Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary: How Businesses Tackle Rising Costs Leveraging Emerging Technologies
In 2025, inflation is easing globally – it is expected to fall to 4.4%, yet core cost drivers are still sticky. As per the FAO Food Price Index (FFPI), food prices rose 6.9% year-over-year in 2025. Red Sea and canal disruptions forced long reroutes that lifted container-ship demand 12%, and real wages are growing 2.5% across most OECD economies.
At the same time, new and threatened tariffs are dragging world merchandise-trade growth to 0.9% in 2025. Whereas, oil markets remain vulnerable despite subdued demand growth. This keeps energy a persistent swing factor for margins. In this article, you will see where inflationary pressure actually comes from and the specific technologies that tackle it.
Global Inflation Risk Scenarios (2025-2026): Tariffs and trade, energy price volatility, food commodity pressures, shipping and logistics disruptions, persistent services/wage inflation, and fiscal/commodity shocks that keep costs sticky.
Technology Levers That Lower the Cost Curve:
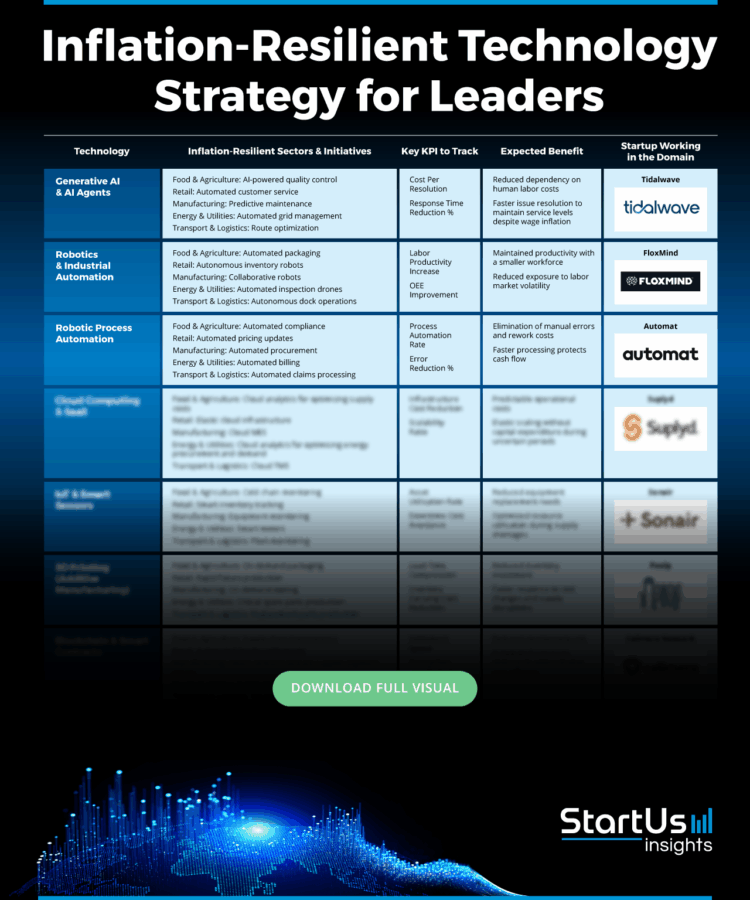
- Generative AI & AI Agents – Replace repetitive, high-volume tasks with AI copilots to slash labor costs and speed up customer response.
- Robotics & Industrial Automation (AMRs) – Deploy robots in warehouses and factories to stabilize unit costs and boost throughput without extra staff.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – Automate finance and admin workflows to cut errors, shrink cycle times, and unlock straight-through processing.
- Cloud Computing & SaaS – Shift from CapEx to elastic OpEx while consolidating tools, improving cost efficiency, and absorbing demand spikes.
- IoT & Smart Sensors– Monitor assets in real time to prevent spoilage, downtime, and fuel waste, turning hidden losses into measurable savings.
- 3D Printing – Print spares and tooling on demand to shorten lead times, cut inventory, and reduce rework costs.
- Blockchain & Smart Contracts – Digitize trade, payments, and compliance to eliminate middlemen, reduce fees, and accelerate settlements.
- Smart Energy Systems & Clean Tech – Flatten peak tariffs and reduce energy volatility with storage, demand response, and cleaner generation.
- Workforce Digitalization Tools – Use digital assistants, e-rostering, and contract automation to reclaim worker hours and stabilize unit economics.
- Business Intelligence (BI) & Advanced Analytics– Apply forecasting, pricing, and digital twins to protect margins, optimize spend, and drive data-led decisions
Sector-Specific Technology Innovation Impact on Inflation: Digital cold chains, AI pricing, D2C commerce, RaaS, digital twins, renewables, hydrogen, autonomous logistics, and pack redesigns that compress input, labor, and intermediary costs to stabilize margins.
Global Inflation Risk Scenarios
- Tariff Hikes & Trade Tensions – Sweeping tariff hikes have pushed the US average effective import tariff rate to approximately 18.6%, generating a 1.8% short-run jump in consumer prices and effectively shrinking real household income by an estimated USD 2400. Supply chain disruptions driven by escalating US-China trade tensions have rippled across industries. Two-thirds of countries globally record inflation above pre-pandemic levels, especially pronounced in over 20 developing, trade-dependent economies.
- Shipping & Logistics Disruptions – Global shipping remains fragile. UNCTAD reports the tonnage of ships transiting through the Gulf of Aden and the Suez Canal fell 76% and 70% respectively. Therefore, forcing rerouting around the Cape of Good Hope and raising container demand by 12%.
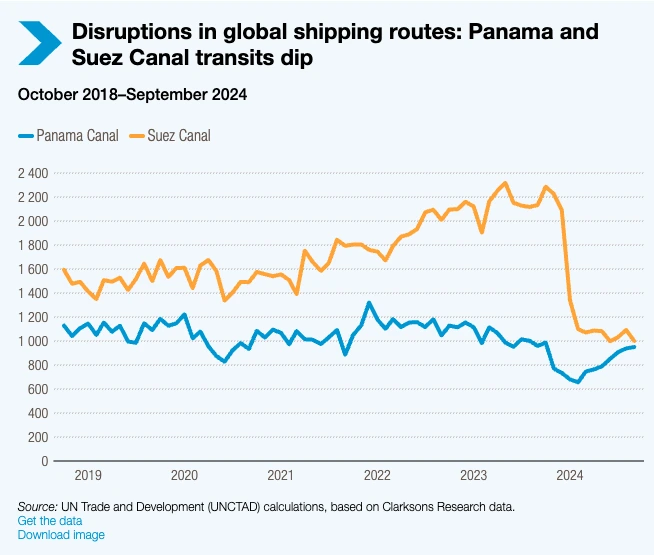
Credit: UNCTAD
- Persistent Services & Wage Inflation – Services inflation, especially housing, continues to weigh on consumers. G20 inflation is projected at 3.6% in 2025 and 3.2% in 2026, while average real wages rose 2.5% across most OECD economies in Q1-2025.
