Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
The emergence of biomaterials has kickstarted revolutionary developments in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, fashion, food, packaging, and more. These industries generate immense volumes of waste and relentlessly use finite resources, causing critical environmental concerns. Bio-based materials encompass a diverse range of metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites derived from natural resources. This data-driven report provides insights into the top use cases of biomaterials based on the analysis of 746 innovative biomaterials startups and technologies. Read more to explore biomaterials examples across 10 industries and how they advance your business.
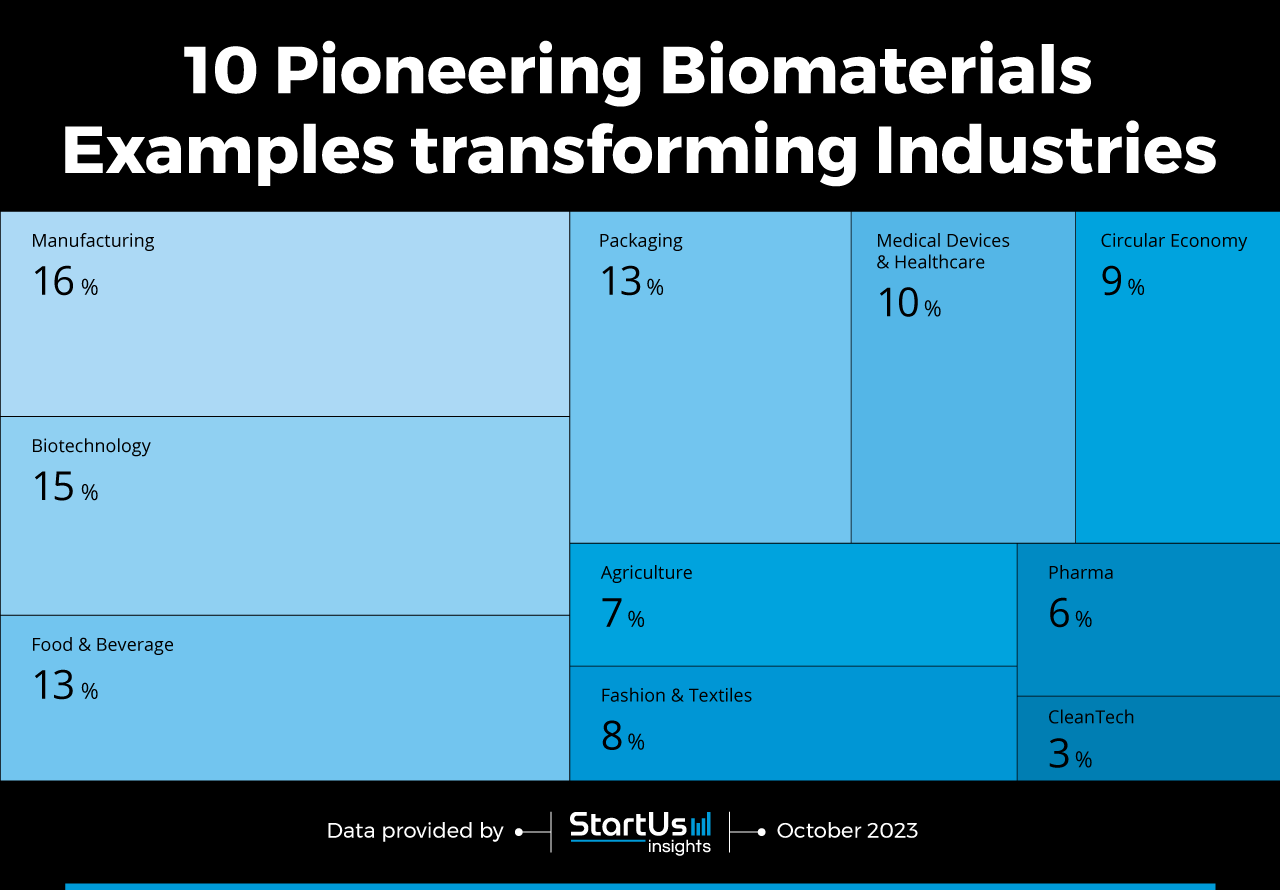
Tree Map reveals the Impact of Biomaterials on 10 Industries
The tree map below illustrates how the biomaterials examples highlighted in this report impact 10 industries. Biomaterials are carving a niche across various sectors due to their sustainable attributes. Within manufacturing, they support the production of eco-friendly products, with bio-composites, biodegradable polymers, and bio-ceramics being prominent materials. Biotechnology harnesses biomaterials like bioplastics and bio-composites, produced using enzymes and microorganisms, to mitigate waste and promote animal welfare. The food and beverage sector employs them in crafting edible packaging and enhancing food quality.
