Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary: What are the Top 10 Shipbuilding Trends in 2026 & Beyond?
The global shipbuilding industry is undergoing a transformative phase driven by digitalization, sustainability mandates, and advanced manufacturing technologies. Key trends shaping its future include:
- AI Integration – Chinese yards secured 74% of global tonnage in 2024, pressuring rivals to adopt AI to meet tight deadlines. Predictive analytics and location intelligence tools reduce risks to enhance traffic control, and deliver cost savings. Orca-equipped vessels cut close encounters by 54% and saved USD 100 000 in fuel annually.
- Smart Shipyards & Digital Transformation – Shipyards are implementing digital twins, 5G edge networks, and IIoT platforms to address labor shortages and improve productivity. Over 72% report higher efficiency post-digital twin adoption. AR inspections, drone hull scans, and SaaS platforms now standardize design and maintenance processes.
- Advanced Materials – The marine advanced materials market is forecast to hit USD 20.18 billion by 2030. Composites like carbon fiber and aluminum reduce ship weight and fuel usage. Innovations such as recyclable thermoplastics and nanocoatings extend vessel lifespans and promote circularity.
- Advanced Robotics & Automation – Automated welding, painting, and AGVs streamline production while reducing injuries. Robotics also enables 3D printing of structural components to enhance speed and precision. Asia-Pacific, led by China, dominates with 80% of global capacity.
- Autonomous Vessels and Smart Navigation – The autonomous vessels market is projected to reach USD 19.17 billion by 2032. AI navigation systems reduce accidents and fuel use. Multi-sensor stacks, edge AI, and remote command centers support deep-sea operations. Ongoing MASS trials and regulatory progress enable real-world deployment.
- Alternative Fuels and Green Shipbuilding – The green methanol ship market is projected to reach USD 15.25 billion by 2030. Methanol, ammonia, and electric propulsion are gaining traction. Over 10 360 ships already use energy-saving devices, and 37 are testing carbon-capture systems.
- Modular Ship Design and Constructions – Modular design enhances flexibility and scalability in ship production. Shipbuilders deliver mission-specific modules for faster assembly and reduced dock time. India’s L&T Shipbuilding is investing INR 1000 crore to improve modular capacity.
- Immersive Technologies – The AR/VR digital shipyard market will hit USD 1.7 billion by 2030, growing at 21.9% CAGR. Digital twins and VR simulations reduce design errors and training risks. AR overlays guide real-time maintenance, inspections, and remote collaboration.
- Cybersecurity Innovations – With 1998 vessels monitored and 39 billion firewall events logged every six months, maritime cybersecurity is essential. The market is expected to reach USD 40.62 billion by 2030. Regulatory mandates like IACS UR E26/E27 and IMO resolutions are driving the adoption of AI-based threat detection, asset mapping, and secure update systems.
- 3D Printing Integration – On-demand additive manufacturing slashes component lead times by 95%. The 3D printing market will reach USD 35.79 billion by 2030, enabling rapid production of mission-critical parts. Wire-arc, continuous fiber, and recyclable polymer technologies allow for custom, durable parts.
Read on to explore each trend in depth – uncover key drivers, current market stats, cutting-edge innovations, and leading shipbuilding innovators shaping the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the trends in the shipbuilding industry?
The shipbuilding industry is trending toward digital transformation, including smart shipyards, IoT, and AI. It is also focusing on green technologies such as LNG, ammonia, and hydrogen fuels, along with modular construction, robotics, and autonomous vessels.
2. What is the forecast for shipbuilding?
The global shipbuilding market is projected to reach USD 203.14 billion by 2030, at a 3.6% CAGR. Trade expansion, defense modernization, and green shipping initiatives drive this growth.
Methodology: How We Created the Shipbuilding Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 5M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the shipbuilding industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the shipbuilding innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Shipbuilding Industry Trends & 20 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Shipbuilding Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 1600+ global startups & scaleups. The Shipbuilding Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the shipbuilding industry trends & startups that impact your company.

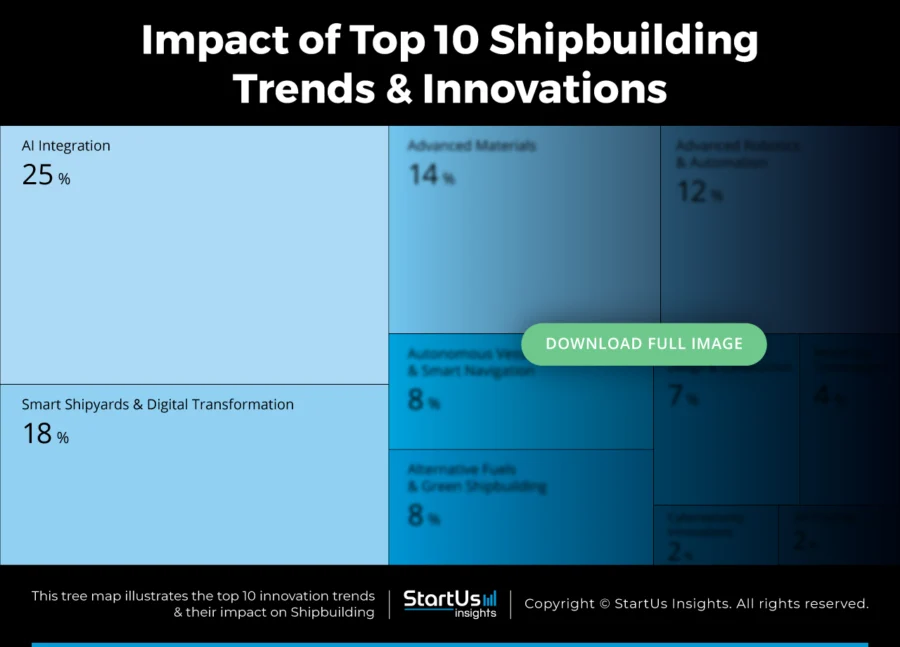
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Shipbuilding Trends
Shipbuilding is shifting as digital and sustainable technologies reshape traditional practices. AI improves hull design, fuel usage, and maintenance forecasting. At the same time, smart shipyards apply digital twins and data analytics to increase visibility and enhance production accuracy.