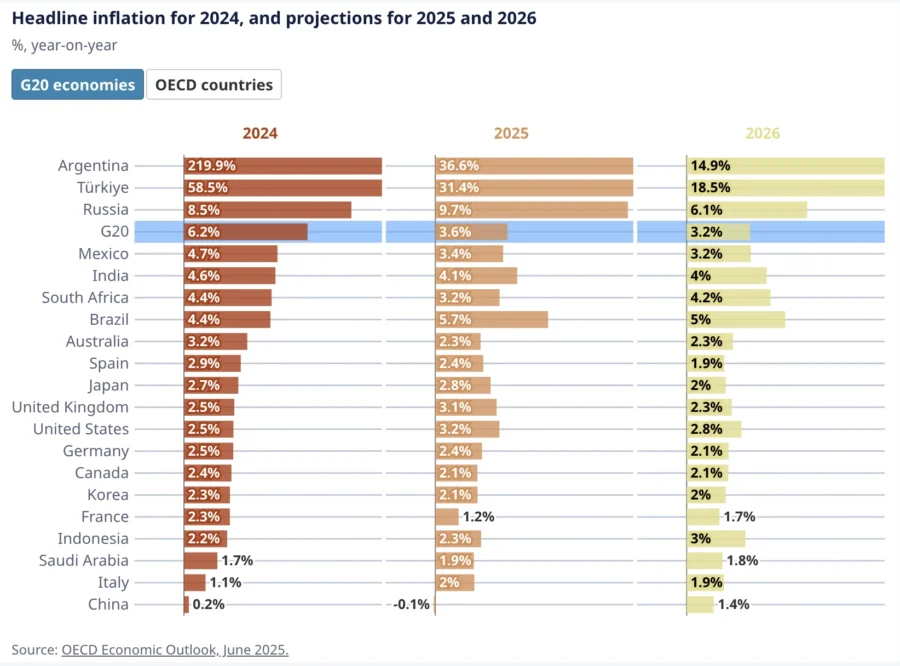
Credit: OECD
- Fiscal & Commodity Shocks – Indirect tax adjustments and commodity swings add further risk. In August 2025, fertilizer prices rose 1.1%, beverage prices increased 7.7%, and precious metals rose by 0.9%.
Technology Levers That Lower the Cost
1. Generative AI & AI Agents
By automating high-volume, routine queries, generative AI handles intense, labor-intensive tasks and buffers enterprises from wage inflation. It also reduces the total number of interactions and associated overhead, such as returns and refunds. This eases out cost pressures when demand and surcharges spike.
Generative AI is increasingly being embedded into business workflows to reduce costs and improve service. For instance, in contact centers, DoorDash implemented a gen-AI, voice-enabled self-service system, using Bedrock and Claude that handles hundreds of thousands of calls per day, with 2.5 seconds response latency and a 50x increase in testing throughput.
Prior to this, Amazon Connect and Lex had already reduced agent transfers by 49% and improved first-contact resolution by 12%. This led to YoY operational cost savings of USD 3 million.
In fintech, Klarna rolled out an OpenAI-powered assistant that managed 2.3 million chats in its first month, roughly two-thirds of all support volume. Moreover, it replaced about 700 full-time agents. Therefore, reducing 25% repeated inquiries, with a lower average resolution time from 11 minutes to under 2 minutes.
Adoption & Reach
More than 71% of organizations report using gen AI in at least one business function.
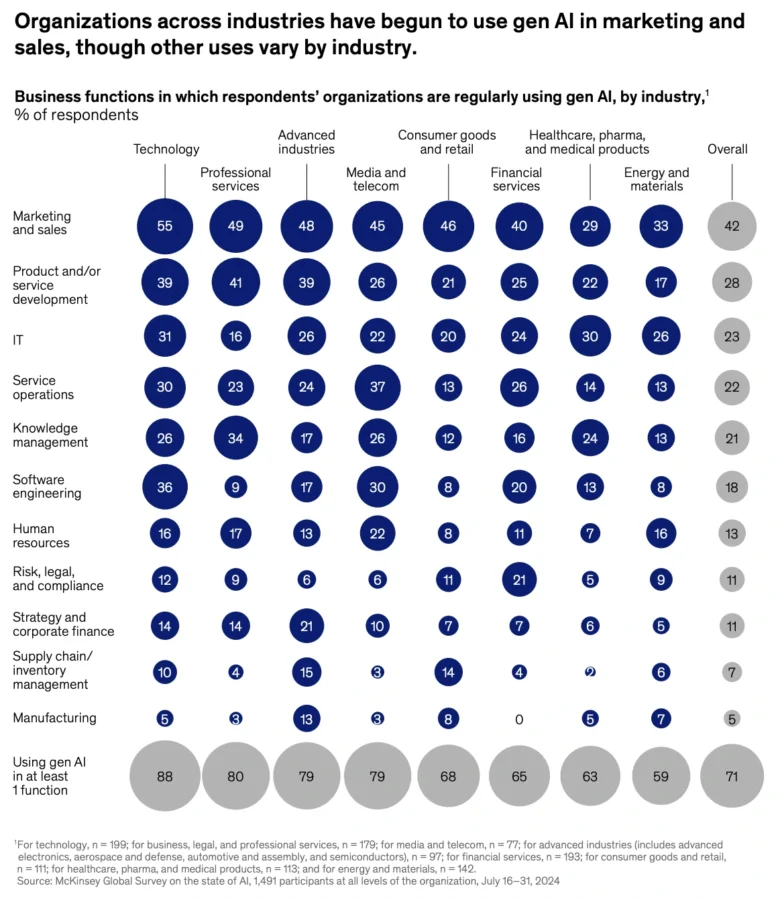
Credit: Mckinsey
21% of respondents reporting gen AI use by their organizations say their organizations have fundamentally redesigned at least some workflows.
