99 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 31.43%.

Credit: Mordor Intelligence
Zebra Insurtech provides Embedded Affinity Insurance
Mexican startup Zebra Insurtech builds Ztech, an insurance-as-a-service platform for embedding digital insurance into fintech and broker ecosystems. It allows insurers, brokers, and platforms to offer tailored coverage through one integration.
Ztech connects stakeholders using a unified, API-based infrastructure. It automates underwriting, claims handling, and policy management while fitting into existing digital workflows.
The platform enables fast deployment of digital insurance products like travel, gadget, pet, and credit protection. These products are backed by insurers such as Zurich, GMX, and Chubb.
Further, its subscription model includes cashback for low claims. It also provides dashboards to track policy activity, profitability, and claims performance in real time.
Walnut Insurance creates a Branded Insurance Program
Canadian startup Walnut Insurance develops an embedded insurance platform for digital businesses. It enables companies to integrate a range of insurance products directly into customer journeys.
The platform connects insurers and distribution partners. It uses APIs and no-code tools to support policy issuance, claims, compliance, and support functions.
Businesses choose integration options such as co-branded links or headless APIs. These options tailor the experience to technical capacity and design needs.
Walnut Insurance delivers group and individual coverage, including mobile device protection, travel insurance, income loss coverage, and cyber protection.
It also handles licensing and broker infrastructure, and provides real-time dashboards for performance tracking and premium setup.

6. Internet of Everything: 18.8 B Connected Devices by 2024 End
IoT enables a proactive model of insurance. Accidents decreased as a result of telematics programs. 72% of fleets report fewer collisions and claims following telematics use (with driver coaching), and 1 in 4 reported lower insurance costs.
IoT-driven insurance products that incentivize positive behavior experience popularity. 87% of drivers showed a positive opinion of usage-based vehicle insurance, and UBI participation increased dramatically.
According to surveys, 92% of customers agree that driving safety should determine rates rather than general criteria. This indicates a movement in consumer sentiment toward telematics fairness.
To secure houses, insurers collaborate with IoT tech companies. For instance, Nationwide and Resideo partnered to provide policyholders with smart thermostats and water leak detectors. The average cost of water damage claims decreased by approximately USD 4K.
Further, John Hancock’s Vitality program tracks fitness using wearable IoT devices (Apple Watch, Fitbit) to encourage healthy behavior with discounts. Hancock took things a step further in 2023 when they announced a new policy that directly links premiums to health measurements from Apple Watches. This IoE was incorporated into life insurance pricing.
Drones and remote IoT sensors handle property inspections and disaster claims. For example, Erie Insurance was among the first to receive FAA certification for claims drones, using IoT-enabled drones to fly over a normal roof check.
With the introduction of 5G networks and edge computing, billions of devices send data almost instantly. 5G’s vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication enables real-time data sharing between infrastructure and automobiles to reduce crashes. These features give insurers access to timely and powerful IoT data (e.g., real-time catastrophe monitoring, fast crash notifications).
Simultaneously, ML algorithms underwrite based on sensor data and computer vision that automatically evaluate car damage via images for claims.
Additionally, the IMARC Group projects that the size of the worldwide IoT insurance market would reach USD 483.2 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 29.2% from 2025 to 2033.
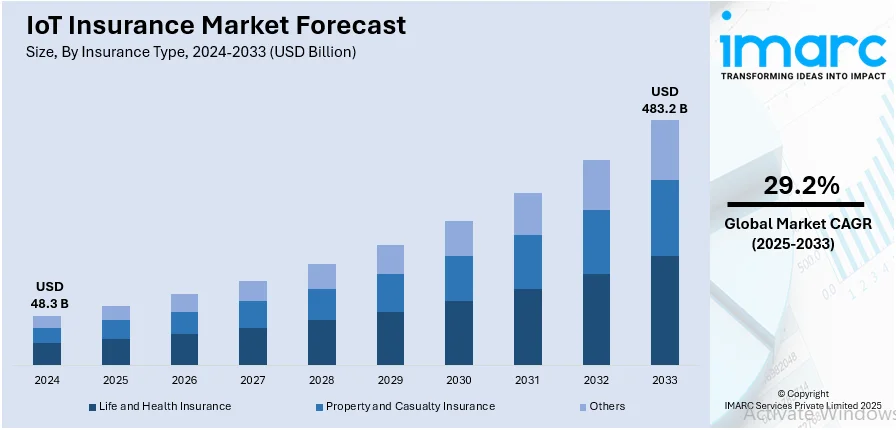
Credit: IMARC Group
ZoJacks builds Leak Detection Technology
US-based startup ZoJacks develops a platform for insurance and property protection. It uses IoT sensors and real-time risk monitoring to prevent water damage in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
The platform tracks water flow, pressure, humidity, and temperature. It detects leaks, freezing, or abnormal activity, then shuts off water to limit damage.
