Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary
- Global automation demand is accelerating amid labor shortages, aging populations, and wage inflation. Industrial robot installations hit a record USD 16.5 billion, while the overall robotics market is set to double – from USD 71.78 billion in 2025 to USD 150.84 billion by 2030. Investor interest is strong, with robotics startups raising over USD 2.26 billion in Q1 2025 alone.
- Generative AI is transforming robotics from programmable machines to self-learning systems. Humanoids like Digit and Figure 02 are moving into full-scale production, and Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) models are making advanced automation more accessible. Most systems now deliver ROI in just 6-18 months.
- Robots are becoming modular, reconfigurable, and cloud-orchestrated, enabling faster, more precise, and always-on operations. With labor costs rising 3-5% annually and the working-age share projected to drop to 53% by 2060, robotics is rapidly becoming essential infrastructure.
- Twelve transformative trends anchor the robotics playbook through 2030. Mastering these levers enables enterprises to lead the next productivity wave:
- Generative AI-Native Autonomy
- Humanoid Co-Workers
- Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS)
- Autonomous Mobile Manipulators (AMMRs)
- Edge-Cloud Robotics Orchestration
- Swarm Robotics & Bio-Inspired Systems
- Self-Reconfigurable & Modular Robots
- Soft Robotics & Advanced Materials
- Simulation-to-Real and Real-to-Sim Training Pipelines
- Task-Specialist Service Robots
- Micro & Nano Robotics
- Sustainable & Green Robotics
- Sector-specific roadmaps translate these innovations into tangible ROI across manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, construction, and public services. The message is clear: robotics is no longer future tech – it’s today’s smartest investment in scalable, resilient growth.

FAQ – Robotics ROI & Reality Check
What is the ROI and Cost Structure of Robotics Implementation?
- Industrial robots typically pay back in 6 to 18 months.
- Most new industrial robots today sell for USD 25K to 100K (refurbished options start near USD 20K).
How will the Future of Robots impact Jobs, and what about Workforce Displacement?
Adding one robot replaces 3.3 jobs and puts downward pressure on wages in directly affected occupations. At the same time, automation generates new roles in robot programming, maintenance, analytics, and system integration.
What are the Safety and Regulatory Compliance Requirements?
Core standards include ISO 10218 for industrial robots and ISO/TS 15066 for collaborative robots; US facilities also follow ANSI/RIA R15.06.
What are the Competitive Advantages and Market Positioning Benefits?
Reduce manufacturing conversion costs by up to 15% and increase yield savings by up to 40% when combined with other technologies, process enhancements, and structural layout changes.
Robots run 24/7 with consistent precision that lowers defect rates and downtime. Moreover, modern systems can also be reprogrammed quickly. This allows firms to switch to new products or align with demand spikes faster than manual lines.
Key Drivers Shaping the Future of Robotics
Labor Shortages and Demographic Shifts
Labor scarcity, intensified by aging populations and skill shortages, makes automation necessary. 63% of employers name skills shortages as their top business challenge.
McKinsey finds that up to 30% of current work hours can be automated by 2030, a figure now growing with gen-AI-powered robotics.
OECD ageing-economy modeling also shows the working-age share will fall toward 53% by 2060, which drives an 8% drag on per-capita income.
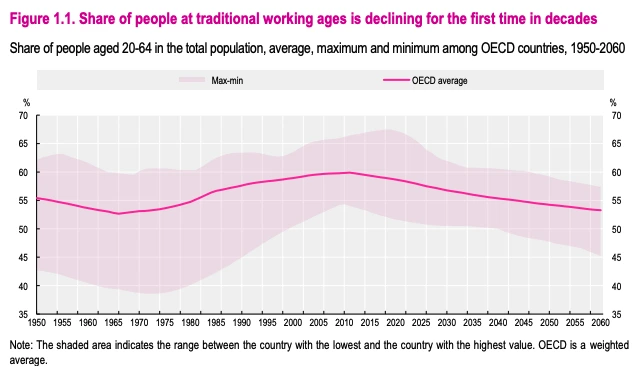
Credit: OCED
Economic Pressures and Cost Efficiency
With hourly labor costs increasing by 3% to 5% per year, companies are driven to find more cost-efficient production methods.
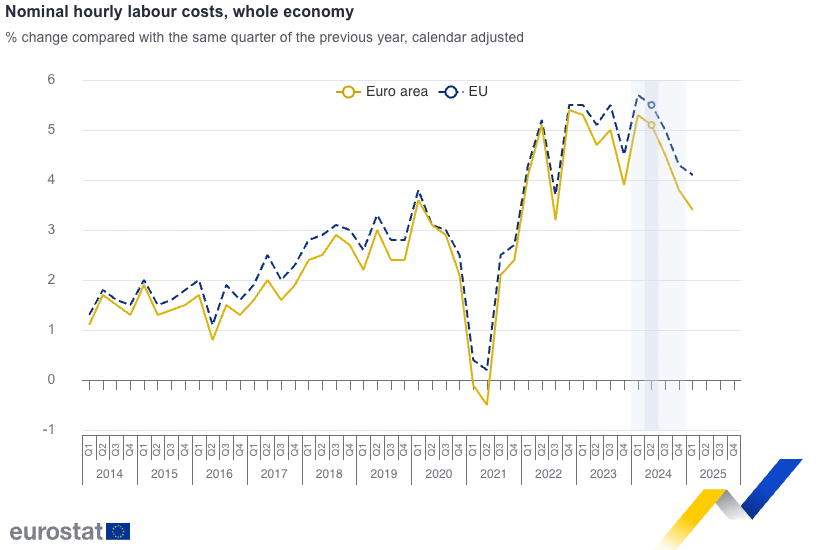
Credit: eurostat
2024 cost survey projects the global average industrial robot price at just USD 10 856 in 2025, down from 2010 levels.
BCG’s analysis shows advanced robots can trim manufacturing conversion costs by up to 15%, and up to 40% when paired with other technologies, process enhancements, and structural layout changes.
Additionally, falling capex plus opex savings flip the ROI equation and open automation to mid-sized plants and warehouses.
12 Trends Shaping the Future of Robotics [2025-2030]

1. Generative AI-Native Autonomy
Generative AI-driven systems learn, adapt, and evolve through embedded models like large language models (LLMs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), and vision-language frameworks.
This shift is driven by mounting pressures as 75% of manufacturers face workforce shortages. For instance, EV companies are turning to robots to offset labor shortages, with Europe’s auto industry installing 23 000 new industrial robots last year.
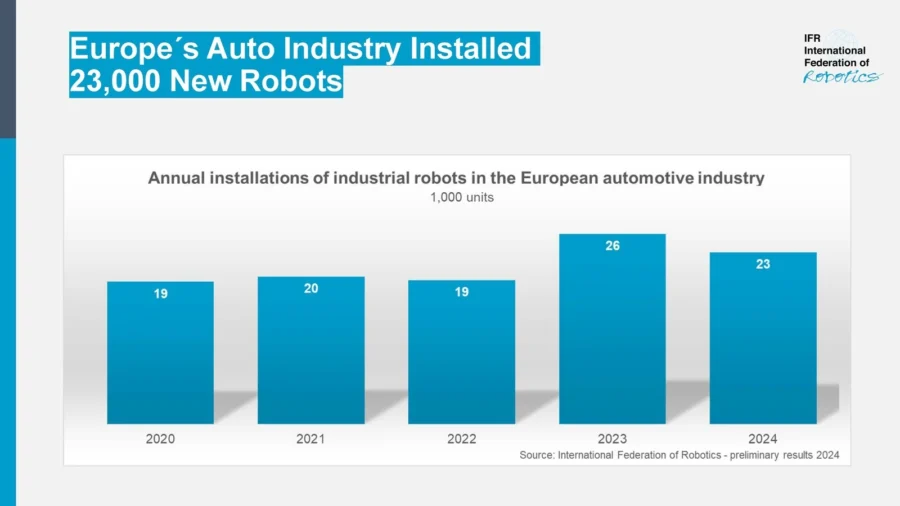
Credit: IFR
Yet conventional deployment requires labor-intensive coding and testing. Gen-AI-powered robots sidestep this burden by simulating scenarios, brainstorming multiple action plans, and self-optimizing. This drives sizable productivity gains and trims overall R&D costs.
