Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
Executive Summary: Global Startup Ecosystem 2026 Report
- Global Landscape: Cities like Singapore, London, and Barcelona are proving how science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) inflows, accelerator density, and pro-founder reforms turn local hubs into global contenders.
- Global Rankings of Startup Hubs: Silicon Valley and New York remain on top, but the map is shifting. London slipped to number 3, while Beijing, Paris, Bengaluru, and Shenzhen surged. This signals Asia and Europe’s rising competitiveness against established US hubs.
- Top Investment Magnets: Generative AI, fintech, climate tech, defense, space, and biotech dominate investor focus. Each reflects structural demand – from AI’s compute bottlenecks to defense’s geopolitical urgency and climate’s regulatory tailwinds.
- The Policy & Governance Dimension: Policy is the decisive lever of ecosystem success. Startup visas in Singapore and Canada, tax breaks in Ireland and Estonia, and India’s angel tax abolition are drawing founders and capital, while fragmented rules in the US and emerging markets risk slowing momentum.
- Collaboration & Networks: Dense networks accelerate scaling. From Medellin to Recife, public-private partnerships and corporate venture arms prove that ecosystems with active collaboration compress timelines, raise more capital, and achieve higher exit multiples.
- Future Trends: By 2030, ecosystems will be AI-first, decentralized, and sustainability-driven. Expect Asia-Pacific and Latin America to climb further, funding to diversify beyond equity, and startups to embed AI and ESG as default business models.

Global venture capital investment dropped from USD 128.4 billion in Q1 2025 to USD 101.05 billion in Q2. The US maintained its dominance by attracting USD 72.7 billion in VC investment in Q2 2025.
At the same time, AI and chip demand have escalated to the point of scarcity, with secondary markets for GPUs becoming an unexpected feature of the innovation economy. Big Tech’s sustained investment, like USD 223 billion in AI R&D and USD 161 billion in capital expenditure in 2022 alone.
Heightened regulatory scrutiny since 2024 has also forced startups to internalize compliance as a core competency. This report provides the critical intelligence that founders, investors, and stakeholders need to make high-stakes strategic decisions with confidence and capitalize on the opportunities ahead.
Global Landscape: Where Ecosystems Are Thriving
A startup ecosystem is a network of capital, talent, infrastructure, policy, and networks that enables startups to launch and scale. The strength of an ecosystem lies in how these five pillars reinforce each other.
- Capital – Capital inflows back ventures and attract global investors to reinforce credibility and deal flow. In 2023, deep-tech VC reached USD 590 billion. Hubs like Singapore (+44.9%), Beijing, and London drive billion-dollar exits.
- Talent – A strong talent base drives innovation cycles and knowledge spillovers. For instance, Singapore hosts 3024 startups (49% of SEA’s total), powered by STEM inflows. Cities like London, San Francisco, and Beijing saw major surges in developer density and university output this year.
- Infrastructure – Physical and digital enablers act like a support system for startups to scale. Barcelona grew 40.4% YoY by investing in accelerators and global accessibility. Singapore and London have hundreds of incubators and coworking hubs.
- Policy – Saudi Arabia jumped 37 global ranks (+236.8%) through founder-friendly reforms, while Cyprus rose with relocation incentives and tax benefits.
- Networks – Dense, active networks create pathways for capital and talent, with faster scaling and higher exit values. Medellin (+40%) grew via public-private partnerships, while Baku climbed 47 spots with international collaborations.
2025 Ranking of Leading Hubs for Startups
According to the Startup Genome report, Silicon Valley and New York retained the top two spots; however, London slipped to position 3 from 2 after four years.
Asia continued its upward trajectory. Beijing rose three places to position 5, driven by AI-native transitions and increased funding, while Shanghai climbed to position 10 on deep tech strength.
Bengaluru gained +7 to position 14, and Shenzhen also gained +11 to position 17. This signals the growing competitiveness of Indian and Chinese ecosystems.
North America remained stable but showed signs of diversification. Boston tied with Beijing at position 6, while Philadelphia surged 12 spots to position 13 on the back of new unicorns and major deal activity. Los Angeles maintained consistency at position 4, while Toronto dipped slightly.