It sends alerts around the clock via push notifications, calls, emails, and texts. Each alert includes the incident location to support a quick response.
For insurers, ZoJacks cuts water-related claims and improves loss ratios. It strengthens policyholder protection by embedding risk controls into insurance offerings.
AiGenix provides Telematics for Regulators & Motor Insurers
Pakistani startup AiGenix develops analytics solutions for automotive and insurance use. It applies AI, telematics, and sensor data to improve safety, simplify claims, and improve fleet efficiency.
The platform includes GenixDrive, a mobile app that tracks driving behavior through smartphone sensors. It rewards safe driving and includes a tool to automate damage inspections.
Its risk engine examines driver habits, trip data, and accident patterns. These insights support underwriting decisions and support model revenue.
The startup also offers fleet management tools. These provide route planning, real-time visibility, and maintenance tracking.
Further, an automated claims module uses sensor input to recreate incidents in 3D. This speeds up settlements and aids in resolving liability issues.
7. Customer-Centric Transformation: 10% More Retention
Insurance customers now expect better service and personalization. McKinsey reports that 71% of consumers want personalized experiences. Meanwhile, 76% express frustration when companies fall short. Insurers that ignore these preferences risk losing ground to digital-first competitors.
To meet expectations, insurers move toward digital engagement. Over half of new customers (53%) begin their insurance journey online. In contrast, 29% choose agents and 18% use call centers.
As of 2024, only 5% of global insurance carriers rank highly for customer satisfaction. Consumers act quickly on dissatisfaction; two-thirds switched insurers due to poor service or lack of personalization.
As a result, insurers redesign products and processes. They prioritize usage-based pricing, flexible policy updates, and faster claims resolution powered by empathy and speed.
Besides, the global usage-based insurance market may reach USD 299 billion by 2033. Analysts expect it to grow at a 25.5% CAGR between 2024 and 2033.

Credit: market.us
According to the World Life Insurance Report 2025 by Capgemini Research Institute, 5% of insurers that lead in customer experience embrace new technologies like generative AI to strengthen onboarding, self-service, and claims processes.
They demonstrate differences in capability: 78% use automated underwriting, compared to 15% of others. 78% offer self-service portals, while only 13% of peers do. 56% enhance claims experiences through AI voice and sentiment tools, versus 3% elsewhere.
These tools create personalized and responsive customer interactions. In 2024, 34.6% of global insurtech funding focused on AI-centric startups.
Data-driven personalization leads to better risk pricing, lower claims costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Besides, digital workflows speed up policy issuance. Real-time quotes, immediate documents, and fast claim processing satisfy customers who once faced delays and complex paperwork.
Lastly, AIA launched Amplify Health, a digital health ecosystem across Asia. It integrates wellness, insurance, and healthcare services in a single platform. Customers manage their coverage and health journeys with support from tech platforms and partner networks.
Surely offers Personalized Insurance
Filipino startup Surely develops AI-driven insurtech platforms that support insurers and fintech partners with customer engagement, underwriting, and claims processing.
It operates Surely Hub, a modular layer that connects with modern and legacy insurance systems. This setup enables API-based deployment across multiple digital channels.
The startup analyzes user behavior and transactions to deliver tailored insurance experiences. It also supports real-time decision-making and automates policy management tasks.
Surely collaborates with partners such as Malayan and Oona. It also allows travel providers to bundle products like international travel medical coverage.