Robotics and automation simplify welding, assembly, and inspection tasks. Meanwhile, 3D printing supports the on-demand manufacturing of ship components. Besides, modular ship design shortens build times and enables customization. In parallel, AR and VR strengthen workforce training and virtual prototyping.
To meet climate targets, shipbuilders are adopting alternative fuels and green construction methods. Autonomous vessels with intelligent navigation systems improve safety and operational efficiency. In response to rising connectivity, cybersecurity measures are also becoming integral to maritime operations.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 1600+ Shipbuilding Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 1600+ exemplary startups and scaleups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and the United States, followed by India. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Top 10 Emerging Shipbuilding Trends [2026 and Beyond]
1. AI Integration: Chinese Shipyards Secured 74% of Global Tonnage in 2024
Designing a ship is becoming more powerful with the ability to consider more parametric data, such as wind, weather, ocean currents, and others. However, this increased data complexity also escalates processing time.
To address this, the shipbuilding industry is integrating AI for design and process optimization. Incorporating AI-based predictive analytics in ports and shipyards allows for to management of the growing volume of ship traffic.
Further, labor shortages and surging order books are driving AI adoption within the industry. Chinese yards booked 74% of all global tonnage in the last year. It is pressuring rivals to implement AI to stay on schedule.
Further, the integration of AI in shipbuilding not only streamlines the construction process but also ensures the production of smarter, safer, and more environmentally friendly ships.
For instance, AI-based optimisation on Orca-equipped vessels cut close-encounter events by 54% and saved USD 100 000 fuel annually. Besides, they avoided 195 000 t CO₂ in 2024.
Further, Windward combines data sources with machine learning and proprietary behavioral analytics to assign distinct identities to maritime entities. As a result, it produces a unified and spoof-resistant view of maritime risk.
xyzt.ai develops a Location Intelligence Platform
Belgium-based startup xyzt.ai provides a no-code big data location intelligence platform to analyze large volumes of shipping data. Its machine learning (ML)-based platform’s spatio-temporal business intelligence solution uses AIS data, IoT sensor data, and ocean wave data to provide vessel builders and operators with analytical insights.
Additionally, its maritime analytics software also visualizes and analyzes spatio-temporal data to monitor the status of vessels, including the location, velocity, and other operational metrics of their vessel or fleet. Hence, through xyzt.ai’s software, maritime engineers are able to optimize vessels based on maintenance, lifespan, operating conditions, and more.
Chartera builds Ship Chartering & Operating AI Assistant
Singaporean startup Chartera develops an AI-driven platform that simplifies ship chartering and operations. It analyzes real-time data, automates workflows, and connects with existing systems.
The platform processes industry data to guide freight decisions, manage costs, and refine vessel selection. It fits into operational workflows and links with communication tools to improve decision-making.
It learns from past chartering activity and provides recommendations that match operational goals. Chartera allows maritime teams to monitor fleet performance with live insights for improving oversight and response times.
2. Smart Shipyards & Digital Transformation: Digital Shipyard Market to Reach USD 12.89 B by 2033
Shipyards face skill shortages due to an aging workforce and reduced interest in trade roles. To address this, they increasingly rely on automation and digital tools.
These technologies aid in reducing manual labor. As shipyards adopt cyber-physical systems, 5G edge networks, and digital twins, they accelerate the design-to-delivery process and ease staffing constraints.
In 2025, the global digital shipyard market is valued at USD 3.19 billion. It is expected to grow to USD 12.89 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 19.1%.
Digital transformation is gaining traction across the industry. About 68% of shipbuilders have adopted these strategies to improve operational efficiency, while 72% report higher productivity after implementing digital twin technology.
IoT sensors are now widely used for real-time component monitoring, with 54% of shipbuilders investing in them. Meanwhile, 60% of new ship designs incorporate digital modeling and simulation.
Moreover, tools are reshaping routine operations. AR-assisted inspections, wearable location trackers, and drone-based hull scans are becoming standard in many shipyards.
For instance, ST Engineering launched Singapore’s Gul Yard. The facility uses predictive analytics and AR-enabled safety gear and serves as a reference for smart yard development.