Europe displayed mixed momentum. Paris advanced to position 12, benefitting from record unicorn creation, while Berlin (-1) and Stockholm (-3) slipped due to slower capital flows and reduced unicorn activity. Barcelona’s climb to position 20 (+3) underscores the value of coordinated infrastructure investment and global accessibility.
Table: Global Ranking of Leading Startup Hubs
| Ecosystem | Rank 2024 | Rank 2025 | Change | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Valley | 1 | 1 | No change | Continues to lead in exits, unicorn creation, and access to VC funding |
| New York City | 2 | 2 | No change | Maintains strong market reach and VC activity |
| London | 2 | 3 | -1 | Slipped after holding #2 for 4 years; fewer exits, lower growth rate |
| Los Angeles | 4 | 4 | No change | Stable performance and consistent startup success |
| Beijing | 8 | 5 | +3 | Increased funding, major exits, stronger AI-native transition |
| Boston | 6 | 6 (tied) | No change | Maintained competitiveness, tied with Beijing |
| Tel Aviv | 5 | 7 | -2 | Slight dip due to lower exit velocity and VC influx |
| Paris | 14 | 12 | +2 | Growth in unicorns and early-stage funding |
| Singapore | 5 | 5 | No change | Top ecosystem growth rate, breakthrough AI/tech investments |
| Shanghai | 11 | 10 | +1 | Improved funding and performance, strong in AI and deep tech |
| Berlin | 10 | 11 | -1 | Slower growth, competitive pressure |
| Amsterdam | 13 | 12 | +1 | Growth in exits, ecosystem collaborations |
| Philadelphia | 25 | 13 | +12 | Major improvement in deals/exits, new unicorns |
| Bengaluru | 21 | 14 | +7 | Surge in deal count, market reach, and unicorn formation |
| Stockholm | 12 | 15 | -3 | Slowdown in funding, lower unicorn activity |
| Sydney | 14 | 16 | -2 | Stable, slight ranking slip |
| Shenzhen | 28 | 17 | +11 | Significant increase in funding, deals, and deep tech ecosystem value |
| Toronto | 16 | 18 | -2 | Moderately declining funding and exit value |
| Sao Paulo | 18 | 19 | -1 | Stable ecosystem performance, slight decrease in value/activity |
| Barcelona | 23 | 20 | +3 | Infrastructure investment, growing tech exits |
Signals of Ecosystem Maturity
In 2025, leading hubs such as Silicon Valley, London, Beijing, and Singapore demonstrate:
- High-Value Exits: Consistent billion-dollar outcomes, expanded unicorn density.
- Sustainable VC Activity: Early and late-stage funding supported by international investors.
- Market Reach: Active international scaling and export success.
- Talent Density: Experienced serial entrepreneurs and deep technical expertise.
- Innovation Output: Strong IP creation, patents, and R&D spinouts.
- Policy & Regulatory Maturity: Founder-centric reforms and predictable rules.
- Rich Infrastructure: Deep pools of accelerators, incubators, and digital hubs.
- Network Connectivity: Dense investor-founder links, public-private partnerships.
- Resilience & Diversity: Cross-sector success, geographic and demographic breadth.
The Capital Dimension: Fueling Growth & Survival
Global Funding Trends
United States
- Total funding: USD 162.8 billion in H1 2025. USD 69.9 billion was invested in US startups.
- Deal flow: Scale AI’s USD 14.3 billion raise. Deal activity expanded 25% year-over-year to 2474 rounds that showcased the depth of capital and breadth of investor appetite.
- Lead sectors: AI and fintech
- Implication: The US remains the center of gravity for late-stage AI and scaled software, with deep syndicates and secondary liquidity supporting runway extension.
Europe
- VC totals: USD 12.6 billion in Q1 2025; USD 5.4 billion in early-stage across 280 deals show resilient SEED/Series A pipelines.
- Country signals:
- UK: Startups raised USD 4.2 billion of venture capital in Q1 2025. This shows 7.7% YoY growth. The largest round in Q1 2025 came from AI drug discovery company Isomorphic Labs.