Transitioning to biomaterials in packaging enables the industry to replace traditional petroleum-based materials, offering biodegradable and compostable solutions. Medical and healthcare sectors integrate biomaterials for crafting biocompatible implants and prosthetics. Contributing to a circular economy, biomaterials facilitate the creation of eco-friendly products and packaging. The agriculture sector leverages them for bio-fertilizers and biodegradable mulches, fostering sustainable farming practices. In fashion and textiles, biomaterials like mycelium leather allow designers and retailers to explore sustainable clothing solutions.
The pharmaceutical sector utilizes biomaterials for precise drug delivery systems and biocompatible platforms for drug testing. Lastly, the cleantech sector exploits biomaterials for biodegradable photovoltaic films and bio-based insulation materials, aiding in energy conservation and environmental remediation. Through these diverse applications, biomaterials are addressing global sustainability challenges across a spectrum of industries.
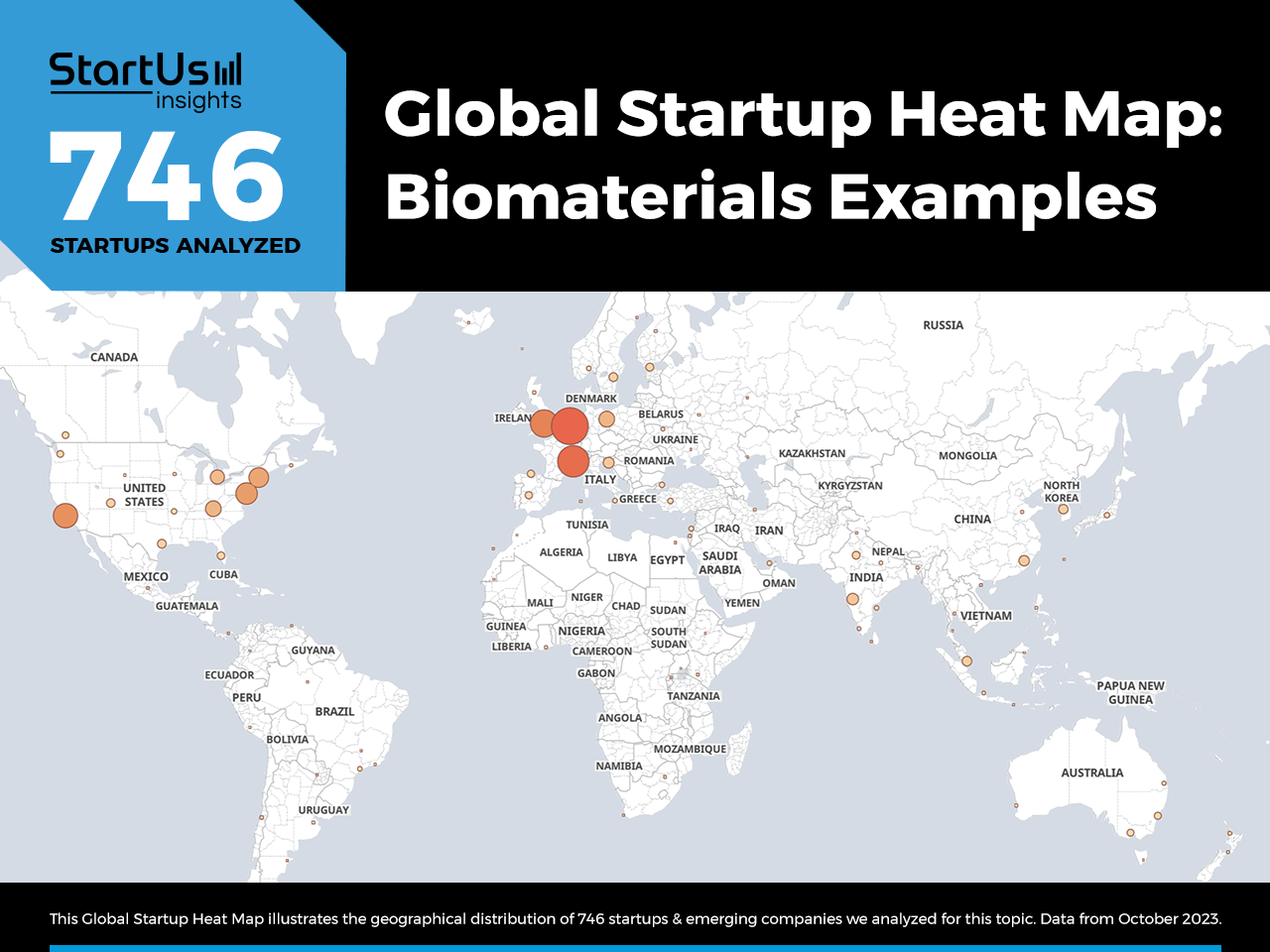
Global Startup Heat Map covers 746 Biomaterials Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 746 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform that covers 3 790 000+ startups & scaleups globally, the Heat Map reveals that Europe has a high concentration of biomaterials startups, followed by the US and Asia.