As 63% of enterprises plan to raise their gen-AI investments by 2026, robotics is becoming a platform for competitive differentiation. From surgical cobots to self-learning warehouse bots, AI-native autonomy redefines how machines reason, collaborate, and respond.
Further, with the gen AI-powered robotics market expected to reach USD 8.57 billion by 2029, this marks a foundational leap, from automation to autonomy anchored in intelligence, flexibility, and speed.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Intelligent robotic cells for high-mix tasks with autonomous task adaptation – Human-robot collaboration using LLMs for personalized interaction – Autonomous pallet jacks with dynamic navigation and route optimization | – 24×7 operation capability and reduces downtime – ChatGPT-powered adaptation system for human-robot interaction achieved a 92% success rate in adapting to user preferences – Improved safety and task accuracy |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Smart coordination robots to optimize resource allocation and scheduling – Autonomous vehicles leveraging generative AI for navigation and real-time decision-making | – Reduced transport and inventory costs – Fewer bottlenecks and improved fleet uptime |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – AI-assisted surgical robots for complex medical procedures – Rehab robots with modular design for personalized therapy – Pharmacy automation robots | – 30% fewer complications – 25% shorter surgeries – Surgical precision improved by 40% – 10% reduction in healthcare costs |
| Construction | – Bricklaying & 3D printing robots with precise and autonomous task execution – Safety monitoring robots that dynamically map worker movements – Equipment positioning robots that optimize heavy machinery placement – 3D concrete printing robots generating complex structural elements directly on-site | – Faster project delivery with less manual labor – Improved safety through real-time hazard identification and congestion reduction – Reduced equipment idle time and unnecessary movement – Enhanced precision in construction tasks with consistent quality |
| Governments | – Smart city robots for traffic management – Public safety robots for handling citizen inquiries – Infrastructure maintenance robots for automated public facility upkeep | – Better traffic flow and emergency response – Improved citizen services with 24/7 automated assistance – Increased transparency through consistent and accessible information |
Real-World Implementations
- Apollo humanoid robot, powered by DeepMind’s Gemini AI, executes component transfer and quality checks in manufacturing.
- Pilots:
- Mercedes-Benz utilized Apollo for automating physically challenging tasks such as bringing parts to the production line and inspecting components.
- GXO Logistics deployed Apollo for warehouse material handling and task learning.
- GR00T N1 foundation model combines reflexive and deliberative reasoning in an open framework for humanoid control.
- Pilots:
- 1X Technologies’ NEO Gamma to demonstrate domestic tidying tasks with minimal tuning.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Deontic
Belgian startup Deontic develops an AI platform that automates regulatory compliance and speeds up autonomous driving validation. It uses generative AI workflows and intelligent agents to process unstructured legal texts and safety requirements.
The platform extracts obligations and scenarios, then integrates them into automated simulations and validation tools. It also converts natural language inputs into OpenDRIVE and OpenSCENARIO formats. This allows businesses to generate and test scenarios across various terrains and regulatory environments.
Further, Deontic supports cross-operational design domain (ODD) coverage and includes quality assurance mechanisms. It also collects compliance evidence automatically.
2. Humanoid Co-Workers
Humanoids are evolving as facility-ready solutions due to acute labor shortages that hit logistics, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Last year, Digit by Agility Robotics became the first humanoid robot deployed in paid production at a GXO logistics site.
Credit: Bank of America
With 18 000 humanoid units expected to ship in 2025 and full-scale adoption forecasted to begin by 2028, humanoids are rapidly moving from pilots to production.
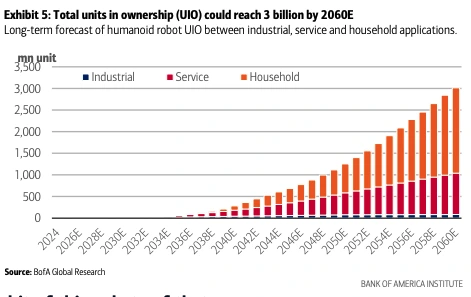
Credit: Bank of America
Investment momentum is strong, as Figure AI alone raised USD 675 million, while China’s public procurement surged from CNY 4.7 million to CNY 214 million in one year. Also, South Korea formed the K-Humanoid with the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy. The government plans to invest USD 770 million by 2030.
This shift is enabled by Isaac GR00T N1 and Cosmos models from NVIDIA that provide multimodal task reasoning and perception. Further, Gemini Robotics leverages the Gemini 2.0 framework to improve robotics through the integration of vision, language, and action.
At scale, Figure AI’s BotQ, the robot building robot plant, aims to produce 12 000 humanoids per year. With the market set to exceed USD 243.40 billion by 2035 at a 49.21% CAGR, humanoids are emerging as an intelligent labor infrastructure.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Manage multi-step assembly lines with adaptive dexterity – Human-robot collaboration for ergonomic support in heavy-duty tasks – Quality inspection and rework automation with bimanual manipulation | – Reduces physical strain and repetitive injuries – Enhances throughput in hybrid assembly cells – Decreases inspection errors through real-time visual analytics |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Automated truck unloading and palletizing by humanoids – Picking & placing irregular objects using advanced gripping – Night-shift workforce substitutes in fulfillment centers | – Cuts unloading time – Operates safely in cluttered environments with minimal supervision – Addresses chronic labor shortages for late-night operations |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Companion humanoids assisting in elder care and patient mobility – Sterile drug handling and delivery in hospital settings – Frontdesk humanoids managing patient inquiries and queues | – Improves patient satisfaction with empathetic interaction – Reduces contamination risks in high-sensitivity areas – Increases operational efficiency in non-clinical tasks |
| Construction | – On-site humanoid assistants supporting tool handover and material transport – Task execution in confined or high-risk environments – Real-time inspection and documentation of construction progress | – Boosts worker productivity and safety compliance – Enhances site coverage during labor gaps – Enables multi-tasking support in complex environments |
| Governments | – Humanoid officers for public-facing duties like information desks – Language-capable humanoids assisting in immigration and civic services – Urban maintenance robots for light repair and monitoring | – Enhances inclusivity in multilingual services – 24×7 availability reduces citizen wait times – Builds public trust in AI-powered civic infrastructure |
Real-World Implementations
Foxconn & NVIDIA – Houston AI-Server Line
Humanoid robots co-developed by Foxconn and powered by NVIDIA’s robotics platform are being trained to handle pick-and-place, cable insertion, and chassis-build tasks on the new Houston production line.
- Pilots: Robots will begin assembling NVIDIA GB300 AI servers when the plant ramps up in Q1 2026, with Foxconn targeting fully automated cells across select units thereafter.
Figure AI’s Figure 02 humanoid (which is 170 cm tall, 70 kg in weight, and capable of a 20 kg payload) is deployed to autonomously pick and place stamped sheet-metal panels into welding fixtures and handle other ergonomically taxing assembly tasks.
- Pilots:
BMW Spartanburg deployed Figure 02. The robot successfully inserted body panels during a several-week pilot at Plant Spartanburg, marking BMW’s first use of humanoids in production.