Moreover, integrated digital platforms also play a key role. By combining ERP, PLM, and IoT data, shipyards are able to manage projects more efficiently and streamline supply chains.
Naval Architect develops a Cloud-based Ship Designing Platform
Naval Architect is a German startup that builds a cloud-based platform to design ships using digital twin technology. It performs feasibility studies, creates 2D and 3D visualizations, and allows effective collaboration across departments. Additionally, it contains analytical tools to keep track of projects and also reliably estimate weight, time, cost, and more.
Moreover, designers use the software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform to create digital ship models with geometrical and non-geometrical information in one unified place. Hence, using Naval Architect’s solution, shipbuilders are able to create 3D digital ship models throughout the ship’s lifecycle.
SOL-X provides Worker Safety Wearables
Singapore-based startup SOL-X specializes in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to improve safety, compliance, and worker well-being on ships. Its solution SAFEVUE.ai manages risk and enhances existing industrial workers’ safety systems by using IIoT and AI to improve visibility and situational awareness for workers across hazardous operations.
Also, its SAFEVUE.ai Crew Protect is a connected wearable device that contains geofencing of hazardous work zones and offers real-time assistance in urgent situations. As a result, SOL-X’s solutions find applications in the maritime, oil & gas industries, and in other hazardous environments.
3. Advanced Materials: Marine Market to Reach USD 20.18B by 2030
In shipbuilding, the use of materials like carbon composites and aluminum leads to cost reduction and superior structural properties. These composite materials aid ships reducing maintenance downtime due to their high corrosion resistance. Smart materials further enhance shipping economics by lowering fuel costs and increasing cargo capacity through reduced structural weight.
The sector focuses on composites that deliver dramatic weight reductions while maintaining structural integrity under extreme marine conditions. The marine composites market is projected to reach USD 13.68 billion by 2037, at a CAGR of 6.6%. The integration of advanced composites enables better corrosion resistance and demonstrates durability in saltwater environments.
3M is partnering with Gurit for marine applications utilizing 3M Matrix Resin technology. This proprietary resin produces stronger, lighter, and more durable composites. Gurit’s SP-High Modulus marine business incorporates this technology into composites used in performance boats.
Additionally, Eastern Shipbuilding Group signed a partnership with Bayou Metal Supply to provide aluminum materials and fabrication services for the US Coast Guard Offshore Patrol Cutter program.
Further, carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) dominate the high-performance segment. However, their adoption remains constrained by cost considerations, with carbon fiber pricing around USD 20-30 per kilogram compared to cheaper glass fiber alternatives.
Moreover, the marine advanced materials market is projected to reach USD 20.18 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2024 to 2030.
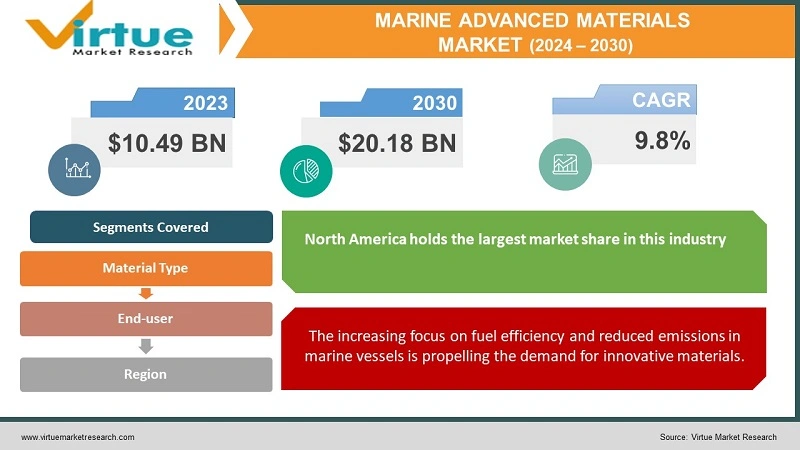
Credit: Virtue Market Research
Northern Lights Composites offers Glass-fiber Reinforced Plastic
Northern Light Composites is an Italian startup that creates sustainable plastic materials to build ships. Its proprietary technology rComposite is a composite based on a thermoplastic matrix of natural or mineral fibers and an Atlas HPE recyclable core. Additionally, its material is made from natural fibers and eco-sustainable flax fibers and resins that are biologically decomposable.
It also uses Basaltex fibers for structural components that cannot be realized with vacuum infusion processing. This way, Northern Lights Composites’ material reduces environmental pollution from abandoned fiberglass boats while promoting a circular economy.
Armus Marine improves Vessel Performance with Coating
US startup Armus Marine offers Hull Pro, a clear protective coating for gelcoat and metal surfaces. Hull Pro uses a nano-epoxy formula to create a durable barrier against scratches, chips, and UV damage. This silicone epoxy system reduces drag to improve vessel speed and fuel efficiency.
By preventing blistering and minor damage, Hull Pro reduces the need for costly gelcoat repairs. It extends the lifespan of boats and preserves their resale value. Armus Marine provides boat owners with a solution for maintaining and enhancing their vessels’ performance and appearance.