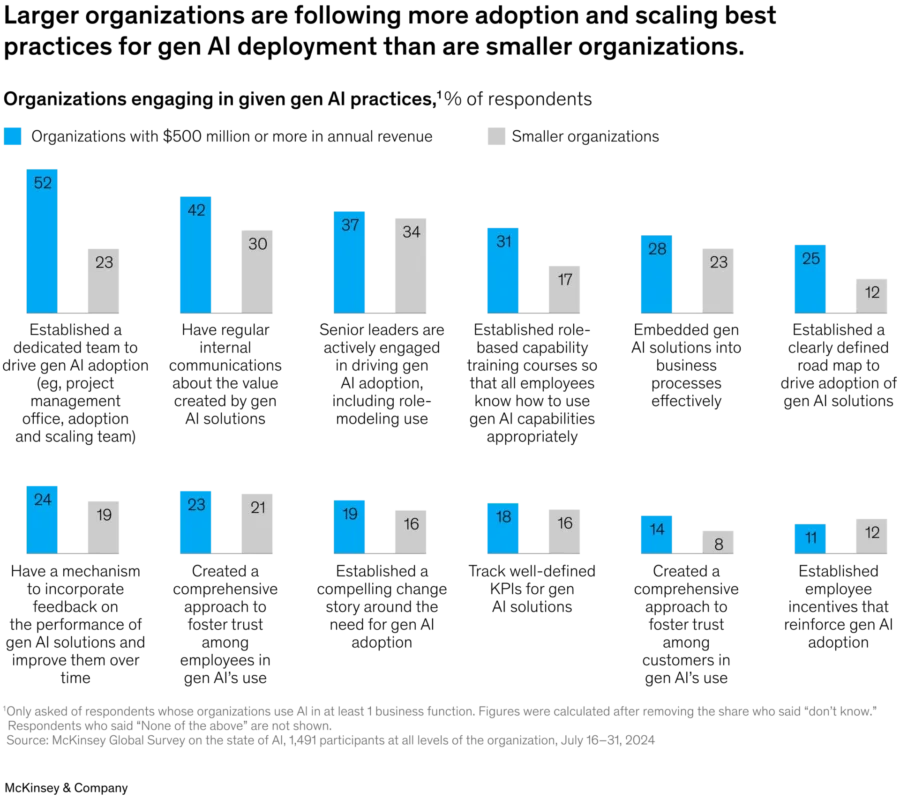
Credit: Mckinsey
Proof of Value
European fashion retailer Zalando introduced generative AI to quickly create imagery and “digital twins” of models for marketing. This innovation trimmed image production timelines from 6 to 8 weeks to 3 to 4 days and reduced associated costs by 90%.
By late last year, around 70% of Zalando’s editorial images were AI-generated. This enabled rapid response to fast-moving fashion trends while optimizing marketing budgets.
Spotlighting an Innovator
Tidalwave is a US-based startup that delivers an agentic AI “Mortgage POS+” platform to streamline borrower intake and orchestrate lender workflows end-to-end. Its copilot engine, SOLO, integrates with automated underwriting systems and ICE Mortgage Technology. It enables real-time document capture, condition mapping, and multilingual borrower guidance within a single interface.
The company is rolling out enterprise deployments with lenders and brokerages, including First Colony Mortgage and NEXA Mortgage, to equip thousands of loan officers with AI assistants that qualify leads, generate letters of explanation, and trigger compliant next steps without manual hand-offs.
Tidalwave’s automation reduces per-loan labor hours, rework, and time-to-decision to support lenders in protecting unit economics when staffing and compliance expenses rise.
Ultimately, Tidalwave’s AI-first workflow streamlines borrower self-service through underwriting orchestration so lenders can raise throughput, standardize quality, and sustain margins even as operating costs climb.
2. Robotics & Industrial Automation (AMRs)
Automation reduces dependency on seasonal labor, stabilizes cost per order, and limits exposure to wage surcharges. Vision-guided workflows minimize mispicks and returns. Robotic machining provides stable cycle times and precision that reduce waste. Energy-optimization services further insulate businesses from power price volatility.
In warehousing, DHL Supply Chain’s deployment of Locus Robotics AMRs in its automotive, engineering, chemical, and energy/industrial (AEMCE) operations delivered a 3x increase in cases picked, faster rollouts, and higher accuracy. This translated directly into a lower cost per unit shipped.
In retail, Walmart’s USD 520 million investment in Symbotic to automate 400 Accelerated Pickup & Delivery (APD) centers curbs wage inflation by scaling throughput without proportional headcount growth.
Industry analysis from Roland Berger projects that broad robotics adoption could cut logistics costs by up to 40% and boost productivity 25-70% by 2025, effectively deflating supply chain cost pressures.
On the factory floor, ABB and Porsche Consulting found robotic machining cells achieve 33% higher productivity and 1200% ROI. This reduces waste, stabilizes energy use, and insulates margins from volatility.
Adoption & Reach
The IFR World Robotics 2024 report shows 541 302 new robot installations with an operational stock of 4.28 million. The humanoid market will ramp up and will reach 40 000 units by 2032. Robotics-as-a-Service and low-cost automation surged in 2025, with cobots and basic arms offered around USD 10k to USD 20k and mobile robots under USD 20k.
Proof of Value
Walmart’s Autonomous Forklifts
Walmart has also piloted the use of autonomous forklifts (FoxBots) from Fox Robotics at four facilities. This allowed a single operator to manage up to six forklifts simultaneously. This transition has resulted in approximately a 40% reduction in labor costs, which mitigates inflation driven by wage increases.
Spotlighting an Innovator
FloxMind is a UK-based warehouse automation startup delivering an all-in-one, robot-agnostic RaaS platform that unifies autonomous hardware with an adaptive orchestration layer. It replaces piecemeal projects and heavy CAPEX with end-to-end deployment evaluation, integration, and operations, so facilities can scale automation without vendor lock-in.
The platform coordinates mixed-fleet AMRs and scales from small pilots to robots without major infrastructure changes. Its traffic control and congestion-avoidance engine raises reliability.
By shifting automation to a service model, FloxMind cuts labor reliance and smooths peak-season surcharges that turn fixed wage pressure into predictable OPEX. Faster orchestration and remote monitoring trim rework and idle time which assist operators in holding unit costs when wages and demand volatility rise.
3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA lowers cost per transaction by cutting labor hours, rework, and compliance errors. It reduces late-payment penalties, captures early-payment discounts, and stabilizes costs when wages or audit requirements rise.
By automating repetitive workflows, for instance, Stant reached 80% straight-through processing, processing 94% of supplier invoices with zero data-entry errors.
Real-world deployments highlight its disinflationary effect: Automation Anywhere processed 170 000 invoices across 3300 vendors in six months. This decreased turnaround from eight days to same-day and saved 12 000 hours.
Also, Omega Healthcare automated 250 million transactions annually with UiPath. This supported Omega reclaiming 15 000 hours per month and reduced documentation time by 40% while achieving 30% ROI.
Adoption & Reach
The SAP Concur/IFOL survey found manual entry in accounts payable dropped from 85% to 60% in 2024, with over half of accounts payable teams spending 10 hours/week on invoices.