GXO Logistics & Agility Robotics – Spanx Flowery Branch DC
Bipedal humanoid designed for warehouse operations, which is capable of lifting totes from autonomous mobile robots and placing them onto conveyors. These tasks are chosen to cut ergonomic strain.
- Pilots:
- GXO Logistics uses Digit robots, the first revenue-generating humanoid deployment under a multi-year Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) agreement. Roll-out roadmap calls for scaling Digit fleets across additional GXO sites starting in 2025, as new warehouse workflows.
- Amazon has begun testing Agility’s Digit at its robotics R&D site south of Seattle, tasking the bipedal robot with retrieving and stacking empty totes.
EngineAI’s SE01 and the lighter PM01 combine a dual-chip compute stack (NVIDIA Jetson Orin + Intel N97), 24-DOF limbs, and a 320-degree waist to deliver natural 2 m/s gait, precision handling, and open-source ROS/ONNX control for factory, logistics, and customer-service tasks.
- Pilots: EngineAI unveiled both models at CES 2025 and set a goal of shipping more than 1000 units worldwide by year-end 2025, with first factory-floor and logistics pilots already in negotiation. Following a public demo in which the PM01 executed a front flip, Shenzhen’s police department began field-testing units for patrol-assist duties and situational awareness training.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Humanoid
UK-based startup Humanoid creates a humanoid robot platform, HMND 01, that automates physical labor in logistics, manufacturing, and service settings.
It uses high-torque actuators and AI for perception and manipulation. Additionally, modular hardware enables it to handle goods, pick and pack items, and support part kitting tasks.
The startup’s robot moves at up to 1.5 m/s using motion control systems that enable it to navigate confined spaces. It operates in both autonomous and teleoperated modes.
Additionally, its features include a 15 kg payload and 41 degrees of freedom. It also offers customizable garments and interchangeable modules to fit different tasks.
3. Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) is driven by a convergence of business-model innovation and AI-native autonomy. The global RaaS market stood at USD 26.93 billion by 2025. This marked a 17.3% year-over-year growth.
Industry analysts forecast RaaS market growth of 18% CAGR through 2032s. This bullish outlook aligns with a record USD 2.26 billion in robotics funding raised in Q1 2025, where over 70% of the capital was funneled into task-focused machines.
RaaS bundles hardware, AI-driven software, maintenance, and uptime SLAs into predictable pay-per-use contracts.
This business model gains additional traction through subscription-based humanoids like Agility Robotics’ Digit, already deployed in GXO-managed warehouses, and platforms such as Robonnement, which raised EUR 15 million to build Europe’s first open RaaS marketplace.
By tackling e-commerce fulfillment pressures and warehouse labor shortages, RaaS also enables enterprises to reliably meet uptime SLAs and energy-efficiency KPIs.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Subscription-based robotic welding and assembly lines – On-demand inspection robots for quality audits – Rentable robotic arms for seasonal or short-run production | – Lowers upfront capital expenditure – Enables rapid scaling of automation for SMEs – Reduces downtime through proactive remote maintenance |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – RaaS-enabled autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for inventory movement – Pay-per-use sorting and picking robots during peak periods – Flexible fleet scaling via cloud-integrated robot management | – Boost in warehouse throughput during seasonal spikes – Cuts storage and labor costs for dynamic operations – Enables real-time analytics and performance upgrades |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Hospital robots for delivery, cleaning, and disinfection on subscription – Temporary surgical assistants in overburdened healthcare systems – Pharmacy robots are leased for inventory and prescription management | – Enhances service quality without high procurement costs – Scalable support in times of medical surge or staff shortages – Improves medicine handling accuracy and delivery turnaround |
| Construction | – Short-term robotic bricklayers, 3D printers, and survey drones – Modular site-cleaning bots for post-shift operations – Subscription-based inspection and safety audit robots | – Increases flexibility in resource planning across project phases – Reduces on-site injuries and clean-up delays – Enables tech access to small contractors lacking capital |
| Governments | – Utility maintenance robots on demand for inspections – RaaS platforms for municipal cleaning and waste segregation – Emergency response bots are deployed during disasters or events | – Enhances service reach without permanent deployment costs – Reduces pressure on public infrastructure budgets – Improves speed and coverage during civic emergencies |
Real-World Implementations
Locus Robotics & DHL Supply Chain
Locus Robotics, under a Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) subscription business model, supported DHL to deploy and scale its robot fleets without a large upfront capital investment. This model provides flexibility and enables DHL to easily add or reduce during peak periods, and pay based on usage or subscription terms.
- Pilots: DHL Supply Chain and Locus Robotics have surpassed 500 million autonomous picks using LocusBot AMRs across 35+ global sites, with the latest 100 million picks completed in just 154 days.
Entertainment-merchandiser Futureshirts is running inVia’s AI-driven Logic warehouse execution system to orchestrate inventory, picking, and replenishment workflows. It delivers a five-fold productivity uplift and near-perfect order accuracy across its Nashville fulfillment operation.
- Pilots: Futureshirts logged a 500% productivity boost and trimmed employee onboarding from two weeks to under one hour. It also reduces restocking transfers from days to mere hours after going live with inVia’s PickMate.
Path Robotics & ALM Positioners (TYCROP)
The Path AI Welding Cell is offered as “welding-as-a-service” that bundles vision-guided autonomous welding, installation, and remote support into a monthly fee.
Pilots:
- TYCROP adopted the system in May 2025 and increased weld throughput while eliminating manual touch-ups.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Agroverse
Greek startup Agroverse provides autonomous farming robots through a robotics-as-a-service model. This approach removes the need for ownership or hands-on operation by farmers.
Its robots handle key field tasks such as spraying, mulching, shredding, and tilling. The Agroverse team oversees deployment and operation.
The systems use perception-driven navigation and modular attachments to adjust across different crops and terrains. They are built to support reliable use at scale.
Agroverse lowers labor demands, improves precision, and enables farms to adopt robotics without upfront investment.
4. Autonomous Mobile Manipulators (AMMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Manipulator Robots (AMMRs) are fusing the mobility of AMRs with the dexterity of AI-driven arms that can see, move, and act autonomously across complex environments.
While the market remains at USD 590 million in 2025 though its explosive 25.30% CAGR and rapid industrial validation indicate a transformative technology on the verge of mainstream adoption.
Industrial implementation is increasing as Nimble Robotics secured USD 106 million in Series C funding to scale its FedEx-integrated AMMR fleets for autonomous warehouse fulfillment. RoboForce raised USD 10 million to commercialize mobile manipulators for industrial use cases, while Cosmic Robotics attracted USD 4 million to develop robotic solutions for solar infrastructure deployment.
The International Federation of Robotics now classifies AMMRs as both industrial and service robots for their hybrid capabilities. With rapid advances in GPU-edge compute, vision-language-action models, and private 5G orchestration, AMMRs are eliminating the need for fixed automation infrastructure.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – AMMRs navigating shop floors to transport parts – Assembly line assistance with real-time re-tasking – Autonomous inspection and tool replacement tasks | – Increases overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) – Reduces human intervention for repetitive intra-facility transport – Boosts multi-tasking agility on dynamic production lines |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Item picking from shelves and autonomous loading – Mobile robotic arms for packing and labeling – Cross-docking and replenishment with real-time route planning | – Reduces picking time – Enhances inventory accuracy with fewer misplacements – Enables continuous warehouse operations with minimal manual support |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Autonomous medication delivery combined with robotic dispensing – Pathogen-free transport of biological samples – Restocking and organizing medical supplies in storage areas | – Cuts manual labor in infection-sensitive zones – Increases efficiency in hospital logistics – Ensures consistent traceability and sterile handling |
| Construction | – On-site AMMRs delivering tools and assisting with light assembly – Dynamic scanning and 3D mapping of construction progress – Support robots performing utility tasks like pipe fitting and wiring | – Enhances productivity on sprawling job sites. – Reduces worker fatigue and risk from repetitive logistics – Improves project visibility through autonomous data capture |
| Governments | – Autonomous robotic arms for public facility sanitization – Mobile info-assist bots at public transport hubs – Emergency logistics bots for supply delivery during disasters | – Increases automation in sanitation tasks in urban areas – Enhances commuter experiences through dynamic guidance – Enables autonomous disaster response with minimal human risk |
Real-World Implementations
Dexterity & Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Mech, a dual-armed “superhumanoid” robot co-developed by Dexterity and Kawasaki, mounts two custom 8-axis arms (65 lb each) on a mobile base. It runs Dexterity’s Physical AI to navigate warehouses, palletize mixed boxes up to 8ft high, and autonomously load trucks (AI vanning).