The startup offers plug-and-play tools, affiliate programs for agents and influencers, and built-in revenue models to support different use cases.
Bind enables AI-Powered Insurance Targeting
Swiss startup Bind builds a modular insurance infrastructure for digital platforms. It enables insurers and partners to embed and personalize coverage with minimal technical effort.
The platform offers a low-code setup and an API for product distribution and policy management. It lets users launch and update insurance in real time.
Bind’s AI engine analyzes customer behavior to identify emerging needs. It then triggers relevant offers that match user context and timing.
This approach improves policy accuracy, supports compliance across countries, and increases engagement through dynamic pricing and personalized experiences.
The startup allows businesses to raise conversion rates by enabling timely, tailored coverage. It supports stronger user retention through context-aware delivery.
8. Microinsurance & Financial Inclusion: A USD 94.3 B Market
The widespread use of digital finance and mobile technology is enabling microinsurance. Mobile money platforms and e-wallets lead to immediate claims payout, even with premiums as low as a few cents.
Insurers handle small transactions and communicate with clients directly using mobile platforms. Microinsurance programs use WhatsApp chatbots, smartphone apps, or SMS-based enrollment. Payouts are deposited into mobile wallets, and claims are made by uploading a photo or sending an SMS code. For instance, insurers in Kenya collaborate with M-Pesa mobile money to enable rural clients to pay premiums and receive claims on their phones.
Further, governments and regulatory bodies across the globe acknowledged microinsurance as a means of promoting financial inclusion and established legislative frameworks that facilitate it. According to the Microinsurance Network report, 40 countries put microinsurance-specific laws into effect, while another 16 are creating frameworks.
More people work outside of conventional employment in both established and emerging markets, whether as informal sector entrepreneurs or gig economy workers like delivery couriers, ride-share drivers, and freelancers. Alternative safety nets are needed because many people do not have access to typical company perks or insurance. In the USA, 82% of full-time employees have health insurance, but only 40% of gig economy workers do.
Microinsurance leverages AI-powered algorithms for fraud detection, risk grading, customer onboarding, and claims triage. For instance, when a customer has no official credit or insurance history, ML models might use alternative data like satellite photography of a farm or mobile phone usage to underwrite a policy.
Many countries introduced national digital ID programs and remote know your customer (KYC) verification methods, which make it far easier and cheaper for insurers to onboard customers who lack traditional documentation. For example, the Aadhaar biometric ID system in India simplifies compliance by enabling quick identification and address verification for penny-priced insurance products with consent-based data access.
Instead of paper documentation and in-person verification, customers sign up via their phone or a kiosk by identifying with a fingerprint or a one-time password (OTP). Digital KYC also allows new distribution models. For example, a fintech app does e-KYC once and then cross-sells different services, including insurance, or a telco uses the SIM registration information they already have to KYC an insurance customer.
Further, the global microinsurance market size is expected to increase at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2025 to 2034, reaching USD 11.6 billion.
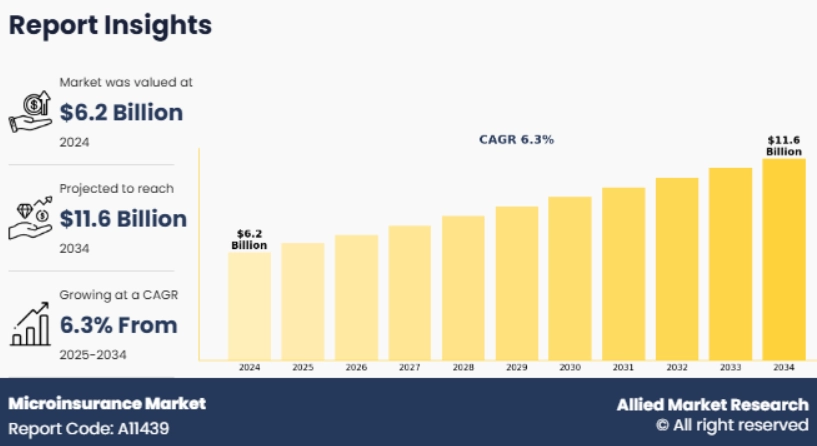
Credit: Allied Market Research
Chhaya creates a Digital Micro-Insurance Platform
Bangladeshi startup Chhaya builds a platform that automates microinsurance and financial services. It applies NLP and ML to understand customer requests, process claims, and deliver services in real time.