In healthcare, NHS trusts run dozens of live automations: UHMBT accelerated bookings by 70%, Aneurin Bevan cut record-update time by 97%, and the NHS expects to save more than 500 000 hours by the end of 2025.
Everest Group’s RPA Products PEAK Matrix 2024 maps 27 platforms in use, showing RPA is mature and multi-vendor globally.
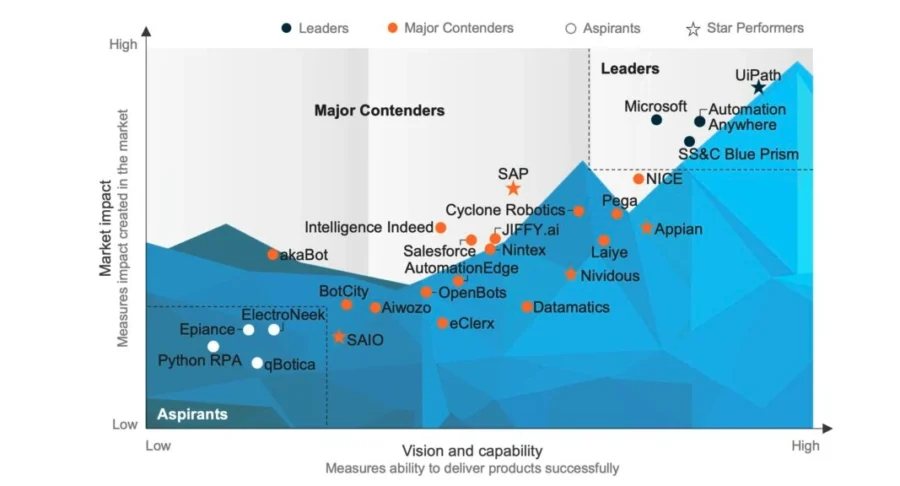
Credit: Everest Group
Proof of Value
Cargill, which operates across 70 countries, deployed RPA combined with OCR to automate order entry processing tasks. It processed 50 000 orders annually and cleaned up over 268 000 dormant vendor accounts.
Since launching 236 automation applications, the company has realized USD 19 million in cumulative savings. By reducing manual labor and streamlining operations, Cargill has effectively insulated itself from cost inflation in labor and transaction handling.
Spotlighting an Innovator
Automat is a US-based startup offering AI-driven RPA that builds, deploys, and maintains automations via managed workflows. Its transformer-based engine allows businesses to submit video walkthroughs, SOPs, or record UI flows, which Automat then turns into scalable automations.
The platform supports open-ended custom workflows across industries such as financial services, insurance, legal, e-commerce, and healthcare. It features observability, analytics, and automated retry logic and integrates with existing tools via API, Chrome extension, or local triggers.
As labor and compliance costs continue to rise, Automat supports enterprises in cutting manual staffing hours and reducing error-induced rework. By deploying automations, it assists firms in protecting margins during wage inflation spikes and volatile demand.
Clients’ backend teams can reallocate headcount from routine tasks to higher-value functions, dampening the inflationary pressure on labor budgets.
4. Cloud Computing & SaaS
Modern cloud architectures deliver better compute price-performance, commitment-based discounts, and elastic burst capacity that absorbs workload surges.
SaaS adoption reduces hardware capital expenditure (capex), improves opex flexibility, and cushions enterprises from wage, rent, and energy-driven inflationary pressures.
Modern architectures deliver superior price-performance, with AWS Graviton4 delivering 30% better performance than Graviton3 (R7g), a foundation for better price-performance on EC2.
While commitment-based models such as Azure Savings Plans reduce compute spend by up to 65% and Google Cloud Spot VMs provide 60 to 91% discounts versus on-demand pricing.
Cloud modernization directly shrinks infrastructure costs under inflation pressure. For instance, Pinterest achieved up to 38% cost savings migrating production workloads to AWS Graviton.
AKA Foods reduced onboarding costs by 90% with Google Cloud. By absorbing workload surges elastically and consolidating SaaS tooling, for example, Microsoft Fabric’s TEI study showed USD 779 000 savings over three years.
Adoption & Reach
Cloud adoption is mainstream and growing. Gartner forecasts public cloud end-user spending to hit USD 723.4 billion in 2025.
Flexera’s 2025 survey shows 84% of enterprises cite cloud spend management as their top challenge, with budgets expected to rise 28%.
Proof of Value
By migrating 55 business-critical applications to AWS, Kmart Australia achieved over USD 1 million in annual savings in infrastructure and licensing. This shields the business from inflation-driven cost pressures. The shift also enabled threefold growth in transaction volume, doubled website speed, improved customer conversion rates, and operated at around one-third of its previous infrastructure cost
Spotlighting an Innovator
Suplyd is an Egypt-based startup offering a one-stop digital marketplace for F&B (Food & Beverage) supplies. It aggregates many product categories, such as cleaning, disposables, dairy, meat, and produce, under one platform.
Suplyd lets restaurants browse many items from multiple suppliers, schedule or automate orders, view analytics & insights, and access payment & supply-chain financing.
The platform integrates full-time support, order scheduling, and supplier aggregation to simplify Suplyd reduces procurement and ordering overhead and cuts redundant supplier markups, lowers stock-outs and emergency orders, and offers predictable pricing via scheduled orders.
Its supply chain financing feature also supports businesses in preserving cash flow when input and logistics costs rise. By aggregating demand, it strengthens purchasing power against inflation-driven supplier price increases.
5. IoT & Smart Sensors
IoT curbs costs by shifting demand away from peak-priced energy, detecting leaks early to prevent waste, and turning unplanned failures into scheduled maintenance. Connected devices also compress logistics fuel spending, reduce accidents, and cut spoilage in food and pharma cold chains.
In energy, a major US smart thermostat demand response program delivered 0.94 kW average demand reduction per enrolled thermostat across five events, with 0.99 kW in the first hour. This directly lowered peak procurement costs for utilities and flattened household bills.
Also, San Antonio Water System (SAWS) reported 10% lower water losses that saved gallons through its ConnectH2O smart meter rollout while improving billing accuracy and reducing truck rolls.
IoT-enabled predictive maintenance in the manufacturing sector to stabilize input costs by avoiding production halts. McKinsey estimates 15 to 30% labor productivity gains and a 50% reduction in unplanned machine downtime despite wage and raw material inflation.
SmartWay partners using efficiency measures, including telematics/route optimization, have saved USD 55.4 billion in fuel costs. These savings insulate transport operators from volatile fuel markets and reduce inflationary pressure on goods movement.