Below, you get to meet 20 out of these 746 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These biomaterials startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Interested in exploring all 700+ biomaterials startups & scaleups?
What are some examples of biomaterials? Explore across 10 industries:
1. Manufacturing
Conventional manufacturing relies on non-renewable, non-biodegradable, and unsustainable materials, especially plastics. The massive use of these materials leads to serious environmental concerns such as landfills and ocean pollution. Companies are thus shifting to sustainable materials to reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing facilities.
Biomaterials are a promising alternative for producing sustainable products with less ecological footprint than traditional materials. Startups are leveraging technology to integrate bio-composites, bio-ceramics, and biodegradable polymers into the production lines. They facilitate a paradigm shift towards conscientious production practices, underscoring sustainability. Some types of biomaterials used in the manufacturing sector include:
- Bio-Circular Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
- Green Nanomaterials
- Bio-Based Polymers for 3D Printing and Molding
- Bio-derived Adhesives
- Renewable Lubricants
NanoTerraTech creates Bio-Graphite from Forestry Waste
Canadian startup NanoTerraTech converts forestry waste into bio-graphite for electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing. With the major transition to electromobility, there is a shortage of essential minerals required for EV battery production. The startup develops a biomaterial with a zero-carbon footprint as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-derived carbon graphite.
Further, NanoTerraTech utilizes renewable energy to convert waste biomass like tree bark, sawdust, and forestry residue into an eco-friendly bio-graphite. Bio-graphite is a clean and net-negative alternative for manufacturers who require sustainable carbon materials.
2. Biotechnology
Startups use biotechnology processes to address waste, plastic pollution, land use, and animal welfare. Biotechnology utilizes enzymes and microorganisms to produce bio-based materials to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Genetic engineering further enables biotechnologists to modify bacteria and algae to synthesize materials like bioplastics, bio-composites, and bioceramics. The biosynthesis of biomaterials includes processes of cell signaling, gene expression, and extracellular assembly.
Emerging startups produce biomaterials such as hydrogel, bio-polymers, biomolecular materials, and scaffold support for cell growth. Moreover, biomaterials integrate living cells, cellular products, and synthetic components designed for cellular biosynthesis. Further, biomaterials facilitate tissue engineering, optimize drug delivery, and serve as scaffolds to improve complex cellular interactions. A few biomaterials used in the biotechnology sector include:
- Biomimetic Materials
- Decellularized Extracellular Matrix (dECM)
- Nanocellulose Hydrogel and self-healing Hydrogels
- Nanostructured Polycaprolactone (PCL) Film
- Conductive Polyaniline-based Nanocomposites
Green Elephant Biotech makes Plant-based Bioplastics
German startup Green Elephant Biotech offers a 3D-printed cell screw made of poly-lactic acid (PLA), a plant-based biopolymer derived from renewable crops. The product’s design promotes optimal cell growth over a larger area of less material, ensuring efficient nutrient exchange and high oxygenation. The crops utilized for PLA production also extract CO2 from the atmosphere and the emissions return to the soil during disposal.