- Pilots: Pilot trials that started in early 2025 at international logistics facilities are evaluating full truck-loading cycles. Data from these runs will feed the first commercial roll-outs slated for late 2025, with one supervisor able to monitor up to 10 Mechs at once.
Brightpick & Superior Communications
A 37-unit fleet of Brightpick Autopicker mobile manipulators is rolling into Superior Communications’ 300 000 sqft warehouse, where the robots will autonomously pick, buffer, consolidate, and dispatch mobile-accessory orders end-to-end. It boosts throughput while running on a RaaS model.
- Pilots: Superior Communications is installing 37 Autopickers at its La Vergne (TN) DC in a two-phase roll-out starting summer 2025. It targets 4000+ items/hr and 88 000 daily picks.
RoboForce introduced Titan for Tier 1 Suppliers
Titan, a modular AI-powered mobile manipulator, combines wheeled- or tracked-based mobility with dual 40 kg-payload arms (1 mm precision, 1.1 m reach). RoboForce’s domain intelligence software to execute the five core industrial primitives, such as pick, place, press, twist, and connect across rugged solar, mining, manufacturing, and even space-sector sites.
- Pilots: The launch coincides with an additional USD 15 million in funding to fuel pilot programs in sectors including solar, mining, manufacturing, and space.
Spotlighting an Innovator: RobotoAI Technologies
Indian startup RobotoAI Technologies makes AI-driven robotic systems for autonomous use in industrial, healthcare, and educational settings. It combines computer vision, motion planning, and navigation to allow robots to operate in complex environments without human control.
Its product range includes mobile robots for material handling and automated guided vehicles for manufacturing. In healthcare, the DYNO SND100 robot delivers supplies, collects waste, and sterilizes spaces while improving on-site security.
For industrial tasks, the iCRA3 system supports precision assembly. The 3-axis Cartesian robots handle dispensing, palletizing, and pick-and-place operations. In education, Roboto AI offers tools like the Alpha Series 3D Manipulators and Aero Pendulum for hands-on robotics training.
Additionally, the startup offers products such as IoT-based monitoring systems and modular conveyors that expand automation capabilities.
5. Edge-Cloud Robotics Orchestration
Edge-cloud robotics orchestration splits tasks between on-device edge AI and scalable cloud platforms. This enables real-time edge processing with centralized intelligence to support intelligent, resilient, and adaptive operations across industries.
Edge-cloud orchestration processes data locally and reduces latency. This avoids obstacles and enables real-time navigation. Even robots can continue functioning during network disruptions.
The global cloud robotics market is projected to reach USD 55.68 billion by 2033. It is growing at a 24.8% year-over-year rate. This growth is driven by the parallel expansion of edge AI and fuels rapid adoption of 5G-enabled cloud robotics at a 45.2% CAGR through 2028.
To support this evolution, orchestration platforms like KubeROS dynamically allocate workloads. It offloads compute-heavy tasks to the cloud while handling latency-sensitive functions locally. Tools like ROS 2 and Kubernetes enable the development of fault-tolerant microservices that can adapt in real time.
As containerization, predictive AI models, and decentralized orchestration frameworks mature, this hybrid model is proving essential. It boosts performance, scalability, and resilience for complex and dynamic robotic environments.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Real-time defect detection using edge vision systems – Cloud-updated task planning for distributed robotic cells – Federated learning across robotic arms to optimize shared performance | – Less than 10 ms latency ensures real-time process control – Enhances predictive maintenance with cloud insights – Increase in system uptime through autonomous fault recovery |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Edge AI-enabled fleet of AMRs for dynamic path optimization – Cloud-driven coordination of picking, packing, and loading – Multi-site synchronization of warehouse operations via shared cloud logic | – Reduces traffic bottlenecks in robot-dense facilities – Enables 24/7 adaptability to changing inventory loads – Simplifies integration of new robots via API-based orchestration |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Edge-based surgical assistance with sub-second responsiveness – Cloud-controlled logistics for patient monitoring and delivery robots – Real-time diagnostic imaging collaboration between edge devices and hospital cloud servers | – Improves precision in latency-sensitive procedures – Enhances data privacy through localized processing – Enables multi-hospital collaboration for faster diagnostics |
| Construction | – Edge-enabled drones for live-site surveillance and analytics – Cloud-connected robotic arms adjusting in real-time to design changes – Multi-robot coordination for infrastructure inspection and updates | – Faster detection of safety hazards – Remote experts can reconfigure robot tasks across sites – Reduces rework with consistent data sync between design and execution |
| Governments | – Public service robots with on-device AI and cloud fallback – City-wide robot networks for cleaning, surveillance, and infrastructure health monitoring – Federated edge-cloud learning to tailor robots to local languages and norms | – Improves service continuity even in low-connectivity zones – Enables centralized monitoring of distributed civic tasks – Enhances personalization and compliance with local regulations |
Real-World Implementations
Agility Robotics – Agility Arc
Agility Robotics’ Agility Arc debuted at MODEX 2024 as a SaaS control layer that deploys, monitors, and optimizes fleets of Digit humanoids. The cloud suite delivers real-time KPIs, uptime, throughput, and mean time between failures (MTBF).
Alongside drag-and-drop work-cell maps and API hooks for warehouse management or execution system (WMS/WES), let operators spin up automation in days instead of weeks and coordinate Digits with AMRs inside mixed-automation warehouses and factories.
- Pilots: MODEX 2024 launch: Arc dashboards streamed live metrics while Digits stacked/unstacked totes and dispatched mobile industrial robots (MiR) and Zebra AMRs. It gives visitors minute-level visibility into fleet performance and AMR–humanoid coordination.
Ocado Intelligent Automation – Porter AMR + Fulfilment Execution System (FES)
Porter is a 1500 kg payload autonomous mobile robot that picks pallets or twin roll-cages straight from the floor. It navigates 1.3m aisles to handle cross-dock, put-away, and high-volume case-picking moves. All orchestrated by Ocado’s fulfillment execution software to cut forklift labor and congestion.
- Pilots: In ProMat 2025 debut, a streamlining case picking & pallet moves with Porter AMR session showed executing point-to-point pallet runs and case-picking workflows.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Olivaw
German startup Olivaw builds a cloud-based platform to manage mixed fleets of service robots in industrial, logistics, and facility management settings. It brings together mobile robots, drones, and third-party systems through a single interface.
The operators are able to track performance, spot errors, and roll out updates in real time. The platform supports devices from different vendors. It also links with infrastructure systems such as elevators and building management software to broaden its applications.
Through its Robot-Resource-Management-Platform, Olivaw enables digital twin simulations, automated skill upgrades, and AI-led task execution. It also offers an open ecosystem for developers to create and add new robotic skills.

6. Swarm Robotics & Bio-Inspired Systems
Swarm robotics & bio-inspired systems are a nature-inspired design with decentralized intelligence. The sector is projected to cross the USD 447.2 million by 2030, with 40.47% YoY growth from 2020 to 2030.