Credit: Dealroom
- Germany: USD 1.6 billion early-stage in Q1 – Berlin/Munich anchor deep tech.
- France: USD 1.4 billion early-stage in Q1; USD 3.5 billion 2025 startup funding with 20 unicorns.
- Spain: USD 1 billion early-stage in Q1 and best in 2 years); ecosystem value EUR 110 billion (2025).
- UK: Startups raised USD 4.2 billion of venture capital in Q1 2025. This shows 7.7% YoY growth. The largest round in Q1 2025 came from AI drug discovery company Isomorphic Labs.
- Sectors: Healthcare/biotech and fintech lead, with consistent early-stage throughput.
- Implication: Europe’s strength is pipeline resilience, but exit velocity and late-stage capital pools remain fragmented relative to the US and Asia.
Asia
- Country signals:
- Singapore: Regional fundraising hub; ecosystem value is USD 144 billion with sustained venture inflows.
- China: Major inflows persist across Beijing/Shanghai/Shenzhen; deal pace is volatile amid geopolitics; deep-tech intensity is rising.
- India: Among the top global ecosystems. It is also a strong capital for SaaS, fintech, and e-commerce.
- Indonesia: USD 909 million in Q1 2025 (+30% QoQ) as digital economy rebounds
- Vietnam/Malaysia: Rapid early-stage momentum; debt financing up in Vietnam; Malaysia attractive for digital enterprise.
- Implication: Asia is policy-enabled and consumption-driven. Deep-tech intensity in China and SaaS/e-commerce scaling in India complement Southeast Asia’s revival. This makes the region a diversified growth corridor.
2025’s Top Investment Magnets Technologies
Even as global venture markets recalibrate, capital is clustering around a few categories that investors see as long-term structural plays.
Generative AI & AI Infrastructure
GenAI startups raised USD 49.2 billion in the first half of 2025. VC-backed AI companies pulled in USD 80.1 billion in Q1 2025, which is a 28% quarter-over-quarter increase.
This is highlighted by OpenAI’s USD 40 billion, Anthropic’s USD 3.5 billion, and SSI’s USD 2 billion in 2025 from January to June. Infrastructure, chips, and tooling are pulling in big checks as compute scarcity becomes the bottleneck for scaling.
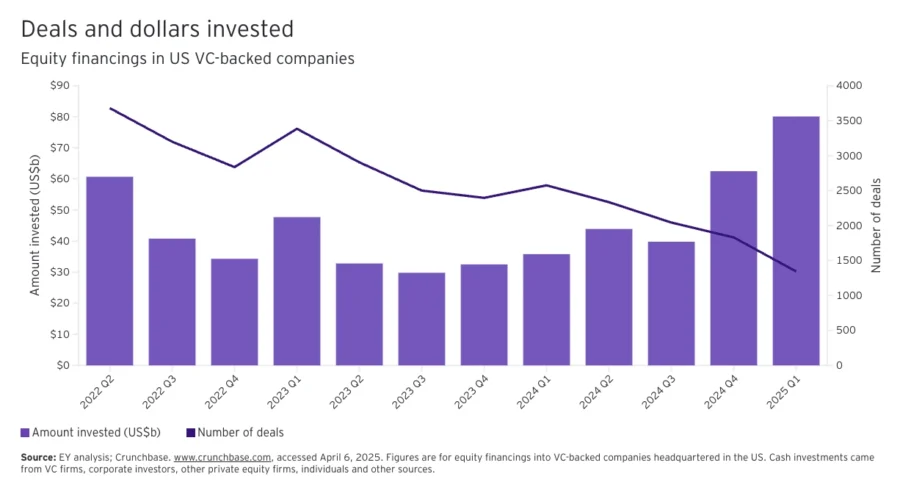
Credit: EY
Fintech
Fintech funding exceeded USD 10 billion for the first time since the venture capital downturn began in Q3 2022. Moreover, Q2 funding reached USD 11 billion. Payments, infrastructure, and insurtech are leading with capital flowing back into platforms that monetize scale and compliance.