4. Advanced Robotics & Automation: Shipbuilding Robotics Market to Reach USD 25.2 B by 2032
In the shipbuilding industry, the use of advanced robotics is on the rise. This trend is driven by the need to automate construction tasks, given the high skill level and labor intensity involved. With the increasing size of ships, the workforce is often faced with long hours and demanding tasks such as welding, cutting, and painting.
Welding automation with robotic systems ensures consistent, high-quality welds while reducing human error and improving production speed. For instance, HD Hyundai is partnering with Persona AI and NEURA Robotics to develop humanoid robots capable of precision welding.
Besides, surface preparation and painting robots ensure uniform application in the coating process while minimizing worker exposure to toxic fumes.
Moreover, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms are used in material handling and assembly applications to simplify component transport and assembly processes.
Saronic Technologies completed a landmark USD 600 million Series C funding round this year to build Port Alpha, a shipyard for autonomous vessel production.
To meet tight deadlines for launching large vessels, robotic systems are employed. These systems not only mitigate the risk of injury but also enhance the efficiency of the shipbuilding process. Furthermore, robotics finds its application in ship maintenance and repair, leading to quicker turnaround times and elevated safety standards.
The robotics in the shipbuilding market is expected to grow to USD 25.2 billion by 2032. It will have a CAGR of around 17.49% from 2024 to 2032.
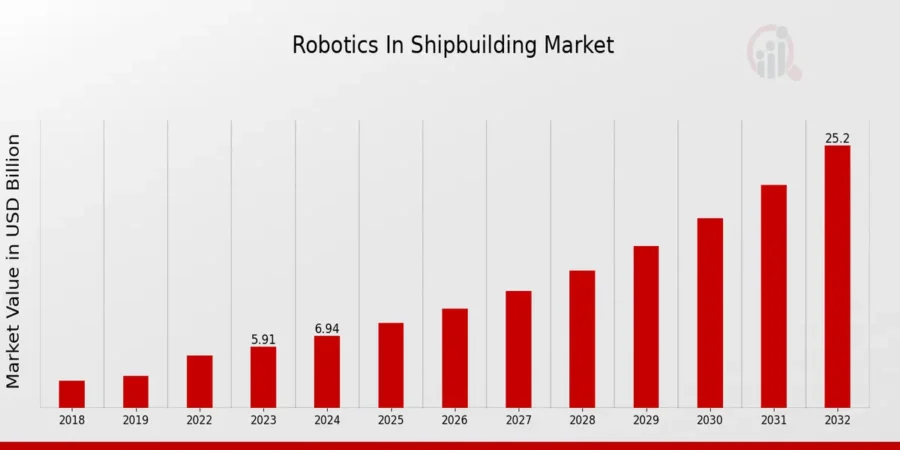
Credit: Market Research Future
Asia-Pacific dominates the advanced robotics shipbuilding market. It accounts for approximately 80% of global shipbuilding capacity. China alone represents 40% of global shipbuilding output, while South Korea and Japan remain major centers of innovation and production,
Adaxis advances Flexible Robotic 3D Printing
Adaxis is a French startup that builds a software platform to turn robots into 3D printers. Its AdaOne software features customizable robot programs and multi-axis path planning. It also generates and optimizes tool orientation based on part geometry.
Additionally, it has collision detection capabilities and optimizes part printing by defining zones with custom path planning settings. Moreover, the software integrates with existing robotic infrastructure to turn them into 3D printers.
This way, Adaxis enables shipbuilders to use 6-axis robots for building the structural components, improving production speed and material use.
IMB Robotics creates Surface Preparation Robots
IMB Robotics is a Turkish startup that manufactures a range of robots to inspect and treat the surfaces of ships. Its ROBOJET is a surface preparation crawler that attaches to ships’ hulls using magnets. It also features a vacuum system to suction off the removed waste material and wastewater.
Besides this, the robot is remotely operable and uses a closed system to collect hazardous contaminants. The robot also functions semi-autonomously with high maneuverability from its two individual electrical drives. IMB Robotics, thus, cleans steel surfaces on ships, reducing the effort in frequent cleaning operations while reducing human exposure to potentially hazardous contaminants.
5. Autonomous Vessels and Smart Navigation: Market to Hit USD 19.17 B at 13.1% CAGR
Maritime autonomy has progressed from coastal trials to commercial deep-sea operations. This shift responds to crew shortages, accident-related costs, and growing pressure to cut emissions.
AI-powered route optimization on autonomous ships often lowers fuel consumption during sea trials. As adoption grows, technical stacks continue to expand. They include sensor fusion using radar, LiDAR, and EO/IR cameras.
Besides, it includes edge AI systems-on-chip with millisecond-level inference, satellite and 5G mesh links with failover support, and remote control centers modeled after UAV command facilities.
For instance, Sea Machines introduced its AI-Ris computer vision sensor. Integrated with its SM300 system, AI-Ris enables real-time object detection and enhances situational awareness during autonomous navigation.
These systems operate under emerging IMO Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS) regulatory frameworks. In June, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA), NYK, and MTI launched a workshop in Singapore to begin new MASS trials. The initiative aims to accelerate decarbonization, enhance digital capabilities, and support workforce development.