In the cold chain, Vodafone and Controlant’s IoT systems target the USD 30 billion in annual pharma losses from temperature excursions that preserve inventory stability and prevent inflationary spikes in drug pricing.
Adoption & Reach
The total number of connected IoT devices worldwide is expected to surpass 18.8 billion in 2025.
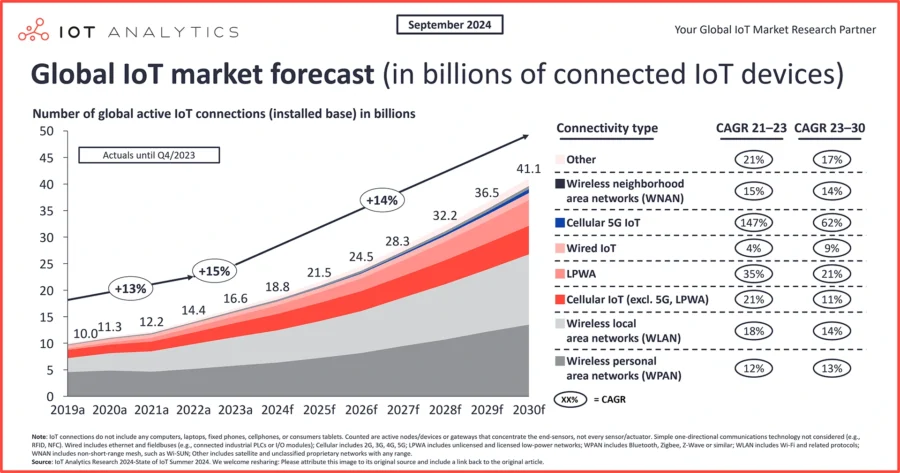
Credit: IoT Analytics
Despite inflationary headwinds, enterprise IoT spending expanded by 10%. Worldwide spending on the IoT is forecast to surpass USD 1 trillion in 2026.
Smart sensors reinforce this trajectory, with the market expected to rise to USD 136.28 billion.
Proof of Value
Nestle deployed AWS IoT Core to build a centralized IoT platform across its global brands (like Nespresso and Purina) to scale up connected-device solutions in more than 90 countries. The rollout supported 2.8 million connected devices, significantly reducing development time (from months to weeks), increasing repeatability of IoT projects across brands, and improving efficiency in operations.
By consolidating IoT operations and reducing duplicative effort, Nestle gained cost savings that mitigate inflationary cost increases in manufacturing, maintenance, and consumer-product operations.
Spotlighting an Innovator
Sonair is a Norway-based startup developing ADAR, the MEMS-ultrasonic 3D sensor designed for safe, full-hemisphere perception in robotics. ADAR detects objects and people via sound, working reliably in darkness, dust, or glare.
Its features include 128 configurable safety or warning zones, low power draw (max 5 W), high ingress protection (IP54), and safety certifications (SIL2 / PL d, Cat. 2). The sensor outputs 3D point clouds in real time via COAP over UDP/IP.
ADAR cuts hardware and maintenance costs. Because the sensor is designed to reduce the cost of ownership (hardware BOM and failure mode risks). Factories and robotics applications can now deploy safer perception systems without the steep price premiums of LiDAR or high-end vision systems.
This reduces capital and operational expenses (less downtime, fewer sensor replacements) in environments where labor, safety compliance, and energy costs are rising.

6. 3D Printing
By shrinking lead times, replacing costly tooling, and enabling distributed production, 3D printing functions as a structural disinflationary force. Over the next five years, its ability to localize supply chains, cut waste, and stabilize repair cycles will create a buffer against inflation in labor, logistics, and energy.
According to the Wohlers Report 2024, metal AM system shipments jumped 24.4% and the broader AM market exceeded USD 20.035 billion, with material providers’ revenues rising 20%.
Protolabs’ 2024 survey found that 70% of manufacturers printed more parts and 82% reported substantial cost savings in their production pipelines, with lead time reduction being cited by 47% as the main reason to shift to AM.
Large-format AM is also reshaping supply chain structure; growing acceptance of localized, distributed manufacturing and digital spare-parts inventories is supporting companies in cutting logistics, labor, and energy inflation risk.
As AM becomes more integrated with digital design tools, hybrid manufacturing, and regional micro-factories, it is increasingly acting as a structural lever for cost compression. Therefore, reducing exposure to material input inflation, shipping surcharges, and labor scarcity.
Adoption & Reach
By the end of 2025, 2.2 million printers are expected to be in use globally.
North America leads with a 43.5% share of the global market, driven by aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing adoption.
Consumer shipments of low-cost 3D printers rose 41% in H1 2024, while industrial printer shipments are forecast to rebound with a 15% increase in 2025 as interest rates ease.
The 3D printing robot market is projected to hit USD 2.17 billion in 2025, with adoption expanding in aerospace, construction, and healthcare.
Additive manufacturing also reduces material waste by up to 70%, enabling localized and on-demand production that lowers input costs and insulates supply chains from inflationary shocks.
Proof of Value
Volkswagen’s Autoeuropa plant replaced externally sourced production aids with in-house 3D-printed jigs, fixtures, and gauges, cutting tooling costs by up to 91% and lead times by 95%.
By eliminating machining backlogs, courier legs, and extended supplier queues, the program reduces line downtime and rework, stabilizes throughput, and shrinks working capital tied up in slow tool cycles.
By stripping out external price adders (labor, energy, freight) and enabling rapid, on-demand replacements, Volkswagen’s 3D-printing deployment directly lowers operational input costs, eases margin pressure, and reduces the need to pass inflationary surcharges on to customers
Spotlighting an Innovator
Poolp is a France-based startup that runs an urban micro-factory producing custom design and architectural pieces using robotic 3D printing, recycled plastics, and bio-sourced compounds.
They craft on demand rather than mass-produce, transforming industrial waste into functional, aesthetic objects via computational design and bespoke fabrication.
Poolp operates a “closed-loop” production process: scrap and plastic waste are recovered, reprocessed, and fed back into new prints. Their workflow ensures every item is tailor-made.
Poolp minimizes raw material wastage, lowers energy usage through local, on-demand fabrication, and eliminates mass-production supply chain overhead. Their circular process and just-in-time 3D printing reduce storage costs, cushion against supply chain delays, and stabilize product pricing even as input costs fluctuate.
7. Blockchain & Smart Contracts
Blockchain and smart contracts are reducing cost pressures in payments, capital markets, and trade by eliminating intermediaries and automating settlement. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) compresses overhead by removing paper-based reconciliation, accelerating claims, and streamlining trade documentation.