Credit: S&P Global
Climate & Energy Tech
Climate remains one of the few categories with secular tailwinds, though equity volumes are off their 2022 highs. By mid-2025, climate tech had raised USD 23.5 billion, with trackers like CTVC reporting USD 13.2 billion for pure VC/growth deals.
Commonwealth Fusion’s USD 1 billion and TerraPower’s USD 650 million showed investors’ willingness to fund long-horizon bets. The focus is shifting from frontier hardware toward grid, storage, and industrial decarbonization plays that scale with policy incentives.
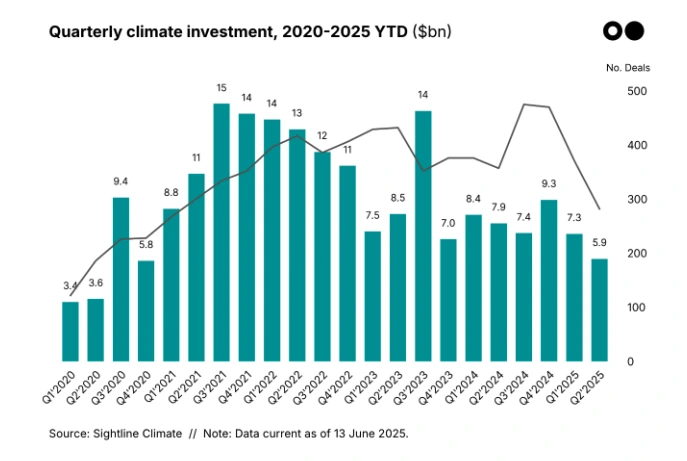
Credit: CTVC
DefenseTech
Defense is squarely back in venture portfolios. Anduril’s USD 2.5 billion round in 2025 and Helsing’s EUR 600 million in Series D funding round in Europe.
Rising geopolitical tensions, larger defense budgets, and dual-use autonomy/sensing applications are pulling private capital into an area long considered inaccessible.
Cybersecurity
US cybersecurity VC deal value in Q2 2025 increased compared to last quarter. Investors are concentrating bets on platforms with broad coverage and AI-native defense capabilities.

Credit: Ropes & Gray
In a market saturated with point solutions, scale and integration breadth are emerging as the true differentiators.
SpaceTech
The space industry quietly posted its second-strongest quarter on record. The sector raised USD 3.1 billion in Q2 2025 alone and USD 8.7 billion over the trailing twelve months. National security demand and defense-driven budgets are catalyzing launch, in-space logistics, and satellite manufacturing plays.
Global Scaling Hubs (2025)
According to the Global Startup Ecosystem Report (2025):
- San Francisco: 15 030+ startups, growth rate 19.9%, global leader in unicorn density and exits.
- New York City: Growth rate 25.5%, strongest momentum among top hubs, deep SaaS and fintech networks.
- London: Europe’s leader, supported by a USD 342 billion ecosystem value and tax-relief schemes.
- Beijing: Growth rate 25.2%, 2350 startups, and accelerating AI-native expansion.
Global Startup Landscape Ranking 2025

Credit: Startup Genome
- Shanghai: Fastest-growing major hub with 38.4% growth and strength in hardware and IoT.
- Paris: Growth rate 34.6%, deep tech and AI scaling rapidly, highest-ever rank.
- Bengaluru: Its ecosystem value is USD 136 billion, and it is ranked #5 globally in AI/Big Data with 32 active unicorns.
- Philadelphia: Largest mover in North America, strong deal and exit data.

Credit: Startup Genome

The Policy & Governance Dimension: How Rules Shape Startup Ecosystems
Policy remains a decisive lever as Singapore’s EntrePass continues to attract foreign founders with renewable residency, grants, and co-working access, while Canada’s Start-Up Visa offers open permits and a fast track to permanent residency.
Programs in Tokyo, Astana, and France are lowering entry barriers to embed international founders directly into innovation hubs.
Also, more than half of government R&D support now flows through tax relief across the OECD. This directly benefits startups and SMEs that rely on experimental development.