3. Food and Beverage
The food and beverage industry seeks innovative materials to develop products that align with dietary, health, and sustainability standards. Bio-based materials are utilized as functional ingredients to fortify foods with essential nutrients and bioactive compounds while enhancing flavor profiles. Moreover, biomaterials efficiently break down food components to ensure smoother production processes and food products that are more aligned with consumers’ dietary needs.
Startups also create edible food packaging from polysaccharides and protein-based films. These innovations extend food shelf life and block harmful elements. Bioactive, biodegradable edible films and nano-based smart materials serve as sustainable alternatives to synthetic packaging, ensuring prolonged freshness and improved quality. Food manufacturers leverage biomaterials such as nisin, chitosan, cactus/mucilage, and bacterial nanocellulose to produce sustainable packaging. Some biomaterials used in the food and beverage industry include:
- Starch-based Biomaterials
- Edible Films and Coatings for Food Preservation
- Biopolymer-based Beverage Bottles
- Algal and Seaweed-derived Thickeners and Stabilizers
- Plant-based Edible Cutlery
BIOWEG specializes in a Bio-based Hydrocolloid
German startup BIOWEG provides a bio-based hydrocolloid for the food industry to address the lack of unhealthy food ingredients. This solution enhances the texture and flavor of plant-based meats and dairy substitutes. Moreover, the hydrocolloid is sustainably produced through a patented zero-waste fermentation process, underscoring the commitment to environmental responsibility. The startup’s products bear clean labels, reflecting their sustainable sourcing and alignment with the expectations of health-conscious consumers.
4. Packaging
The widespread use of traditional petroleum-based polymers in the packaging industry raises serious ecological and economic concerns. As a response, startups provide bio-based materials for food, pharmaceutical, and consumer goods packaging. These biomaterials are biodegradable, compostable, and derived from renewable sources. Due to these properties, manufacturers utilize biopolymers to produce food product films, bio-waste bags, transport packaging films, and compostable items for agriculture.
For example, biopolymers used in food packaging are polysaccharides, proteins, and aliphatic polyesters that have barrier properties for controlling the exchange of gasses, moisture, aroma, and lipids from the external environment. Further, the use of plastic in food packaging raises health concerns as it may spread harmful chemicals into the food. Startups accelerate innovations around biodegradable, recyclable, and edible packaging.
Adopting biomaterials, such as PLA, creates packaging solutions that directly address the challenges posed by persistent plastic waste. The packaging industry seeks lightweight materials to reduce raw material use, waste, and transportation costs. Leading innovations in biomaterials for the packaging industry include:
- Polylactic Acid
- Lignin
- Bio-Polyethylene Terephthalate (Bio-PET)
- Natural Fiber-based Packaging Material
- Packaging from Agricultural Waste & Residue
- Cellulose-derived Films Packaging
BUYO Bioplastic develops a Biodegradable Bioplastic
Vietnamese startup BUYO Bioplastic produces biodegradable bioplastics as an alternative to non-renewable and fossil fuel-based resources. The startup converts bio-waste and plant-based materials into durable bioplastics. This solution is comparable to regular plastics in strength and elasticity but differentiates in biodegradability and antibacterial features.
The company’s bio-process consumes less energy than conventional manufacturing processes, ensuring a minimum carbon footprint. BUYO offers natural-based bioplastics to promote more sustainable packaging and environmental protection.
5. Medical Devices & Healthcare
The medical and healthcare industry seeks materials that integrate efficiently with the human body while ensuring optimal performance. The widespread recognition of biomimetic and bioresponsive biomaterials arises from the need to enhance the longevity of medical devices and regenerate injured tissues. Natural biomaterials offer great potential for clinical use due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, cost-effectiveness, and safety.
Utilizing biomaterials in medical devices enhances patient comfort, extends implant longevity, and reduces the risk of complications. Scaffold materials like biodegradable polymers and decellularized extracellular matrix furnish a supportive three-dimensional framework that facilitates tissue growth and regeneration. Biomaterial-based scaffolds, combined with stem cells and growth factors, facilitate the efficient regeneration and repair of damaged organs and tissues.