These mechanisms reduce liquidity traps, administrative costs, and transaction fees, all of which tend to inflate under wage, FX, and energy volatility.
In cross-border finance, the BIS Innovation Hub’s Project mBridge reached MVP, which enables multi-CBDC payments with settlement and materially lower costs during trials (BIS).
By reducing intraday liquidity needs and settlement exceptions, mBridge offers a structural hedge against rising per-payment costs. In capital markets, Broadridge’s DLT repo (DLR) is operating at scale, processing USD 280 billion on average daily and reducing reconciliation frictions across tokenized repo workflows.
In trade finance, the ICC’s 2024 survey found electronic Bills of Lading (eBL) adoption rose to 49.2%, while the Digital Container Shipping Association (DCSA) estimates USD 6.5 billion in direct savings and USD 30 to 40 billion in additional global trade from full eBL adoption.
Blockchain’s automation of parametric insurance has also proven inflation-mitigating in crisis scenarios. The Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility (CCRIF) used smart contracts to deliver USD 85 million in payouts within 14 days for Hurricane Beryl, while Arbol issued USD 20 million in 30 days for Hurricane Milton. This compressed post-disaster cost inflation by accelerating liquidity into affected economies.
Adoption & Reach
The global blockchain market grew from USD 26.9 million to USD 41.1 billion, with smart contracts expanding from USD 2.0 billion to USD 3.7 billion. Adoption is led by finance (48% of usage), with USD 1 trillion in tokenized assets and USD 85 billion in real estate handled via smart contract.
North America holds 35 to 38% of the market share, while Asia-Pacific posted a 69% YoY rise in on-chain activity in 2025.
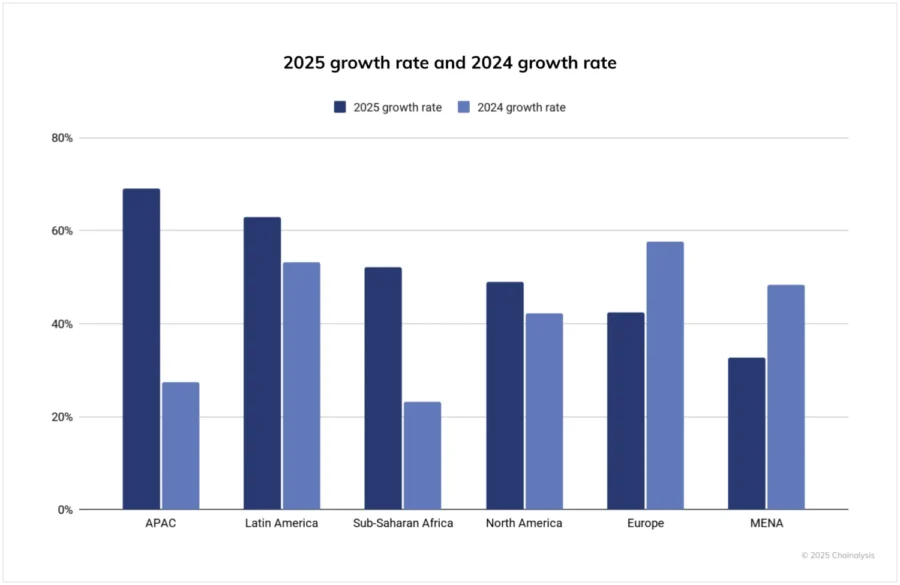
Credit: The Chain Analysis
By automating USD 75 billion in retail and logistics transactions and cutting cross-border settlement times by up to 80%, blockchain and smart contracts directly reduce transaction costs and inflationary frictions.
Proof of Value
Lloyds Bank completed its first cross-border trade using WaveBL’s electronic Bill of Lading (eBL) and a digital Promissory Note that replaced traditional paper-based processes in a deal between Paull’s Matting (UK) and an exporter in India.
The transaction reduced settlement time from 15 days to just over 24 hours, significantly lowering working capital needs, courier and storage costs, and the risks tied to manual documentation.
By removing these inefficiencies, the deployment demonstrates how blockchain-enabled documentation and smart contracts directly cut operational input costs, reduce margin pressures, and limit the need for businesses to pass inflationary costs on to customers.
Spotlighting an Innovator
Calimero Network is a framework for building self-sovereign, privacy-preserving applications that give users control over their data ownership and on-device state transitions.
It enables developers to build peer-to-peer “SSApps” (Self-Sovereign Apps) with verified off-chain computing, local encryption, and composability with blockchains and identity protocols.
The technology supports secure local data vaults, WASM runtimes across browsers, mobile, desktop, and servers, and identity verification through off-chain signatures.
It enables private interactions in encrypted form, and data remains under user control. The project is backed by investors such as Khosla Ventures, GSR Ventures, Eniac, and Near, among others.
Calimero reduces overhead from centralized infrastructure, data egress charges, and third-party data handling. By storing state and computation locally, it cuts down on server/compute usage and associated energy and bandwidth costs.
Moreover, firms using SSApps can avoid surcharges tied to data-transaction volumes and regulatory compliance expenses. This tackles inflation of operational costs in data-intensive industries.
8. Smart Energy Systems & Clean Tech
Smart energy systems and clean tech are serving as practical disinflation tools by flattening peak energy costs and improving grid efficiency. In California and Texas, utility-scale battery storage grew significantly, driving net market revenues for batteries down from approximately USD 78/kW-yr to USD 53/kW-yr in 2024. This means that the rising storage capacity is tamping down peak price volatility.
Across the UK, Octopus Energy’s winter “Saving Sessions” invited over 700 000 customers to flex their demand and deliver an average load reduction per hour.
This resulted in GBP 5.3 million in customer payouts, which is clear evidence that responsive demand management can lower wholesale energy costs and relieve inflationary pressure for households.
With both enhanced storage and dynamic demand flexibility scaling quickly where it matters, clean energy technologies are stabilizing operational expenses for businesses and consumers alike.
Adoption & Reach
35% of global corporate clean energy procurement comes from data centers. Data centers alone are projected to secure an additional 300 TWh of clean energy annually by 2030.
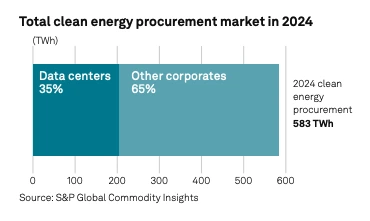
Credit: SP Global
With North America responsible for 60% of this increase, Europe and Asia-Pacific are also scaling up but face resource constraints.