India has doubled down with new research parks, lower patent filing costs, and expanded venture capital pools to ease compliance, so founders can focus on innovation.
Further, tax structures remain a magnet for global entrepreneurs. Jurisdictions like Estonia (0% retained profits), Ireland (12.5% corporate rate), and the UAE (0-9% in free zones) combine low tax environments with investor-friendly regimes.
In Asia, Singapore offers partial exemptions and robust IP protections, while India provides three-year tax holidays and angel tax abolition to accelerate domestic growth.
Global Tax Structures Shaping Startup Ecosystems in 2025
| Country/Jurisdiction | Corporate Tax Rate | Key Startup Incentives & Structures | Notes & Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hong Kong | 0% (offshore), 8.25-16.5% | No tax on offshore income; streamlined setup; FSIE exemption | Gateway to Asia, strong privacy |
| Singapore | 17% | Tax exemptions and rebates for startups; first 3 years partial exemption on profits; R&D incentives | Southeast Asia hub, IP protections |
| United Kingdom | 50% relief on investments under the SIES Scheme | Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS) and the Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS) provide major tax reliefs for investors funding startups | Strong VC ecosystem, quick incorporation |
| Estonia | 0% (retained profits) | No corporate tax until profits are distributed; e-Residency allows remote incorporation | Digital business leadership |
| India | 15% (new tax rate) 22%/25% (optional rates), up to 30% (traditional regime) | 3-year tax holiday for eligible startups in the first 10 years; reduced rates for MSMEs; presumptive taxation and angel tax abolition | Rapidly reforming, large domestic market |
| Ireland | 12.5% | Low tax, R&D incentives, international HQs | EU access, skilled workforce |
| Netherlands | 19-2 (Innovation Box on profits from R&D) | Innovation Box regime: reduced rate for qualifying innovative income | EU base, strong startup ecosystem |
| UAE | 0-9% | Free zones offer a zero-tax environment for startups and ease rules for foreign ownership | Middle East hub |
| United States (Delaware) | 8.7% corporate tax, no state tax for non-operating entities | Delaware offers business-friendly statutes and no state corporate tax for companies not conducting business there. LLC/small business pass-through options | Ease of investment, legal stability |
| Switzerland | 11.9-20.5% | IP tax relief, stable regulatory environment | Financial center, innovation |
| Luxembourg | 14-16.5% | Tiered rates, IP & holding company benefits | EU headquarters, efficient banking |
| Netherlands | 19-25.8% | 9% Innovation Box rate for qualifying R&D income | EU access, innovation focus |
Finally, regulatory clarity is creating the predictability ecosystems need. For instance, India’s self-certification reforms and fast-track closures reduce friction, Saudi Arabia’s Premium Residency removes sponsorship hurdles, and France’s Tech Visa simplifies relocation for global talent.
How Policy Shapes Startup Ecosystem Trajectories
Policy acts as both an accelerator and a bottleneck, directly influencing capital flows, founder behavior, and ecosystem competitiveness.
When policy accelerates growth, ecosystems scale rapidly.
India’s 2025 Union Budget injected an additional INR 10 000 crore fund of funds, abolished the angel tax, and simplified compliance. The result was record-breaking fundraising IPO successes and a surge past 150 000 DPIIT-recognized startups.
Similarly, the UK’s SEIS/EIS tax relief schemes and streamlined registration fueled a population-adjusted growth rate in 2025, while Switzerland’s low corporate taxes and innovation agencies (Innosuisse, Venturelab) anchored billions in biotech and ICT investments.
When policy lags, ecosystems stall.
India’s gains were tempered by legacy challenges, complex registration, patchy seed funding, and talent shortages, which contributed to 35 000 startup shutdowns in 2023.
In the United States, visa hurdles and inconsistent policy support slowed growth; six of its top 10 cities slipped in global rankings, with leading hubs posting only 18.2% growth.
Across other emerging markets, fragmented rules and ambiguous tax regimes continue to delay incorporation and deter foreign investors.