These systems mimic collective behaviors seen in ants, bees, and fish, where simple agents follow local rules, yet their coordination yields complex, emergent results.
Swarm robotics is highly scalable. Systems grow or shrink based on task size. If one unit fails, the rest continue. Flexibility is a core strength. Swarms adapt quickly to environmental changes.
The paradigm is now being supercharged by generative-AI-powered swarm programming and neuromorphic chips like Intel’s Loihi-2, which run spiking neural networks at ultra-low power, ideal for micro-bots.
Sweden’s military used UAV swarm technology to control 100 drones at a time to gather intelligence. Additionally, Shield AI raised USD 240 million in 2025 to scale its Hivemind swarm-autonomy platform at a USD 5.3 billion valuation, and Germany’s SWARM Biotactics closed a EUR 13 million seed round for insect-mimetic collectives.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Self-organizing micro-robots for surface inspection and micro-assembly – Swarm bots for cleaning and maintenance in hard-to-reach machinery – Bio-inspired arms mimicking muscle movement for flexible handling | – Reduces inspection time for complex machinery – Minimizes machine downtime through continuous micro-maintenance – Increases precision in flexible assembly with adaptive actuation |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Swarm drones for inventory audits and barcode scanning – Decentralized robotic agents for shelf restocking and dynamic routing – Bee-inspired bots coordinating parcel movement autonomously | – Enables real-time inventory visibility – Adapts instantly to layout changes or stock flow – Reduces warehouse congestion and improves throughput |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Fish-inspired swarm robots for targeted drug delivery – Micro-swimmers for cell-level diagnostics – Soft-bodied crawlers for internal surgeries | – Enhances precision in non-invasive treatments – Reduces diagnostic delays in remote or complex cases – Improves patient recovery by minimizing surgical footprint |
| Construction | – Ant-inspired bots collaborating on autonomous bricklaying – Swarm drones for aerial 3D mapping and site surveying – Modular crawlers exploring confined areas for structural monitoring | – Accelerates pre-construction surveys – Increases safety in hazardous zones – Enables multi-point data collection without added manpower |
| Governments | – Urban maintenance swarms for cleaning and garbage sorting – Bee-like robots for environmental monitoring (e.g., air, water quality) – Swarm units for search-and-rescue in post-disaster zones | – Enhances coverage across large public spaces – Reduces the costs of recurring manual checks – Increases success rate and safety in emergency responses |
Real-World Implementations
SwarmFarm Robotics & Australian Growers
Queensland-based SwarmFarm fields lightweight, autonomous SwarmBots that mow, spray, and seed broad-acre crops, vineyards, and orchards. It supports growers with precision coverage while reducing labor and chemical inputs.
- Pilots:
Exyn Technologies & Mining Clients
The Nexys payload that runs ExynAI Autonomy Level 4 free-flight navigation, mounts on an aerial platform to self-plan routes through GPS-denied stopes and stockpiles. It captures colorized LiDAR point clouds at up to 16 million cubic meters per sortie, equivalent to scanning nine football stadiums in one flight. Surveyors can model volumes without entering hazardous zones.
- Pilots: Canadian Royalties’ Nunavik mine replaced tripod cavity monitoring system (CMS), Nexys drone-plus-handheld workflow cut surveyors’ exposure on unstable stockpiles, raised volumetric accuracy, and trimmed monthly stope-mapping cycles from days to hours.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Pheratech Systems
US-based startup Pheratech Systems develops swarm robotics systems powered by onboard AI and pheromone-based communication for safety and emergency use. It applies the Stratis Software Protocol, which blends boid-like movement and pheromone tracking. This enables decentralized decisions and adaptive swarm navigation.
Each robot processes data locally while staying connected to the swarm. This setup supports coordinated action in shifting environments. Moreover, the startup’s SENTINEL system deploys drone nests in areas such as schools and disaster zones. The drones detect threats using vision models and respond together in real time.
These units operate independently of central servers by using onboard intelligence for direction and speed. A control hub manages real-time tracking, maintenance, and custom commands. It also allows operation through manual inputs or natural language.
Pheratech Systems further supports use cases in public safety, border patrol, disaster response, and environmental monitoring.
7. Self-Reconfigurable & Modular Robots
Self-reconfigurable and modular robots address core limitations of fixed-form automation with agility, adaptability, and resilience. The global modular robotics market surged from USD 9.41 billion to USD 10.94 billion, which reflects a 16.3% year-over-year growth.
While the self-reconfiguring modular robotics is projected to surpass USD 1.8 billion by 2033 is tracking a 15% CAGR through 2033.
NASA’s mission-adaptive digital assembly system (MADAS) deploys modular bots to autonomously construct lunar infrastructure, while Yale’s soft starfish robot pioneers fully reversible limb connections using thermoplastic foam joints that offer self-healing capabilities in hazardous environments.
Investors’ interest is growing, as seen in startups like ARX Robotics, which secured EUR 31 million in 2025 to scale defense-grade modular ground units. Also, Sunrise Robotics raised USD 8.5 million to commercialize plug-and-play industrial arms.
Neuromorphic edge AI, electro-adhesive connectors, and standardized APIs are enablers of these modular robots. Together, these enable on-the-fly reconfiguration, scalability, and software-driven updates to robotic systems.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Modular robotic arms with interchangeable tools for multi-tasking – Reconfigurable assembly bots adapting to varied product lines – Plug-and-play robots for small-batch and lot-size-1 manufacturing | – Reduces setup time during changeovers – Enhances product customization with minimal downtime – Supports agile manufacturing without full-line redesign |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Reconfigurable bots switching between transport and sorting – Modular conveyor bots adjusting layout for peak loads – Field-upgradable robots adapting to changing inventory types | – Boosts operational flexibility across varying warehouse sizes – Cuts deployment time for new SKUs – Extends robot lifecycle through scalable upgrades |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Modular rehab robots tailored to individual patient therapy – Configurable cleaning robots for various hospital zones – Self-repairing robots in sterile environments using soft joints | – Enables personalized care without new hardware – Reduces pathogen spread with zone-specific configurations – Lowers maintenance disruption through partial component swaps |
| Construction | – Modular bots for excavation, bricklaying, and 3D printing – On-site robotic retooling for task-specific configurations – Self-assembling scaffolding bots for vertical builds | – Reduces the need for multiple specialized robots on-site – Speeds up task switching in mixed-use projects – Enhances worker safety with autonomous reconfiguration in hazardous zones |
| Governments | – Disaster-response robots adapting to debris navigation and rescue – Infrastructure inspection bots with configurable sensor modules – Modular civic maintenance bots for roads, parks, and sewage systems | – Increases versatility for unpredictable field conditions – Reduces downtime through hot-swappable parts – Optimizes budget by deploying multipurpose robotic units |
Real-World Implementations
NASA & ARMADAS Self-Assembling Voxel Structures
The Automated Reconfigurable Mission Adaptive Digital Assembly Systems (ARMADAS) program pairs inchworm-like builder robots with lightweight cuboctahedral voxel blocks and path-planning algorithms. It enables teams of backpack-sized robots to climb through, pick, place, and bolt voxels into habitat shells, antennas, and other large space infrastructures without human oversight.
- Pilots: ARMADAS is now engineering a small-satellite-class payload that will launch as a flat-pack, unpack itself, and assemble a habitat module and antenna entirely in space.
University of Tokyo & BEATLE Seld-Reconfigurable Aerial Robot
BEATLE is a modular quad-rotor platform whose identical “drone-brick” units autonomously dock and undock while flying. Then share thrust through a contact-wrench controller so the newly merged craft can lift heavier loads or perform torque-hungry jobs such as valve turning and antenna deployment.