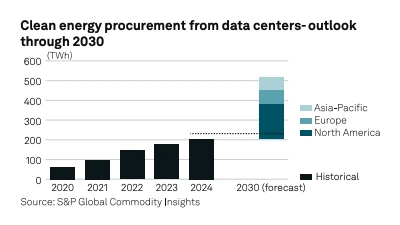
Credit: SP Global
The industrial sector is the leader, accounting for 68.9% of the smart energy market share in 2024. Adoption is driven by regulatory requirements, demand for operational efficiency, and cost savings amid rising energy prices.
Proof of Value
Reid Gardner Battery Energy Storage System
The Reid Gardner BESS in Nevada leverages abundant daytime solar power, storing it and discharging it during evening peaks. This reduces reliance on expensive spot-market purchases, particularly from CAISO, and smooths price peaks that would otherwise contribute to inflation.
The project cost USD 257 million and benefited from approximately USD 100 million in tax credits under the US Inflation Reduction Act.
Spotlighting an Innovator
Epyr is a French energy-technology startup developing modular thermal energy storage (TES) systems that convert low-cost renewable electricity into high-temperature heat.
Their core hardware uses firebrick “heat batteries,” packaged in container-style modular units. It is also combined with AI-powered heat optimization to store surplus renewable energy and deliver on-demand process heat to industrial users.
The company raised a EUR 3 million pre-seed round. Epyr stabilizes heat costs by storing electricity during renewables’ off-peak surpluses and releasing it as heat when energy prices spike.
Epyr reduces exposure to volatile fossil fuel prices and energy tariff hikes. Its modular design lowers CAPEX and installation friction. The startup assists industries in avoiding large fixed costs and reducing operational cost escalations tied to labor, fuel, and grid instability.
9. Workforce Digitalization Tools
Workforce digitalization tools offset wage inflation by compressing labor hours. It also stabilizes unit costs by automating routine knowledge work and streamlining workforce management.
They also optimize staffing through e-rostering and accelerate revenue capture via contract lifecycle management (CLM) systems. In the public sector, the UK government ran the world’s largest pilot of Microsoft 365 Copilot. It covered 20 000 employees across 12 organizations.
The 2025 evaluation found measurable time savings in writing and summarization tasks, alongside strong staff willingness to continue using the tools.
In the private sector, Zoom Workplace quantified an average USD 38.7 million financial impact across five enterprises in 2025 by automating meeting summaries and follow-ups. These deployments show how digital workplace platforms directly counter wage-driven inflation by reclaiming labor capacity.
In contract management, DocuSign CLM’s 2024 TEI study reported a 449% ROI and 90% faster contract generation. Thus, reducing revenue leakage and transaction costs.
Digital adoption platforms like WalkMe delivered a 368% ROI with under three months’ payback.
An Adecco 2024 study found workers saved 1 hour per day using AI tools, which is 66 minutes in tech, 57 in finance, 62 in manufacturing, and 75 in energy/cleantech. This shows sectoral breadth in inflation-mitigation potential.
Adoption & Reach
78% of businesses report using at least one AI technology, with 36% of employees citing frequent AI use in their daily workflows. The digital workplace market is projected to expand to USD 166.27 billion by 2030 at a 22.8% CAGR from 2025.
Adecco finds that workers using AI save about one hour per day on average, which reclaims time from routine tasks.
On sourcing, Deloitte’s 2024 survey shows 83% of executives leverage AI in outsourced service,s and 20% are already developing digital workforce strategies using remote collaboration and automation to control labor costs.
Proof of Value
Yum Brands, including its Taco Bell chain, has been deploying “Byte by Yum,” an AI-powered workforce management/assistant tool. The tool assists managers with scheduling, inventory alignment, and staff utilization.
In particular, Taco Bell showed a push towards staffing optimization using the AI assistant to adjust staffing and shift coverage dynamically in response to demand (especially in drive-through operations).
Spotlighting an Innovator
Tako is a Brazilian startup offering an AI-powered payroll & HR operations platform. It uses trained AI agents to automate end-to-end payroll processes. Such as onboarding, vacation & leave management through resignation. It includes integration with Brazilian regulatory systems like eSocial and real-time compliance enforcement.
The system is built for companies handling payroll at scale in Brazil. It tracks laws and contracts, supports multiple branches and contracts per company, interprets local labor legislation, computes payroll continuously, and handles benefit integration and tax & legal compliance without manual spreadsheets.
Tako reduces payroll back-office labor, minimizes error-driven rework, and avoids costly penalties. By halving payroll processing time and replacing fragmented tools with agents that automate manual compliance tasks, Tako stabilizes labor overhead when wage rates and regulatory burdens climb.
10. Business Intelligence (BI) & Advanced Analytics
Business intelligence (BI) and advanced analytics reduce inflationary pressures by consolidating platforms, automating reporting, and powering faster, more accurate decisions.
By rationalizing IT costs and eliminating overlapping licenses, they minimize capital-heavy infrastructure requirements. Forecasting and pricing analytics further stabilize margins, while spend analytics contain supplier-driven cost pass-throughs.
In IT operations, Microsoft Fabric’s Total Economic Impact (TEI) study found USD 779 000 in infrastructure savings over three years from stack consolidation, while Google BigQuery with Looker delivered 205% ROI.
This reduced 5200 analyst hours annually, saving USD 1.9 million in labor and also reducing reliance on legacy tools by saving USD 921 000 in legacy tools that generated USD 6 million in productivity gains.
Power BI users, on average, save 2 hours per week, which translates into thousands of reclaimed analyst hours each year. This reduces wage-driven inflationary strain on knowledge work.
In supply chain and retail, McKinsey documented that digital twins uplift revenue by 5% and lower labor costs by 10%. This provides direct insulation from logistics cost inflation.
Unilever leveraged AI-driven demand signals to improve ice cream forecast accuracy by 10% in Sweden. This shows how analytics stabilize demand planning in inflation-sensitive categories.
In procurement, McKinsey finds analytics-driven transformations often target 30% cost reductions, while BCG reports that nearly half of industrial firms using advanced pricing tools expanded margins by more than 10% points within two years. These approaches allow firms to protect profitability even as input costs rise.
Adoption & Reach
67% of the global workforce had access to BI tools, with adoption highest in finance, manufacturing, and services. Despite this broad reach, only 26% of organizations have fully adopted BI.
Notably, 80% of manufacturers reported measurable business improvements from BI analytics that underscore its role in stabilizing operations amid inflationary pressures.
Adoption is functionally led by IT departments, which account for 41% of BI deployments, followed by finance, healthcare, and retail.
43% of enterprises now embed analytics directly into operational applications to enable real-time responses to pricing volatility, supply chain disruptions, and other inflation drivers.
Proof of Value
Lufthansa used advanced analytics to reduce procurement costs and improve spend visibility across its supply chain. Via a platform called Spendscape, the airline combined real-time pricing, supplier cost data, and environmental metrics (like carbon emissions) to inform purchasing decisions.