Biomaterials revolutionize the industry by providing biocompatible implants, prosthetics, and surgical tools, leading to safer and improved patient outcomes. Below are a few biomaterials used in the medical devices and healthcare industry:
- Nanostructured Biomimetic Materials
- Bioactive Analogues of Growth Factors (Synthetic Pro-Morphogens)
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
- Metallic Biomaterials
- Neuroregenerative Biomaterials
NABIHEAL provides Antimicrobial Nanostructured Biomaterials
Spanish startup NABIHEAL develops antimicrobial nanostructured biomaterials to improve wound management. It addresses the challenge of treating complex wounds like chronic wounds or burns that are prone to microbial infections and biofilm formation. Current antimicrobial products to treat wound infections use silver, which is expensive as well as poses environmental and safety threats. Overall, antimicrobial nanostructured biomaterials offer affordable management of complex wounds and prevent complications throughout the wound-healing journey.

6. Circular Economy
Driven by the shortage of resources and the shift from fossil-based polymers to more renewable alternatives, the use of bio-based materials becomes crucial for the circular economy. In response to resource scarcity, innovative concepts for designing and selecting suitable materials have emerged. Natural fibers or polymers result in more sustainable and biodegradable materials with lower environmental impact.
Startups and scaleups produce bioplastics made from bio-based polymers to ensure sustainable life cycles for commercial plastics. Innovations like biodegradable packaging and bio-based textiles assist apparel businesses in adopting sustainable practices. This meets the demand for eco-friendly products and supports a regenerative economic model. In the circular economy era, integrating biomaterials is crucial for establishing a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and optimizes resource use. Some examples include:
- Biodegradable Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
- Bio-based Aliphatic Polyesters
- Bio-based Polyolefins
- Fossil-based Plastics
- Hemp Fibers
Dama BioPlastics enhances Sustainable Carbon Replacement
US-based startup Dama BioPlastics enables the sustainable replacement of carbon black for the construction industry to reduce its carbon footprint. It is made from plant waste and is strong, durable, and resistant to fire and water. The startup specializes in processing, refining, and upcycling waste biomass into eco-friendly alternatives
The startup’s solution supplements nonrenewable feedstocks in contemporary manufacturing facilities. Further, the company’s carbon-negative biocarbon contributes to the circular economy by reducing landfill waste and carbon emissions. It also absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it produces during manufacturing.
7. Agriculture
The main challenges in the agriculture industry include reduced productivity, nutritional scarcity, and climate change. Overapplication of fertilizers and pesticides to increase crop yield is a widely adopted unsustainable agricultural practice. Further, continuous fertilizer application severely degrades soils, pollutes water systems, and escalates climate change.
Startups employ nanotechnology in agriculture to make use of nanoscale materials to address challenges including nutrient delivery, sustainable farming, and crop protection. For instance, the use of nano bio-fertilizers as a substitute for traditional micronutrient fertilizers contributes to enhanced food security.
Additionally, startups create biomaterials such as biodegradable mulches, bio-based fertilizers, and biostimulants to replace synthetic chemicals in the agri industry. Biomaterials degrade harmlessly into the soil, thus minimizing pollution. The adoption of biomaterials also economically benefits farmers by reducing reliance on costly, non-renewable resources and inputs. Some biomaterials in the agriculture industry are:
- Soil-biodegradable Mulch Film
- Microbial Pesticides
- Biochemical Pesticides
- Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms
Zymolent Biosciences makes Biofertilizers and Bioformulations
Indian startup Zymolent Biosciences offers microbial inoculant-based bioformulations, biostimulants, and biocontrol for crop yield improvement and sustainable pest control. These solutions promote crop growth with increased soil fertility by complementing conventional chemical fertilizers. This way, the solutions enhance the availability of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
The startup thus assists farmers in optimizing their return on investment (ROI) for crop fertility by increasing soil and phosphorus efficiency. Consequently, this facilitates nitrogen fixation and addresses crop nutritional needs through natural mechanisms.
8. Fashion & Textiles
Producing and discarding clothing fast is a serious concern. Fabric selection serves as a pivotal factor in promoting sustainability, impacting the stages of production and thereby facilitating the transition towards a more circular economy. To address this challenge, startups offer designers and brands bio-based materials that have a lower environmental footprint.