Geopolitical Shifts: New Rules of Engagement for Startups
In 2025, three fault lines – supply chain security, data localization, and AI regulations – are defining factors in startup ecosystem competitiveness.
Supply Chain Resilience
In 2025, one-third of global data breaches originated from third-party suppliers.
US tariff hikes on Asian imports and retaliatory trade measures have fragmented global sourcing that forces startups to adopt multi-country vendor strategies and nearshoring to politically stable markets.
For founders, supply chain resilience now demands both cybersecurity hardening and political risk hedging. Any disruption can erase investor confidence overnight.
Data Residency & Localization
Every major market enforces residency requirements: GDPR in Europe, DPDP in India, PIPL in China, and state-level AI/data rules in the US.
For SaaS, fintech, and healthtech startups, this means re-engineering products country by country and investing in local cloud partnerships.
Payment firms have already been barred from India for failing residency obligations. As a result, hubs like Singapore, the EU, and the UAE are emerging as compliance-friendly bases.
AI Compliance Laws
75 countries have passed 1000+ AI-related laws. The EU AI Act sets a high bar that applies extraterritorially with penalties up to EUR 35 million or 7% of global revenue.
In contrast, the US landscape is fractured, with state-level rules diverging, while China imposes stringent restrictions on generative models and enforces content censorship. For startups, this creates spiraling legal costs and compliance risks.
Many are now embedding “ethical-by-design” frameworks to invest in automated governance tools and strategically base operations in jurisdictions with stable, predictable AI laws.
Collaboration & Networks: The Connective Tissue of Startup Ecosystems
The strength of a startup ecosystem also depends on the density and quality of its collaborative networks.
Cross-Sector Interaction:
The government provides enabling policies and funding mechanisms, corporates and VCs inject capital and market access, while academia anchors research and talent pipelines. Universities increasingly connect through joint labs, tech transfer offices, and innovation clusters.
In parallel, corporate-startup engagement is increasing. By 2025, 372 corporations across 30 countries and 11 major countries will be actively engaging with startups. It offers investment, accelerators, and pilot opportunities that directly shorten time-to-market for new technologies.
Accelerators, Incubators, and Corporate Venture Arms as Connectors.
Empirical evidence shows startups emerging from accelerators raise 23% more capital and are 50% more likely to be acquired than peers. Incubators provide survivability through long-term support on IP, compliance, and infrastructure.
Alumni networks and demo days expand founders’ strategic relationships, while corporate venture arms deliver distribution pipelines, supplier networks, and customer validation.
Also, corporate VCs became central to the ecosystem’s 19% CAGR with investments explicitly tied to collaborative partnerships rather than financial returns alone.
Future Trends that will Define the Startup Ecosystem
1. AI-Native Startups Fueling Local Ecosystem Value
AI-native ventures are becoming anchor tenants of local ecosystems. These firms also act as talent magnets – AI usage jumped from 27% to 36%. India and Singapore reported record enrollment in machine learning programs. The clustering of AI specialists fosters knowledge spillovers, and spin-off ventures are strengthening local resilience.
2. Asia-Pacific and Latin America Accelerate
The global startup map is decentralizing. APAC ecosystems post the fastest average annual growth rates, with Bengaluru (+7 ranks) and Shenzhen (+11 ranks) climbing global rankings.
Latin America is following a similar trajectory, such of Medellín. Structural drivers include smartphone penetration projected to reach 91% in LATAM by 2030 and middle-class expansion across APAC.
3. Funding Models Diversify Beyond Equity
In the US, venture debt set a record and is tracking near that pace in 2025. This gives founders a meaningful, non-dilutive runway. Public money increasingly flows through tax credits rather than grants, as 55% of OECD government support for business R&D now comes via tax incentives, further expanding non-dilutive options.
4. Crucial Upskilling in AI, Blockchain & Product Management
Global skills report found that 70% of startups are prioritizing upskilling in AI, blockchain, and product management. 56% wage premium for AI skills compared to workers with the same job roles without AI skills. The “hire-train-deploy” model, widely adopted in India’s IT sector, is now extending to startup ecosystems.