By monitoring cost volatility and supplier risk more closely, Lufthansa projects reduced input cost inflation and more stable forecasting of procurement budgets
Spotlighting an Innovator
Onum is a Spain-based startup offering a real-time data intelligence platform that reduces data overload by filtering, enriching, routing, and transforming incoming data before it reaches analytics stacks. Its engine enables routing transformation at the source and minimizes analytics-platform billable volumes.
The platform is used by security, observability, and infrastructure teams to “unburden analytics budgets” by sending only high-value events to long-term storage. This reduces data ingestion costs, lowers alert fatigue, and accelerates response times.
Onum supports firms to reduce downstream costs by reducing storage burden, improving pipeline efficiency, and avoiding over-provisioning. Teams lower spending on cloud logs/observability/ELT pipelines, which often scale costs aggressively under usage inflation. By enriching and filtering at the source, Onum stabilizes analytics budgets even as data volumes grow and cloud costs climb.
Sector-Specific Technology Innovation Impact on Inflation
Food & Agriculture
- Pressures: Fertilizer costs remain volatile, with the World Bank’s fertilizer index up 15% in Q2 2025. Input costs tied to energy (used in nitrogen fertilizer, etc.) are subject to sharp swings, especially when fuel, natural gas, or related inputs spike.
- Innovations:
- Digital cold chains & IoT sensing: Improving storage and transport conditions to reduce spoilage. UNEP/FAO estimates 14% of food is lost pre-retail globally.
- Blockchain-based trade rails: Use of electronic bills of lading and smart contracts to reduce paperwork and streamline settlement.
E-marketplaces: In India, platforms such as eNAM enhance price discovery and reduce middleman inefficiencies.
- Impact: India provides a proof point, as food inflation turned negative with -1.76% YoY as logistics improved and digital marketplaces scaled, while wholesale food prices dipped by 2.15% YoY. Cold-chain programs and digital trading platforms are compressing spreads and stabilizing consumer prices.
Retail
- Pressures: Retailers are experiencing upward pressure on costs from rising wages, especially in labor-intensive activities, along with volatile and unpredictable consumer demand. Operating costs are being squeezed, and shifting demand patterns force frequent adjustments in inventory, pricing, and staffing.
- Innovations:
- AI-powered dynamic pricing: Retailers are increasingly using real-time demand and competitor analytics to adjust pricing more responsively.
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) models: Bypassing intermediaries preserves margins. For example, US D2C e-commerce sales are forecast at approx. USD 239.75 billion in 2025
- Automation & robotics: Firms like Ocado use robotics and automation in order fulfillment to increase efficiency and reduce labor dependency.
- Impact: By compressing labor reliance and intermediary costs, these tools stabilize retail margins. US and EU data show retail inflation holding at multi-year lows versus other sectors, supported by AI pricing and D2C scale.
Manufacturing
- Pressures: Manufacturers continue to face input cost inflation, though easing North American firms expect raw material costs to rise 2.7% over the next 12 months, down from earlier double-digit levels. Labor shortages persist, pushing companies toward automation to sustain output without wage escalation.
- Innovations:
Credit: Formic
- ERP/SaaS & digital twins: Use of digital twins, simulation, and ERP tools is growing, with reports of manufacturers achieving throughput improvements and cost reductions in some cases; many firms report seeing initial ROI from AI or digital transformation, and several are preparing to scale.
- Impact: RaaS provides flexible capacity without labor inflation, AM reduces logistics and lead-time costs, and digital twins optimize throughput while cutting scrap. Together, these tools shift manufacturing from reactive cost-cutting to proactive, data-driven optimization.
Energy
- Pressures: Energy price volatility remains a major inflation driver, with fuel swings closely tracking headline inflation. India’s total installed power capacity reached 235.7 GW from non-fossil sources, creating pressure on grid infrastructure as non-fossil sources increase their share.
- Innovations:
- Solar grids & renewables: India’s installed capacity hit 462 GW by Dec 2024, with 97.9 GW solar and renewables now 45.3% of the mix.
- Hydrogen technologies: Clean hydrogen output is set to grow 30x to 16.4 million tons annually by 2030. This enables lower-cost steelmaking and industrial use.
- Impact: Declining renewable tariffs are moderating utility inflation, while hydrogen adoption buffers cost risks in energy-intensive industries. IoT-enabled grids and distributed systems provide stable, affordable power, reducing inflationary shocks across economies.
Transport & Logistics
- Pressures: Fuel costs remain inflationary, with India’s Fuel & Light inflation rising from 2.55% in June to 2.67% in July 2025. Global driver shortages add to road freight bottlenecks and wage pressures.
- Innovations:
- Autonomous logistics: Gatik’s Level-4 trucks reduce driver dependence and improve safety in “middle-mile” freight.
- EV delivery & AI routing: Locus.sh enables optimized dispatch; Samsara’s IoT platform cuts fuel by 4%, maintenance by 9%, and extends vehicle life by 10%, with 815% ROI.
- Warehouse automation & AMRs: Robotics in fulfillment centers reduces labor reliance and raises throughput.
- Impact: India’s transport inflation fell from 3.9% in June to 2.12% in July 2025.
Consumer-Facing Inflation Plays: Shrinkflation & Pack Redesign
- Pressures: Shrinkflation, or downsizing products while maintaining price, has impacted 1/3 of consumer goods since the pandemic. With an average downsizing of 16.2% in 2024 and reductions of over 30% in some categories. It accounts for 10% of inflation in household paper and snacks. 81% of consumers notice it, and 56% report repeated encounters.
- Innovations:
- Price-pack architecture: Smaller SKUs, like “half loaves” or single-serve packs, preserve affordability.
- Brand redesigns: PepsiCo, Mondelez, and Campbell’s use packaging tweaks and branding to mask reduced quantity.
- Impact: 48% of American shoppers have abandoned a brand due to shrinkflation. Unit costs rise steeply, eg, paper towels increase 12% and coffee +32%. While consumers dislike stealth downsizing, emerging smart packaging could shift focus toward freshness and transparency, offering ethical differentiation.
Explore the Latest Innovations & Startups to Stay Ahead
With thousands of emerging technologies and startups, navigating the right investment and partnership opportunities that bring returns quickly is challenging.
With access to over 7 million emerging companies and 20K+ technologies & trends globally, our AI and Big Data-powered Discovery Platform equips you with the actionable insights you need to stay ahead of the curve in your market.
Leverage this powerful tool to spot the next big thing before it goes mainstream. Stay relevant, resilient, and ready for what is next!