- Pilots: Indoor tests presented at ICRA 2024 showed two- and three-module BEATLE rigs completing repeated mid-air merge/undock cycles with stable cooperative hover.
Northwestern University & FireAntV3 Team
FireAntV3 uses full-body to attach anywhere with continuous docks and a three-motor flip gait. So, identical units can crawl over one another, fuse on contact, and free-form self-assemble without alignment, sensors, or lattice constraints. This supports scalable swarm construction in confined or unstructured terrain
- Pilots: Lab trials logged 100 out of 100 successful 5 kg pull tests and validated phototaxis-guided rendezvous, proving the docks’ strength and FireAnt V3’s ability to locate and latch onto neighbors at arbitrary orientations
Spotlighting an Innovator: Envimo
Spanish startup Envimo builds autonomous delivery robots and an urban intelligence platform to support last-mile logistics. Its robots use onboard AI, modular compartments, and sensor-based navigation to operate across cities. Each unit travels up to 50 kilometers and carries payloads of up to 25 kilograms.
The system connects with Envimo’s Urban Insight Platform, which processes delivery data to generate logistics insights for city planners. The startup also reduces delivery costs and emissions while easing traffic congestion.
Further, Envimo supports both businesses and municipalities in adopting cleaner, scalable delivery models.
8. Soft Robotics & Advanced Materials
Soft robotics is enabled by advances in stretchable polymers, self-healing elastomers, magnetic muscle fibers, and liquid-metal printing. This gives machines the flexibility, resilience, and safety of living tissue.
Last year, the global soft robotics market reached USD 1.89 billion and is projected to reach USD 35.33 billion by 2034.
These systems are now powering medical micromanipulators, self-healing mobile bots, and hybrid rigid-soft arms that can “feel” and adapt in real time. Even the magnetic-fiber muscles now exceed the power density of human tissue.
In the field, Amazon’s Vulcan robot, equipped with soft sensory skins, processed over 500 000 warehouse orders in 2025 pilots.
Startups like MMI are also scaling, with a USD 110 million Series C backing soft-actuated microsurgery platforms. Meanwhile, self-healing hydrogel skins, neuromorphic edge chips, and printable electro-fluidic actuators are pushing untethered, damage-tolerant robots into frontline roles.
With safety regulations, ergonomic demands, and labor shortages converging, soft robotics is the human-compatible layer essential to the next-gen autonomous economy.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Soft robotic grippers handling delicate items like electronics or glass – Shape-morphing manipulators for variable object packaging – Flexible exoskeletons to support factory workers in repetitive tasks | – Reduces product damage – Increases handling accuracy for non-rigid goods – Enhances worker ergonomics and reduces fatigue-related errors |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Adaptive gripping bots for irregularly shaped parcels – Soft-material bots co-working safely in human-robot shared zones – Cushion-padded mobile robots for fragile product transit | – Decreases packaging waste due to fewer breakages – Enables closer human-robot collaboration in high-density settings – Supports last-mile automation for sensitive inventory |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Soft wearable robots for mobility rehabilitation – Gentle robotic arms for pediatric or geriatric care – Bio-compatible surgical tools with tissue-safe materials | – Improves patient comfort and safety during physical therapy – Reduces injury risk in clinical interactions – Expands robotic surgery to complex, soft-tissue procedures |
| Construction | – Inflatable or soft-crawling robots for pipeline inspection – Material-adaptive bots navigating unstable terrains – Bio-inspired robotic actuators for painting or surface treatment | – Enhances reach in confined or high-risk areas – Minimizes damage to fragile structural zones – Enables safer inspection of volatile or hazardous environments |
| Governments | – Public-assist robots in crowded spaces using soft skins – Community engagement bots interacting safely with children and the elderly – Soft aerial bots for infrastructure inspection without collision risk | – Increases citizen acceptance through friendly design – Enhances safety in high-footfall areas – Reduces accidental damage |
Real-World Implementations
Tompkins Solutions & Soft Robotics
Tompkins Solutions has teamed up with Soft Robotics to integrate the mGripAI system, soft elastomer fingers paired with 3-D vision and deep-learning perception, into high-throughput tote-picking cells for logistics and e-commerce fulfillment.
- Pilots: Visitors watched mGripAI pick random items from moving totes in a proof-of-concept cell. This validated the soft-grip + AI stack for large-scale warehouse roll-outs at MODEX 2024.
Squishy Robotics – 4-GasPLUS Tensegrity Sensor Robot
Squishy Robotics‘ spherical tensegrity robot houses LEL, O2, CO, and H2S sensors inside a carbon-fiber rod and elastomer-cable lattice. It survives drone drops from up to 1000ft while streaming real-time gas data over long-term evolution (LTE) or mesh links. Making it ideal for hazardous-materials response and confined-space monitoring.
- Pilots:
- San Jose Fire Department: Multiple robots are on contract for hazmat and confined-space calls. Firefighters deploy them by hand toss or UAV to read gas levels before entry.
- TEEX Disaster City tests: At Texas A&M’s 52-acre rubble field, the robot completed autonomous communications and navigation tests. It proves to be reliable telemetry in GPS-denied rescue scenarios and earns a TEEX-Tested report.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Embodied AI
Swiss startup Embodied AI creates multimodal AI systems and soft robotic arms for real-world robotics tasks. It trains in-house Visual Language Action (VLA) models that merge vision, language, and motion to turn human instructions into physical actions.
The startup also produces the Helix Manipulator, a soft arm designed with a patented trimmed helicoid structure. It offers more than nine degrees of actuation, a one-meter reach, and precision to within one centimeter. Its inverse kinematics algorithms handle motion with accuracy.
Further, the manipulator includes SDKs for Python, MATLAB, and ROS2. This supports quick setup within research workflows.
9. Simulation to Real and Real to Sim Training Pipelines
Simulation-to-Real (Sim2Real) and Real-to-Simulation (Real2Sim) pipelines are replacing trial-and-error with data-driven precision. These closed-loop training cycles now enable robots to pretrain skills in photorealistic digital twins.
These training cycles validate them under randomized conditions and refine them through real-world feedback that continuously updates the simulator.
This virtuous cycle is scaling fast as the AI-powered simulation and digital-twin market grow to an estimated USD 81.3 billion in 2034.
Some of the enablers are MIT’s RialTo, which generates digital twins from smartphone scans, and NVIDIA’s Isaac GR00T. That synthesizes motion datasets from minimal input and reduces data needs while boosting policy robustness.
Real-to-sim calibration is also becoming fully automated. Logistics giant Dematic unveiled an AI Control Tower digital-twin platform at GTC 2025, and KION now offers real-time warehouse simulation services.
Moreover, investor interest in synthetic-data tooling is increasing. For instance, DiffuseDrive’s recent USD 3.5 million seed round was to build photorealistic pipelines. Such platforms enable faster iteration, safer fine-tuning, and cost-effective training across the AI stack.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Simulated training for robotic welding and assembly with zero production downtime – Real-world sensor feedback enhancing digital twin accuracy – Domain-randomized learning for task-generalist robots | – Cuts deployment time – Enables safer prototyping of high-risk tasks – Enhances robot performance across diverse workpiece variations |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Virtual warehouse environments to train navigation and picking – Real-to-sim feedback loops to fine-tune robotic behavior – Multi-scenario testing for edge-case handling before live rollout | – Reduces crash and collision rates – Accelerates robot training without interrupting live operations – Improves adaptability to warehouse layout or SKU changes |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Surgical robot training using patient-specific simulations – Diagnostic robots learning from synthetic datasets enhanced with real scans – Continuous fine-tuning of assistive robots based on patient interaction data | – Improves surgical precision and reduces human training cycles – Lowers risk in early-stage trials of medical robotics – Enhances personalization in care delivery systems |
| Construction | – Realistic simulations for robotic excavation, bricklaying, and welding – Simulation-based risk analysis for autonomous equipment | – Reduces error margins in high-stakes tasks – Enables pre-validation of robotic routes and blueprints |
| Governments | – Emergency response bots trained in disaster scenarios using sim-to-real – Smart city bots simulating public interactions before rollout | – Increases preparedness for rare, high-risk public events – Ensures regulatory and social compliance through virtual testing |
Real-World Implementations
RialTo turns a quick smartphone scan into a NeRF-based digital twin, runs reinforcement learning in that twin, and then uploads the trained policy to a real Franka Emika Panda arm, lifting policy robustness by 67% across six household chores (toaster, shelf, drawer, cabinet, mug-rack, plate-rack) in both lab and real-home settings.