Moreover, the global autonomous vessels market stands at USD 8.10 billion in 2025. By 2032, it could grow to USD 19.17 billion, reflecting a 13.1% CAGR.
Clearbot builds Self-Driving Boats
Chinese startup Clearbot offers AI-powered intelligent tools to automate marine services. Its autonomous self-driving boat has a payload capacity of 200 kg. It collects up to 15 L of oil and autonomously cleans treatment plants using foam.
Furthermore, the electric-powered beat creates no emissions and also generates accurate data reports to track environmental sustainability goal (ESG) metrics. Clearbot’s AI-based solution, thus, improves hazardous environment cleanups while simultaneously reducing labor and fuel costs.
Eight Knot enables Automated Ship Navigation
Japanese startup Eight Knot builds autonomous navigation systems for ships using AI, robotics, and proprietary sensors. It integrates ship control, embedded software, cloud computing, and real-time state estimation to support automated maritime operations.
The system calculates a vessel’s position and orientation in dynamic conditions by processing data from GNSS, QZSS, and IMU sensors. It also identifies nearby ships and obstacles using LiDAR and image recognition.
It generates routes and real-time avoidance maneuvers using AI that encodes navigational expertise. Additionally, the startup develops predictive motion models for different vessel types to ensure accurate control in varied sea states without relying on observational tools.
Further, Eight Knot offers cloud-based remote monitoring and data visualization to improve visibility and oversight. Its integrated stack of hardware and software allows tackling operational challenges and promotes autonomous transport across maritime sectors.

6. Alternative Fuels and Green Shipbuilding: 10 360 Ships Use Energy-Saving Devices
Maritime transportation, a dominant force in global trade, comes with a downside – environmental pollution. 2023 IMO GHG Strategy obliges the sector to reach net-zero by or around 2050, with at least 5% – 10% of all marine energy from zero/near-zero fuels by 2030.
The green methanol ships market is estimated to be USD 4.29 billion in 2025 and will reach USD 15.25 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 28.9%. It will grow to USD 30.98 billion by 2035 with a CAGR of 12.2% from 2031 to 2035, averaging a CAGR of 21.9% from 2025 to 2035.
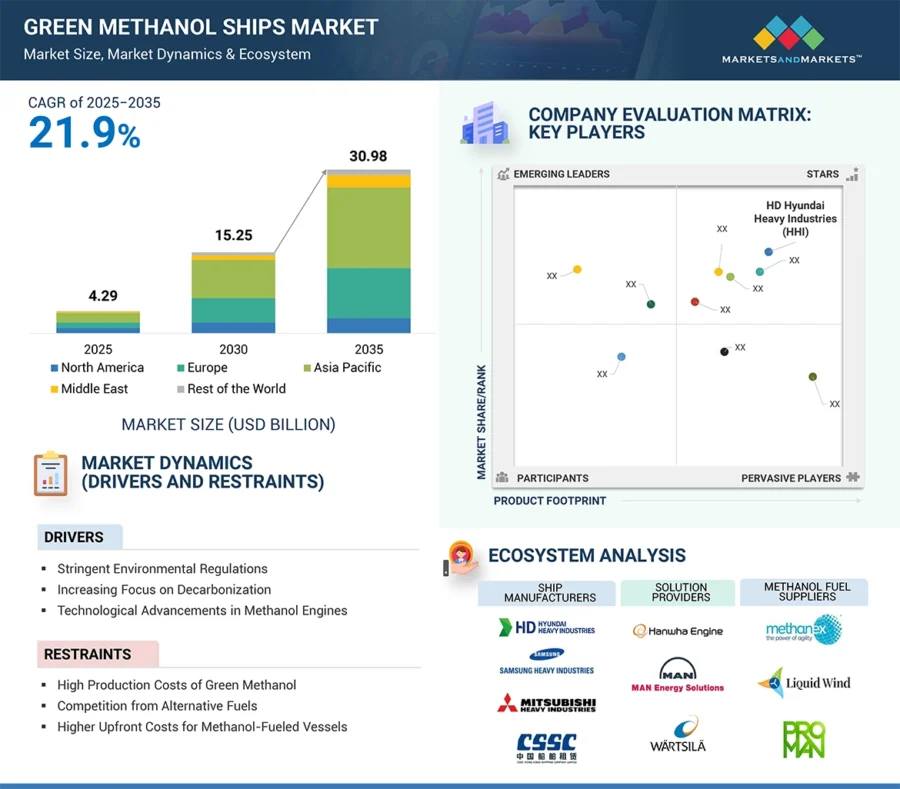
Credit: Markets and Markets
Further, Lloyd’s Register reports 600 new alternative-fuelled vessel orders in the last year. This marks a 50% increase from the previous year.
Methanol currently leads adoption. The global fleet includes methanol-powered vessels along with hydrogen-powered ships. Methanol offers a higher volumetric energy density and remains stable as a liquid at room temperature. As a result, operators integrate it into existing bunkering systems more easily.
Maersk enters a long-term bio-methanol offtake agreement with LONGi Green Energy Technology. The agreement will contribute to lowering GHG emissions from Maersk’s growing fleet of dual-fuel methanol container vessels.