The startup offers modular insurance products across health, motor, travel, and enterprise categories. It supports a few-minute registration and runs an end-to-end paperless claims process.
Further, through its partner network, it offers subscribers discounts on medical services, including radiology tests, pathology, and hospital stays.
Chhaya simplifies insurance workflows and expands access for individuals and businesses alike.
BettaLyfe provides an Integrated Financial Platform
Nigerian startup BettaLyfe develops a digital platform that offers health insurance, micro-pension savings, and business loans tailored to Nigeria’s self-employed workers. It allows users to register quickly and select flexible payment plans, daily, weekly, or monthly.
The startup’s platform includes health insurance with national coverage and loans without collateral. Its pension program lets contributors access up to 40% of their funds when needed.
In addition, the Betta-Driver scheme supports commercial drivers with routine vehicle servicing, family health insurance, and structured retirement savings.
It also enables users to build skills through vocational training and business development tools, and provides access to microfinance, which helps them grow their enterprises.
9. Omnichannel Customer Experiences: 90% Greater Retention
Shifting customer demographics reshape insurance engagement. Millennials, Gen Z, and urban dwellers prefer digital self-service over visiting brokers.
Digital disruptors and tech firms offer faster experiences through apps and platforms. Their presence puts pressure on traditional insurers to modernize or risk losing customers. The COVID-19 period intensified this shift. Demand for self-service insurance rose by 36% as users became familiar with managing policies online.
Meanwhile, digital-first consumers now expect round-the-clock support. They move between frequently asked questions (FAQs), chat apps, mobile platforms, and live agents fluidly. They want consistency without repeating information.
Customer experience also affects retention. Insurance remains a low-touch service, and interactions occur just once a year. One in six customers receives no follow-up. Among those who do, 40% must explain their issue more than once.
Looking ahead, automation will play a larger role. McKinsey estimates that by 2030, AI will handle over half of claims tasks, lower costs, and improve turnaround times. Forrester expects insurance tech spending to grow 8% this year, driven by interest in data and omnichannel tools.
Insurers adopt customer data platforms to integrate data across touchpoints. For example, when a customer updates their address in an app, the change reflects instantly across channels. This eliminates repetition and ensures all teams work with current information.
Similarly, API-based integrations allow legacy systems to connect with modern digital interfaces smoothly.
For instance, HUB International carrier launched VIU, a platform where customers compare quotes online, buy through an advisor, or use both methods as needed.
Usage-based insurance programs rely on omnichannel engagement. GEICO’s DriveEasy app tracks driving habits and provides real-time feedback, and also connects customers to agents for changes or support.
In health and wellness, insurtechs like Dacadoo use smartphone and wearable data to engage policyholders. Customers who meet fitness goals earn rewards or lower premiums.
Functional Finance provides an Insurance FinOps Platform
US-based startup Functional Finance creates an AI-driven platform for financial operations in insurance. It automates billing, payments, reconciliation, and reporting for insurers and reinsurers.
The platform integrates with policy administration, accounting, and banking systems. It extracts and processes financial data in real time using rule-based automation.
Users configure billing logic, set up premium financing, and activate auto-pay or instant commission options. These features support flexible payment plans and simplify collections.
It also enables touchless reconciliation, live financial tracking, and direct ledger posting to maintain audit-ready records.
Functional Finance secures operations through SOC 2 Type II compliance. It uses encryption and adaptable access controls to protect financial data.
Easy2Life supports Omnichannel Insurance Distribution
Brazilian startup Easy2Life builds a digital platform that connects wearable monitoring, real-time analytics, and multichannel distribution. It modernizes insurance sales and healthcare delivery.
The platform collects biometric data through connected sensors. It syncs this data with cloud-based analytics to support health tracking and early intervention.
Easy2Life also works with C2L BIZ to deploy the SymbioSys Suite. This setup lets insurers launch new products, manage digital campaigns, and engage distributors more effectively.
The system supports flexible tools for sales automation, product simulations, and risk analysis at the point of sale.