- Pilots: On-the-fly twin + RL Cycle: Researchers captured a room with Polycam/NeRFStudio in minutes and fine-tuned policies entirely in sim before zero-shot transfer to the physical arm.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Sim2real
South Korean startup Sim2real offers an AI-powered simulation platform and synthetic data pipelines to support autonomous systems in complex environments. It operates SIM2SAT, a tool that fuses real satellite images, 3D simulations, and labelled data to create geo-specific training datasets.
The startup applies generative models and rendering techniques to simulate scenes for military detection, damage assessment, and climate analysis. Its platform also covers areas up to 10×10 kilometers and provides views from aerial and satellite perspectives with strong visual clarity.
Sim2real further combines real-time data, segmented imagery, and synthetic scenes to train AI models used in defense, mobility, agriculture, and environmental systems.
10. Task-Specialist Service Robots
Task-specialist service robots are dependable frontline workers across hospitality, healthcare, logistics, and retail. From barista arms and hospital couriers to waiter bots and autonomous scrubbers, these narrowly focused machines are now generating revenue.
The global professional service robot market grew to USD 74.39 billion in 2025, with subsegments like cleaning robots growing at 27.1% YoY, and robot waiters tracking a 35% CAGR.
Combined with over-the-air (OTA) software pipelines, 5G/Private-5G coordination, and application-specific hardware bundles, task robots can now be deployed at scale with minimal integration overhead.
Serve Robotics recently closed a USD 80 million Series A round to scale its sidewalk fleets. As safety regulations tighten and service expectations rise, these purpose-built robots are delivering consistent service, measurable ROI, and round-the-clock uptime across sectors.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Welding robots trained exclusively on joint types and metal grades – Polishing or deburring bots specialized for surface finishing – Inspection bots tuned for visual and thermal anomalies | – Increases precision on repetitive tasks – Reduces defect rates in critical assembly lines – Delivers faster ROI due to minimal reprogramming needs |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Labeling and scanning bots for package verification – Tote-handling robots designed for fixed-path retrieval – Autonomous floor-cleaning bots working outside peak hours | – Cuts average processing time per item – Lowers maintenance with simplified design – Optimizes task scheduling with plug-in deployment |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Phlebotomy robots for automated blood collection – Sterilization robots with fixed-path UV-C routines – Pill-dispensing units integrated into hospital workflows | – Reduces human error in critical healthcare operations – Ensures consistent infection control across shifts – Streamlines repetitive clinical tasks to free up medical staff |
| Construction | – Rebar-tying robots deployed for structural consistency – Painting robots trained on specific wall types and surfaces – Floor-measuring bots for layout validation and leveling | – Increases construction speed in repeat tasks – Improves uniformity and finish quality – Decreases human labor in high-fatigue or toxic environments |
| Governments | – License plate recognition and tolling robots – Sidewalk delivery bots with fixed-route constraints – Document-verification bots at service kiosks | – Enhances speed and accuracy of public services – Reduces staffing needs in repetitive administrative roles – Offers scalability for urban services with minimal configuration |
Real-World Implementations
Bear Robotics – Servi Plus Food-Runner
Servi Plus is a tray-toting “server assistant” that shuttles entrees, drinks, and dirty dishes between the kitchen and dining room. Bear Robotics showcased multi-robot Servi Plus workflows at the 2025 National Restaurant Association Show and is scaling commercial fleets nationwide.
- Pilots: Bear targets 10 000 Servi-family units across 44 US states, with deployments already running in dozens of multi-unit chains.
Diligent Robotics – Moxi Hospital Service Robot
Moxi is a mobile manipulator that fetches meds, lab samples, PPE, and supplies, riding elevators and opening doors to lighten nurses’ non-clinical load. The fleet surpassed 1 million autonomous deliveries in early 2025 and now serves a growing network of US hospitals.
- Pilots: Moxi completed its millionth run at a Chicago hospital. Financial Times coverage notes Moxi operating in 30 hospitals nationwide, validating its fetch-and-carry niche at scale.
Knightscope – K5 Autonomous Security Robot
The fifth-generation K5 is a 420-lb wheeled sentry that patrols indoor/outdoor perimeters. It streams 360° video, license-plate reads, and thermal anomalies while auto-recharging between shifts.
- Pilots: The 10th K5 under a master agreement began 24/7 rounds on the gaming floor perimeter that extends Knightscope’s casino fleet.
Spotlighting an Innovator: Rosiwit
Chinese startup Rosiwit manufactures autonomous cleaning robots for industrial, indoor, and outdoor use. It integrates AI with advanced sensors and cloud-based tools to manage robotic operations across varied environments.
Its TITAN 810 handles sweeping and scrubbing using a 340-liter tank system, dual-purpose brushes spinning at 600 RPM, and a 6-in-1 workstation that delivers up to 115 kg of down pressure.
Additionally, for indoor applications, the Skywalker 50 uses LiDAR-based SLAM navigation and smart zone mapping. It charges in one hour and adapts to surfaces like marble and epoxy.
Besides, the Pilot One supports compact, manual operations. It features a swappable battery, cloud connectivity, and a 90-minute runtime in a 20 kg frame.
For outdoor tasks, the X-Rolling robot combines GNSS and multi-lidar fusion to map large spaces with centimeter-level precision. It cleans up to 4000 m² per hour and carries 100 liters of waste while avoiding obstacles in all directions.
Lastly, all units connect to the Rosiwit 365 platform for centralized control, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance.
11. Micro & Nano Robotics
Micro-robots (millimeter to sub-millimeter) and nano-robots (sub-micron) exploit magnetic, acoustic, chemical, or light-driven actuation to navigate fluidic or porous environments that are inaccessible to conventional machines.
Operating at cellular and sub-cellular levels, these robots enable minimally invasive procedures, targeted drug delivery, and access to previously unreachable areas.
The market is gathering speed for the values of the global nanorobots segment as it is projected to reach USD 20.4 billion by 2030 (15% CAGR).
