Accelerate Productivity in 2025
Reignite Growth Despite the Global Slowdown
What are the Top Telecom Trends for 2026?
The telecom industry is transforming through AI, network disaggregation, and next-gen connectivity to meet global demand for speed, security, and sustainability. The following trends define the sector’s direction in 2026 and beyond:
- AI and Network Automation – Nearly 90% of telecom companies use AI, shifting operations from reactive to proactive. AI reduces operational costs by 30% and enhances 5G network performance by 25%. With data traffic expected to surpass 300 exabytes monthly by 2027, AI processes massive datasets to predict congestion, optimize resources, and improve customer experiences.
- Cybersecurity Innovations – Telecom cybersecurity faces increasing threats as cybercrime costs rise toward USD 10.5 trillion annually. Regulatory frameworks like India’s 2024 Telecom Cyber Security Rules mandate stronger defenses. AI-powered tools, zero-trust architectures, and endpoint protection systems are being deployed to defend complex, real-time networks.
- IoT Integration – Cellular IoT connections are projected to exceed USD 6.2 billion by 2030, driven by demand for connected devices and smart environments. 5G RedCap, eSIMs, and edge computing enhance reliability and reduce latency.
- 5G Expansion – As of April 2025, global 5G connections reached 2.25 billion. Besides, 320 providers are launching 5G services. Standalone 5G deployments, such as India’s 469 000 base stations, improve bandwidth, speed, and network responsiveness.
- Satellite Communication – Satellite broadband is expanding with LEO constellations, direct-to-device access, and multi-orbit integration. Micro-satellites and metamaterial antennas improve affordability and performance. The satellite communication market is projected to reach USD 33.2 billion by 2029, offering global coverage, especially in remote areas.
- Digital Twins & Network Virtualization – Digital twins and network functions virtualization (NFV) lower costs by 20% and reduce energy use by 15%. These tools simulate network behavior, predict faults, and simplify upgrades. NFV adoption enables flexible service delivery and reduces capital costs.
- Edge Computing & Ultra-Low Latency Applications – Edge computing supports ultra-reliable low-latency applications like augmented reality (AR)/(VR), autonomous vehicles, and smart factories. Spending is expected to grow to over USD 5.1 trillion by 2034. MEC, AI at the edge, and 5G-powered nodes allow real-time processing near users, improving service delivery and efficiency.
- 6G – 6G networks will deliver terabit speeds, microsecond latency, and AI-native infrastructure. Operating in terahertz bands, 6G supports zero-energy devices and self-learning networks. Research milestones include 938 gigabit data rates and direct integration of AI into hardware.
- Fixed Wireless Access Growth (FWA) – FWA adoption is rising, with 78% of providers offering it and mid-band 5G reaching millions of homes. It provides fast broadband in underserved areas at a lower cost than fiber.
- Open RAN & Vendor Diversification – Open RAN adoption promotes supply chain resilience and avoids vendor lock-in. Backed by USD 420 million in U.S. government support, Open RAN deployments are expected to surpass 2 million base stations by 2029.
Read on to explore each trend in depth – uncover key drivers, current market stats, cutting-edge innovations, and leading telecom innovators shaping the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the next big thing in the telecom industry?
Telecom companies are integrating generative AI into smartphones and expanding fixed wireless access (FWA) and satellite-based connectivity. As a result, internet access is becoming faster and more widely available.
2. What is the future of telecoms?
Looking ahead, telecom networks will rely on AI for greater efficiency and automation. Alongside the spread of 5G and the emergence of 6G, operators are moving to cloud-based systems and investing in stronger cybersecurity. These shifts are also prompting new business models, which support intelligent connectivity and consistent digital experiences for users and industries alike.
Methodology: How We Created the Telecom Trend Report
For our trend reports, we leverage our proprietary StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 7M+ global startups, 20K technologies & trends plus 150M+ patents, news articles, and market reports.
Creating a report involves approximately 40 hours of analysis. We evaluate our own startup data and complement these insights with external research, including industry reports, news articles, and market analyses. This process enables us to identify the most impactful and innovative trends in the telecom industry.
For each trend, we select two exemplary startups that meet the following criteria:
- Relevance: Their product, technology, or solution aligns with the trend.
- Founding Year: Established between 2020 and 2025.
- Company Size: A maximum of 200 employees.
- Location: Specific geographic considerations.
This approach ensures our reports provide reliable, actionable insights into the telecommunication innovation ecosystem while highlighting startups driving technological advancements in the industry.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 10 Telecommunications Industry Trends & 20 Promising Telecom Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top Telecommunication Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 3100+ global startups & scaleups. The Telecommunication Innovation Map created from this data-driven research helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you a comprehensive overview of the telecommunication industry trends & startups that impact your company.