5. Creator Economy Tools Evolve with AI Integration
The creator economy is projected to reach USD 480 billion by 2027 with AI as its growth engine. In 2025, 63% of YouTube creators used AI-powered tools for editing, captions, and personalization.
Platforms such as Canva, Runway, and Descript reported double-digit adoption growth among creators. AI integration enables micro-creators to operate at a scale previously limited to established media companies.
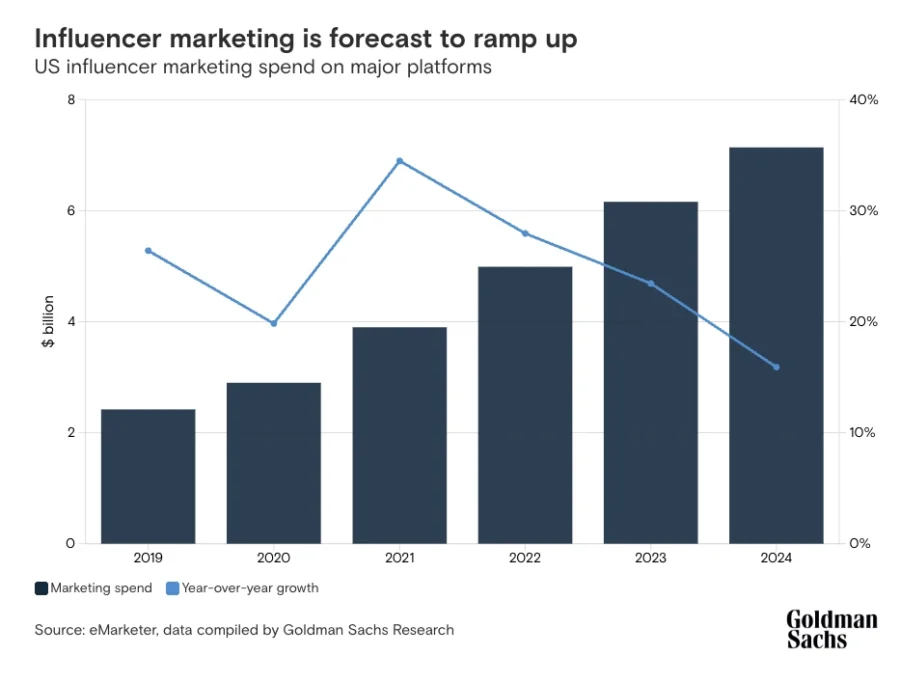
Credit: Goldman Sachs
6. AI-Fueled Consumer Tech and User-Led Platforms
Personalized e-commerce recommendations lifted average order values by 50% globally, while AI chatbots now manage over 60% of first-line support queries in the US.
The next phase is agentic AI, as its systems proactively act on behalf of users. This is leading to user-led platforms, customized around individual needs rather than platform-driven design.
The Ecosystem of 2030: Interconnected, AI-First, and Sustainability-Driven
- Interconnected Networks: By 2030, ecosystems will operate as globally networked clusters, connected via shared cloud platforms, data marketplaces, and cross-border accelerators. The AI ecosystem alone is forecasted to grow to USD 1.01 trillion by 2031, fueled by network effects across healthcare, finance, and logistics.
- AI-First Business Models: Startups will embed AI into every process, such as automating workflows, hyper-personalizing customer interactions, and enabling agentic decision-making. The global generative AI market is projected to grow at a 44.2% CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- Sustainability-Driven Entrepreneurship: Climate finance must increase to meet global goals of energy transition and sustainable supply chains. Regulatory pressure and consumer demand reinforce this trajectory.
Explore the Latest Innovations & Startups to Stay Ahead
With thousands of emerging technologies and startups, navigating the right investment and partnership opportunities that bring returns quickly is challenging.
With access to over 7 million emerging companies and 20K+ technologies & trends globally, our AI and Big Data-powered Discovery Platform equips you with the actionable insights you need to stay ahead of the curve in your market.
Leverage this powerful tool to spot the next big thing before it goes mainstream. Stay relevant, resilient, and ready for what is next.