In response to increasing environmental regulations, shipbuilders are turning to sustainable materials and software to improve the fuel efficiency of ship engines. Advanced hull designs and propeller optimizations are being employed to enhance energy efficiency in these green ships, resulting in reduced fuel consumption.
As per Clarksons Research, 10 360 ships have energy-saving devices such as rotors or air-lubrication. Besides, 37 are already testing onboard carbon-capture units.
Amogy develops Carbon-Free Ammonia Fuel
US-based startup Amogy provides emission-free, high-energy-density power fuel to decarbonize ocean transportation. Its energy system uses ammonia as a renewable fuel which has a higher energy density than traditional lithium battery-based systems.
Moreover, its ammonia fuel is less complex, lower in cost, and needs less storage space than liquid hydrogen and liquefied natural gas (LNG). Amogy furthers sustainability by using existing ammonia production and distribution infrastructure from the agriculture industry to decarbonize ship propulsion.
Also, Amogy secures USD 56 million to commercialize its ammonia-to-power solutions.
Fleetzero develops Electric Container Ships
US-based startup Fleetzero designs zero-emission electric container ships, emphasizing sustainability in ocean freight. Its vessel, Pacific Joule, operates entirely on electricity, which significantly reduces the emission of greenhouse gases and particulates.
Further, the startup’s battery technology ensures these ships cover vast ocean distances and recharge swiftly through battery swapping.
7. Modular Ship Design and Construction: L&T to Invest INR 1000 Crore in Modular Fabrication
Modular ship design has shifted from a niche efficiency strategy to a flexible framework for building configurable vessels. It uses standardized components that are swapped to change ship functions over time.
This method moves major fabrication tasks from constrained shipboard spaces into controlled workshops. Shipyards build modules such as engine casings, accommodation blocks, and bridge units simultaneously, which speeds up production and reduces costs.
Technology is now pushing modularity toward true plug-and-play systems. For example, CUBEDIN, a Danish joint venture between Systematic and Odense Maritime Technology, created interchangeable Cube modules. These allow ships to switch roles from patrol to mine countermeasures or cargo transport by replacing mission-specific payloads. Parallel design timelines also enable hulls and modules to evolve together.
Further, global partnerships are scaling modular construction. HD Hyundai and Edison Chouest Offshore plan to co-build container ships at ECO’s US shipyard by 2028, using Korean modular methods and automation tools like robotic welding.
In India, L&T Shipbuilding plans to invest INR 1000 crore to expand its modular fabrication capacity. It aims to handle 50 000 tonnes and deliver up to 25 vessels per year.
Meanwhile, the modular container market continues to grow. It is projected to reach USD 52.05 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 7.8% from 2024 onward.
Veer makes a Modular Container Ship
The Bahamas-based startup Veer builds zero-emission cargo vessels that use clean propulsion and comply with the United Nations International Maritime Organization’s shipping standards. Its model, Design Nº1, is a modular container ship built for long-distance, fast travel. It runs on wind propulsion and green hydrogen and covers up to 10 000 nautical miles per trip.
The ship uses carbon fibre masts with embedded pressure-sensing fibre-optic cables to enhance stability and reduce weight. It also works with the current port infrastructure. Design Nº1 carries up to 152 TEUs, including refrigerated containers. It sails at 18 knots without releasing carbon emissions.
Further, a streamlined steel hull enables replication and scaling. Veer focuses on clean propulsion, modular structure, and global compliance to offer freight operators and charterers a path to low-impact maritime logistics.
ETA Shipping builds Modular Electric Cargo Vessels
Dutch startup ETA Shipping designs modular electric cargo vessels to lower energy use and support autonomous operations. Instead of a traditional main engine, each vessel uses an electric motor powered by three diesel generators. These are swapped out for ammonia or methanol-based systems.
The design supports plug-in energy containers such as hydrogen units or compact fuel cells. This enables emission-free or low-emission sailing and port operations.
Modular components improve adaptability and simplify maintenance. Meanwhile, autonomous systems manage hatches, ballast, and onboard surveillance.
Further, the cargo layout increases revenue potential. It uses a box-shaped hold with an open top, tween deck option, and movable bulkheads. ETA Shipping offers flexible solutions for short-sea shipping and fleet renewal.
8. Immersive Technologies: AR/VR Digital Shipyard Market to Reach USD 1.7 B by 2030
In the complex process of ship design, startups are turning to Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). These immersive technologies allow the creation of 3D virtual models of designs and user avatars. Engineers use these models to conduct ergonomics reviews, reachability studies, and maintenance operations.
Digital twins enable shipbuilders to create photorealistic models of entire vessels. It allows engineers to identify and resolve design issues before physical construction begins. For instance, Seaspan Shipyards develops HoloShip facility, an immersive visualization system that enables teams to experience detailed 3D ship models.
Further, VR enables crews to gain hands-on experience in safe environments. They get to practice emergency procedures and complex operations without the risks associated with real-world training. Varjo partners with FORCE Technology to deliver maritime training solutions.