Biomaterials used in the fashion and textiles industry include plant-sourced high-performance fibers to make clothing more renewable and sustainable. Further, companies produce leather derived from fungi roots that are biodegradable and a cruelty-free alternative to animal leather. Simultaneously, technological advances allow the creation of durable textiles that promote waste reduction. Below are some biomaterial solutions for the fashion and textile industry:
- Microplastic-free Textile Fibers
- Bio-based Leather
- Mycelium Leather
- Bacterial Cellulose
- Algae-based Textiles
Modern Synthesis offers Bacteria-made Biotextile
UK-based startup Modern Synthesis manufactures nanocellulose-based biomaterials for sustainable fashion. The materials used in fashion products raise environmental concerns due to excessive pollution. The startup’s biotech platform leverages microbes to grow cellulose-based composite material that is naturally biodegradable.
The production at the nanoscale offers nanocellulose fibers high strength and natural binding ability. Modern Synthesis provides fashion brands with a natural, plastic-free, and sustainable bio-textile to minimize their environmental footprint.
9. Pharmaceuticals
Biomaterials significantly advance the pharmaceutical industry by enhancing the design, cost-effectiveness, and development of novel drug delivery systems. Biocompatible materials enable precise drug delivery systems, controlled release, and improved patient treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects. To advance this, startups create biomaterials with exceptional biocompatibility and bio-functional properties. Additionally, they facilitate the creation of biocompatible platforms for drug testing and disease modeling in tissue engineering.
Biomaterials also find use in the production of pharmaceutical-grade medical devices, such as biodegradable drug carriers and implantable drug reservoirs. Bio-based materials’ versatility drives innovation in pharmaceutical research, providing solutions to complex drug delivery challenges and advancing personalized medicine. Some examples in pharma include:
- Injectable Hydrogel
- Porous Materials
- Hydrolysis and Enzymatically Responsive Polymers
- Temperature-responsive Polymers
- Magnetic-responsive Polymers
Cysbio produces Sulfated Biochemicals
Danish startup Cysbio employs its patented sulfation technology to modify microbes for enzymatic sulfation of phenolic compounds. Through this approach, the startup makes a range of sulfated biochemicals using non-toxic compounds. This expands the possibilities in drug development and delivers improved, cost-effective therapeutic solutions.
Further, the technology facilitates the modification of pharmaceutical compounds to enhance their solubility and bioavailability. Cysbio utilizes advanced metabolic engineering and synthetic biology techniques to create bacterial cell factories. These innovative methods enhance biochemical production, making it more sustainable by utilizing renewable feedstocks.
10. CleanTech
Advances in biomaterials are paving the way for enhanced sustainability and efficiency. Cleantech emerges as a beacon in response to unprecedented economic challenges posed by escalating energy prices, resource shortages, and carbon dioxide levels. With solar energy being a sustainable energy source, there comes the rapid development of photovoltaic technologies. Cleantech startups harness solar energy using phototrophic microorganisms as a pathway to sustainable bioenergy. Moreover, polymeric biomaterials with polypeptide structures are mainly used in photovoltaic technology.
Further, startups develop biomaterials and natural compounds that enable green buildings and organic electronics. Biomaterials have a pivotal role in environmental remediation, energy conservation, and waste reduction. Cleantech startups ensure a sustainable and low-carbon economy by developing biomaterials like:
- Biodegradable Photovoltaic Films
- Biobased Insulation Materials
- Bio-based Lubricants for Wind Turbines
- Algae-derived Bioinks
- Biodegradable Battery Components
Bio Graphene Solutions makes Green Graphene
Canadian startup Bio Graphene Solutions leverages nanotechnology to break down carbon from organic source materials (biochar) without using graphite. The primary hurdle associated with traditional graphene lies in achieving consistent product quality and cost-effectiveness.
Additionally, the startup produces green graphene made from organic source materials. This cleantech production process is eco-friendly and non-invasive as it does not rely on harsh chemicals, acids, or solvents. The startup’s solution also reduces embodied carbon in concrete construction.
Discover All Examples of Biomaterials & Emerging Startups
The future of biomaterials is closely linked with sustainability, remodeling, and regeneration. With advancements in the field of biomaterials, we anticipate a broader spectrum of applications, leading to innovative solutions for significant global challenges in various industries. Lastly, technological advancements in biomaterials enhance the quality of life for individuals and foster a healthier and sustainable world. Get in touch to identify specific biomaterials startups & solutions that advance your business!


![10 Top Startups Advancing Machine Learning for Materials Science [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Machine-Learning-for-Materials-Science-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)
![10 Emerging AI Solutions for Material Science [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/AI-Solutions-for-Material-Science-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)