Some of the notable venture rounds included Theranautilus raising USD 1.2 million in seed capital for medical nano-robotics, and Khosla/Upfront’s USD 20 million investment in nanorobot brain-drug delivery by Bionaut Labs.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Micro-robots for assembling MEMS and nanoelectronic devices – Nanoscale robots for defect detection in semiconductor wafers – Atomic-level bots for surface coating and material etching | – Enables sub-micron level manufacturing precision – Reduces defect rates in chip fabrication – Supports next-gen product miniaturization without yield loss |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Embedded micro-sensors in packages for condition monitoring – Nano-tagging for real-time supply chain tracking – Microfluidic bots for sorting micro-components or sensitive goods | – Enhances traceability and anti-counterfeiting in high-value goods – Reduces spoilage and loss through in-package monitoring – Improves inventory accuracy in microscale product categories |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Nano-robots for targeted drug delivery to cancer cells – Micro-swimmers for navigating blood vessels for diagnostics – Cell-repair bots for tissue regeneration and gene delivery | – Minimizes side effects through pinpoint drug action – Speeds up diagnosis and monitoring at cellular resolution – Unlocks regenerative therapies without invasive procedures |
| Construction | – Microbots inspecting concrete integrity and internal pipe structures – Nano-sensors embedded in smart materials for real-time feedback – Robotic dust detection in clean construction environments | – Improves long-term structural health monitoring – Reduces the need for destructive testing methods – Enables predictive maintenance in embedded systems |
| Governments | – Airborne nano-bots for pollution mapping and air quality analysis – Nano-scale surveillance units for disaster zones or sensitive missions – Microbots for hazardous material cleanup in public spaces | – Enhances environmental governance with real-time data – Increases safety in chemical or radioactive exposure scenarios – Enables stealth and precision in high-risk government operations |
Real-World Implementations
Bionaut Labs – Magnetically Steered Brain Micro-Robots
Bionaut’s sub-millimeter “Bionauts” are guided through cerebral spinal fluid by external magnetic fields. It pierces the membrane of Dandy-Walker or arachnoid cysts and releases drugs directly at the target.
- Pilots: Bionaut Labs raises an extension round in preparation for micro-robot clinical trials, starting Q3 2025 at the Mayo Clinic and UCLA.
Microbot Medical – LIBERTY Endovascular System
Disposable, joystick-controlled micro-catheter robot operating on a tabletop console outside the radiation zone.
- Pilots: First-in-human peripheral vascular intervention completed, now pivotal study enrolling up to 50% of the patients ahead in its pivotal human clinical trial.
ETH Zurich – Micro-Bubble Drug-Delivery Jets
ETH’s micro-bubble platform uses low-pressure (100 kPa) ultrasound to cyclically deform sub-10 µm gas bubbles, creating liquid jets that pierce cell membranes at 200 km/h. It enables pinpoint, needle-free drug delivery across barriers such as the blood–brain interface.
- Pilots: In-vitro / ex-vivo study visualised jet-mediated uptake that paves the way for ocular and oncology therapies.
Spotlighting an Innovator: NanoCube Health
Australian startup NanoCube Health manufactures AI-powered nanorobotic devices for early detection, targeted treatment, and real-time monitoring of pancreatic cancer. It develops nanoscale systems with autonomous navigation and programmable electrostimulation to identify cancer cells at a cellular level.
Moreover, the device uses soft bioelectronics and imaging tools to gather diagnostic data wirelessly. This removes the need for invasive biopsy procedures. After detection, it delivers anti-cancer agents, both standard and novel, directly to malignant cells. This increases treatment accuracy while lowering side effects.
NanoCube Health also enables real-time monitoring and enables clinicians to track responses and adjust care as needed.
12. Sustainable & Green Robotics
Vendors began opening carbon-neutral robot factories, investors funnelled capital into AI-powered recycling platforms, for instance, Glacier raised USD 16 million, and the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) named sustainability and energy efficiency.
Yamaha Motor‘s Hamamatsu plant achieved Scope 1 & 2 carbon neutrality using on-site renewables and certified offsets. ABB and AUAR launched a climate-neutral micro-factory project in Belgium.
A Franco-Ukrainian team recently debuted the world’s first fully 3D-printed off-road robot made entirely from recycled plastic. Jetson-class edge AI modules enabled 24/7 mobile robots to run transformer models under 30 watts.
The Swiss Battery Technology Center’s LAMBDA project deployed cobots for safe dismantling. FANUC’s ROBOSHOT servo systems reduced electricity use by up to 70% versus hydraulic systems.
These efforts are more than ecological. Recycling robots can sort up to 80 items per minute and reduce contamination. Moreover, as ESG audits, UN SDG alignment, and eco-regulatory pressure shape purchasing and investment decisions, green robotics is emerging as a core driver of climate resilience.
Strategic Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Use Cases | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | – Energy-efficient cobots with low power consumption – Robots built using recyclable or biodegradable materials – Lifecycle-optimized bots with modular components for reuse | – Reduces operational energy costs – Lowers e-waste footprint through end-of-life recyclability – Supports compliance with green manufacturing standards |
| Logistics & Warehousing | – Solar-charged autonomous robots for yard logistics – Fleet optimization software reduces unnecessary robot idling – Recyclable packaging handled by green-certified robots | – Cuts warehouse energy use and carbon emissions – Minimizes power consumption during non-peak operations – Supports sustainability certifications for logistics providers |
| Healthcare & Pharma | – Battery-optimized service robots with eco-conscious design – Robots sterilized using UV-C instead of chemical disinfectants – Smart hospital logistics minimize single-use waste | – Reduces chemical use and energy footprint in hospitals – Enhances green building compliance in medical facilities – Supports circular healthcare supply chains |
| Construction | – Autonomous electric machines replacing diesel-powered ones – Robots for selective deconstruction and material recovery – On-site 3D printing using recycled materials | – Cuts carbon emissions from heavy construction equipment – Increases recycling rates in demolition processes – Promotes sustainable architecture with low-waste methods |
| Governments | – Municipal cleaning robots using water-saving technologies – Waste-sorting robots for recycling optimization – Green drones for environmental surveillance and land monitoring | – Enables smart, resource-conscious urban services – Increases recycling throughput and purity – Enhances policy enforcement with real-time environmental data |
Real-World Implementations
Aerones & GE Vernova – Robotic Wind-Turbine Service
These robotic climbers scale high towers to clean, repair, and coat blades, trimming rope-access hours and downtime while delivering up to a 12% annual-energy-production lift after leading-edge repair.
- Pilots: Aerones’ new Texas operations center now dispatches robot crews to GE Vernova wind farms across the state. Leading-edge pilots show triple-speed repair cycles and ten-fold idle-time cuts versus rope teams. Aerones secured USD 62 million.
EDP Renewables & BladeBUG – Magnetic Blade Inspection Crawlers
BladeBUG’s six-legged robot adheres to turbine blades and performs contact phased-array ultrasonic and lightning-protection tests without rope crews or nacelle cranes.
- Pilots: A two-day campaign on Vestas turbines verified on-blade phased-array NDT for EDP Renewables’ Parque Sierra el Boquerón site.
EcoRobotix – ARA Plant by Plant Precision Sprayers
ARA’s AI camera array targets individual weeds with 6×6 cm micro-bursts. It reduced herbicide use and drift by 60-95% compared with broadcast spraying.
- Pilots: Bean, corn, and soy plots recorded 70% average chemical savings while preserving yields.
Spotlighting an Innovator: IC GREEN
French startup IC GREEN builds autonomous robots for natural turf maintenance, with a focus on precision weeding through the Sportee C-Series platform. It uses sensor-guided navigation and AI-powered weed recognition to detect and remove turf weeds like clover, dandelion, plantain, and crabgrass.
The robot has a modular design that supports remote diagnostics and simple component swaps. This setup keeps maintenance straightforward and minimizes downtime. It also uses durable parts that hold up in tough outdoor conditions, including rain and saline soil.
ICGREEN’s Sportee C-Series supports sustainable turf care by removing the need for herbicides, cutting labor and energy use. Further, IC GREEN operates across parks, golf courses, and sports fields.
Explore the Latest Robotics Trends & Startups
With thousands of emerging robotic technologies and startups, navigating the right investment and partnership opportunities that bring returns quickly is challenging.
With access to over 7 million emerging companies and 20K+ technologies & trends globally, our AI and Big Data-powered Discovery Platform equips you with the actionable insights you need to stay ahead of the curve in your market.
Leverage this powerful tool to spot the next big thing before it goes mainstream. Stay relevant, resilient, and ready for what is next.

![Future of Robotics: 12 Trends Powering the Next Wave [2025-2030]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Future-of-Robotics-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)