10. Climate & Natural Catastrophe Risks: A USD 181 B Protection Gap
In the last year, global insured losses rose due to hailstorms, tornadoes, and urban flooding. This trend reflects climate science, which links a warmer atmosphere to more energy and moisture. These conditions drive both intense downpours and prolonged droughts.
Insurance regulators now treat climate change as a financial risk that requires disclosure and management.
Legal liability also drives concern. A growing number of lawsuits aim to hold companies, particularly fossil fuel firms, responsible for climate-related damage.
Insurers adopt environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investment strategies in response to public pressure and growing climate exposure. They manage large asset portfolios that face both physical and transition risks from climate impacts.
Traditional catastrophe models use historical data and physics. Today, insurers also apply AI and ML to improve forecasting. These models use satellite images, light detection and ranging (LIDAR) maps, and social media to predict loss patterns.
Zurich Insurance launched AI-powered software to assess wildfire risk. It analyzes home images for features like dry vegetation in gutters and flags properties that need action.
Besides, insurers monitor catastrophes using radar, Earth observation satellites, and IoT sensors that provide real-time disaster maps. During the 2024 European floods and 2025 California fires, such data aided in assessing damage before adjusters arrived.
This information supports parametric insurance, which pays out when a specific threshold, such as wind speed or rainfall, is reached. These models depend on independent data sources like satellite readings.
Startups like ICEYE map flood depths within hours using radar satellites that allow insurers to use this data to prioritize claims and design flood coverage.
Further, reinsurers turn to green bonds to fund renewable energy projects, flood barriers, and sustainable infrastructure. These investments align risk management with climate goals.
Meanwhile, the parametric insurance market continues to expand. It is projected to reach USD 26.31 billion by 2032, growing at a rate of 7.8% from 2024 to 2032.
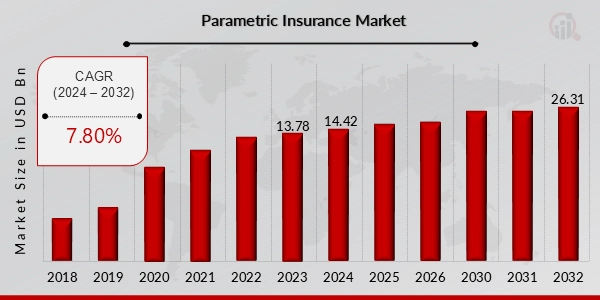
Credit: Market Research Future
Orakle Weather offers Parametric Insurance
French startup Orakle Weather develops a weather intelligence platform that combines hyperlocal forecasts with automated rain insurance for weather-sensitive activities.
The platform collects data from satellites, ground sensors, and scientific sources, and uses proprietary algorithms to assess rain risk with detailed precision.
The startup offers event-based insurance that users are able to buy online or through partner sites. Further, pricing depends on time, location, and selected coverage options.
Orakle Weather’s platform removes the need for manual claims. It alerts users about compensation eligibility a day before the event using email and SMS.
It speeds up payouts and reduces disruption to support individuals and businesses in managing weather-related risks with ease.
Sprout provides Seasonal Climate Insurance
US-based startup Sprout delivers climate risk insurance and microinsurance to support outdoor events and smallholder farmers facing weather-related losses.
The platform uses hyperlocal weather tracking, remote sensing, and machine learning to monitor conditions such as rainfall, temperature, and soil moisture. When thresholds are met, it triggers payouts and sends mobile alerts, without needing users to file claims.
Sprout offers protection for recreational events and seasonal crops. Its products target farmers in global supply chains, including those in coffee, cocoa, and rice production.
Using satellite-based risk models and partnerships with insurers, it delivers accessible protection through mobile and blockchain-based tools.
Discover all Insurance Trends, Technologies & Startups
AI-driven underwriting, parametric models, and behavioral analytics are gaining ground for faster, more flexible coverage within the insurance industry.
Moreover, digital identity checks and real-time pricing tools will support personalized products. At the same time, new categories such as space weather and climate resilience are entering the insurance landscape.
These developments will assist insurers in being more relevant and agile in an increasingly uncertain environment.
The Insurance Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.