Moreover, AR systems overlay digital information onto physical environments, which allows technicians to visualize hidden systems, access real-time maintenance data, and receive step-by-step instructions directly in their field of vision. For instance, Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems implemented AR to eliminate the need for 2D drawing sheets in submarine construction and enable drawing-free production processes.
AR and VR also enable real-time collaboration between design offices and shipyards. This allows immediate review and approval of design changes. ABS and Crowley have pioneered the use of AR for remote classification surveys, where surveyors conduct inspections using goggle technology that provides real-time visuals to shore-based experts.
Besides, the global AR/VR digital shipyard market is projected to reach USD 1.7 billion by 2030. From 2025 to 2030, analysts expect it to grow at a CAGR of 21.9%.
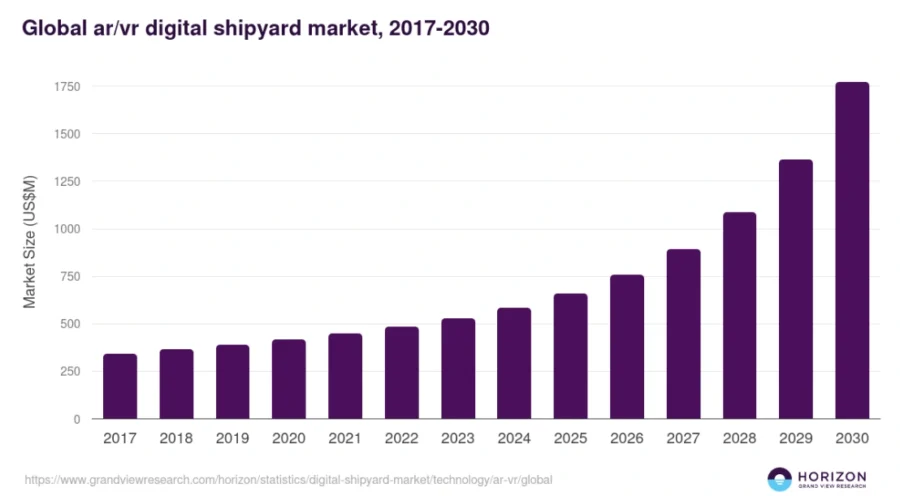
Credit: Grand View Research
Alphaabets Digital Labs develops Digital Twin Technology for Shipbuilders
Indian startup Alphaabets Digital Labs leverages 3D technologies to revolutionize shipbuilding, offering innovative solutions to industry challenges. For example, extended product development cycles or a lack of digital collaboration between shipyards and suppliers. By employing ‘3D Engineering Twins’ and advanced simulations, the startup identifies and rectifies design flaws, leading to substantial cost and time savings.
Apart from digital twins, other applications of Alphaabets’ solutions include enhanced collaborative shipbuilding design, digital manufacturing integration, and 3D mock-ups for shipyards and machinery, among others.
Exxar Cloud develops Extended Reality (XR)-powered CAD
Exxar Cloud is a US-based startup that develops no-code VR and AR software for design collaboration. Its solution lets ship designers and builders conduct design reviews in VR and monitor production and inspections with AR.
The solution also connects a variety of 3D CAD applications like Aveva, SOLIDWORKS, Navisworks, Catia, Creo, Solid Edge, and Siemens NX to stream lossless 3D CAD data into Exxar’s Reality Visualization engine. Moreover, this solution reduces delays in shipbuilding by eliminating rework and improving project efficiency, thus, leading to better client satisfaction.
9. Cybersecurity Innovations: Maritime Security Market to Reach USD 40.62 B by 2030
Modern ships employ a variety of IoT sensors for tasks such as navigation, inventory management, and equipment monitoring. As the size of the ship increases, the role of these sensors becomes more critical.
However, an increase in the number of connected sensors also escalates the potential for cyber vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities could lead to voyage delays, information loss, or even equipment damage.
IMO Resolution MSC.428(98) made cyber-risk part of every Safety Management System from 2021. Besides, IACS unified requirements UR E26 & E27 rendered ship- and yard-level cyber-barriers compulsory for all newbuild contracts signed after 1 July 2024.
Moreover, Wartsila and ABS are certifying software-signed updates and multi-factor bridge log-ins to meet UR E26/E27 demands.
Startups are developing cyber risk management solutions. These solutions protect the IT systems and devices on ships, with a particular focus on securing the sensors’ internet connections. Additionally, these solutions encompass the securing of the ship’s hardware and software systems and the training of crew members in cybersecurity practices.
Marlink now monitors 1998 vessels continuously, ingesting 39 billion firewall events per six-month period to triage 718 000 alerts.
Additionally, the maritime security market size reached USD 25.57 billion in 2025. It is expected to reach USD 40.62 billion by 2030, growing at a 9.70% CAGR.
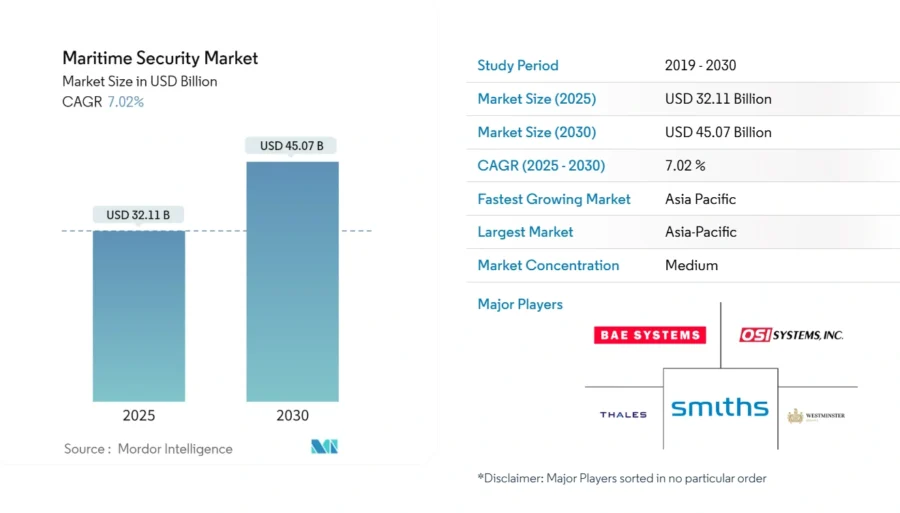
Credit: Mordor Intelligence
ShipSafe Maritime Technologies offers Cyber Security-as-a-Service
ShipSafe Maritime Technologies is a Canadian startup that develops AI and AR-based cyber security and vessel inspection solutions. Its ShipSafe IT suite features endpoint strength management, reduction of unnecessary alerts and false positives, and task scheduling.
Additionally, its policy-based automation lets users schedule tasks and view results in real time. This solution enables IT security personnel to manage device proliferation while automating time-consuming network tasks. ShipSafe Maritime Technologies also simplifies the time and effort of onboard cybersecurity personnel in securing vessel operations and client environments.
Cydome provides a Maritime Cybersecurity Platform
Cydome is an Israeli startup that creates a maritime cybersecurity platform to protect the operation of maritime vessels. The platform provides a real-time map of assets connected to ships’ networks, removing blind spots.
It also conducts automated, built-in cybersecurity checkups, validating ongoing compliance with maritime regulations. Besides providing visibility of assets, Cydome also analyzes a large number of data points for cyber risk mitigation. Thereby, ships receive real-time alerts of any unauthorized access to protect the assets.
10. 3D Printing Integration: US Navy Cuts Lead Times by 95% with Onboard & Near-Base Printing
The pandemic-era supply-chain shocks have turned shipowners toward on-demand spare parts. The US Navy reports 95% lead-time cuts on mission-critical components when printed onboard or near-base.
The large scale of components and the need for materials to withstand harsh ocean conditions present challenges. However, startups are innovating with new techniques such as upgraded Wire Arc and Powder Bed Fusion.
RAMLAB’s wire-arc cells deposit several kilos of steel or bronze; a complex prop segment that once took months to cast is now CNC-finished within hours of printing.
These methods produce medium to large components with high-rate deposition and unlimited build size. Additionally, the ability to print parts on demand streamlines the supply chain and reduces inventory costs, marking a significant shift in the industry.
Moreover, the global 3D printing market size is expected to increase from USD 16.16 billion in 2025 to USD 35.79 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.2% from 2025 to 2030.
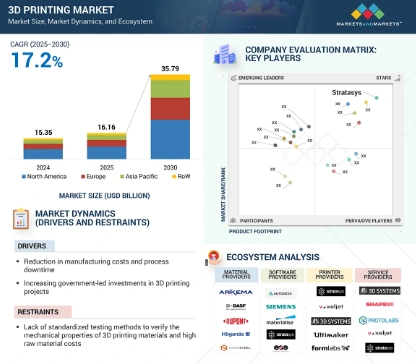
Credit: Markets and Markets
Moi Composites leverages Continuous Fiber Manufacturing
Italian startup Moi Composites manufactures lightweight products in various sizes and shapes using 3D printing. Its patented Continuous Fiber Manufacturing technology uses continuous, oriented fibers with resins to produce strong, lightweight, and durable 3D prints. It also uses proprietary software that enables robots to print in any direction using smart generative algorithms to effectively use materials.
Moreover, the printing process incorporates advanced composites such as carbon, aramid, and sustainable materials. By doing this, Moi Composites enables shipbuilding companies to use existing robotic systems to print components quickly and economically.
Tanaruz manufactures 3D-Printed Customizable Boats
Dutch startup Tanaruz makes 3D-printed customizable boats built from reusable polymers. Its 3D printing material consists of reclaimed polypropylene (PP) with 30% glass fiber. This provides resilience to elongate strain and high resistance to heat, fire, and chemicals.
Besides this, its 3D printers use ABB-manufactured Track Motion system, resulting in great accuracy and fast cycle times. So, Tanaruz not only manufactures boats faster but also promotes a circular economy by reducing environmental waste.
Discover all Shipbuilding Trends, Technologies & Startups
As the shipbuilding industry continues to grow, innovations in technologies such as laser construction tools, automated guided vehicles, and more will serve to further reduce the time to construct ships. With advancements in material sciences and clean fuels, startups are making shipping more affordable and sustainable.
The shipbuilding trends and startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.