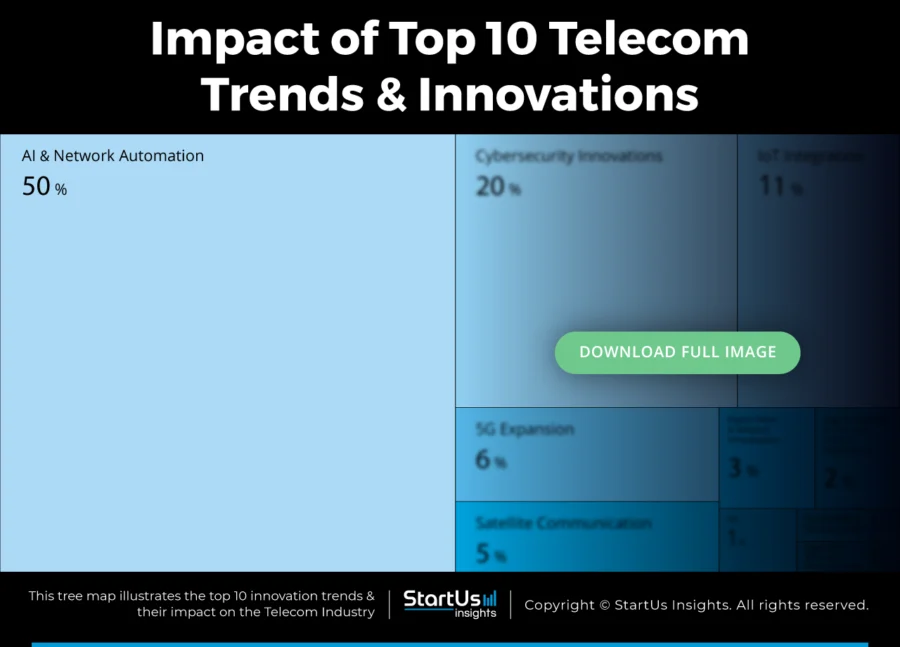
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 10 Trends in Telecommunication
Telecom innovation in 2026 focuses on building faster, smarter, and more adaptable networks. AI and network automation simplify operations, optimize bandwidth, and reduce downtime. At the same time, Open RAN architectures and vendor diversification promote interoperability and cost control across network equipment.
Edge computing and ultra-low latency applications are enabling new use cases in various industries. Fixed wireless access continues to expand last-mile connectivity, particularly in underserved regions. Satellite communication supports coverage in remote areas, while IoT integration increases device connectivity across smart cities and industrial systems.
Moreover, digital twins and network virtualization improve network planning, testing, and performance. Meanwhile, early 6G research explores higher frequency spectrum, network sensing, and AI-native design. Together, these developments are shaping the foundation for the next phase of global connectivity.
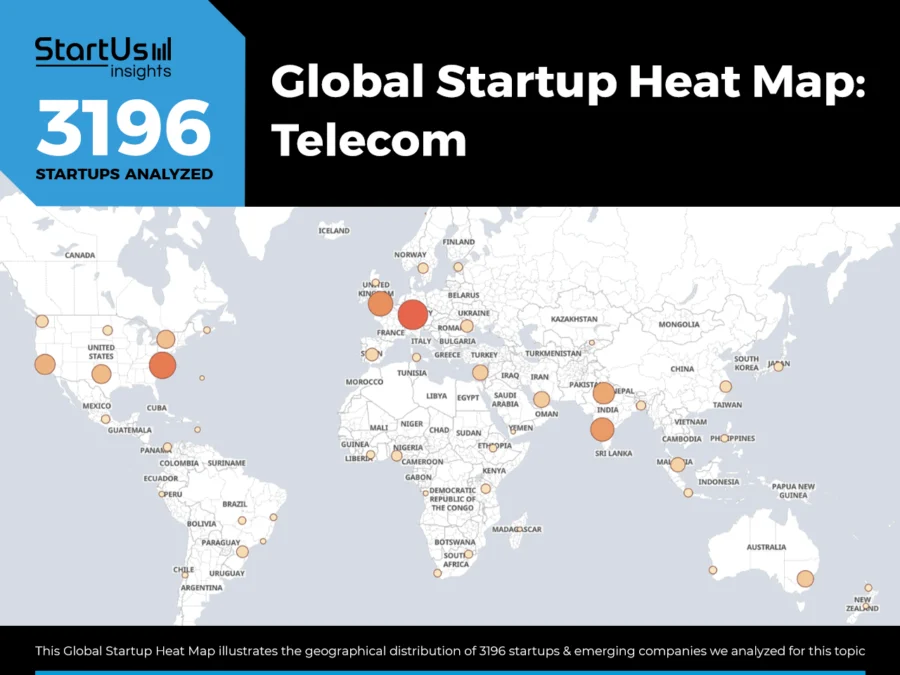
Global Startup Heat Map covers 3196 Telecom Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map showcases the distribution of 3100+ exemplary startups and scale-ups analyzed using the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. It highlights high startup activity in Western Europe and the USA, followed by India. From these, 20 promising startups are featured below, selected based on factors like founding year, location, and funding.
Want to Explore Telecom Innovations & Trends?
Top 10 Emerging Trends in Telecom Industry (2026 & Beyond)
1. AI and Network Automation: Nearly 90% of Telecom Companies Use AI
Network complexity and operational demands are driving the adoption of AI in telecom automation. Operators face growing pressure to manage dynamic networks while lowering costs. AI-powered automation reduces operational expenses by 30% and improves network efficiency by 25%.
The global 5G deployment is accelerating, and AI algorithms aid in improving 5G network performance by 25%. These tools support faster data transfer, lower latency, and dynamic spectrum management. They also enable ultra-reliable low-latency communication and easy connectivity across devices.
Telecom operations are shifting from reactive to proactive models. AI supports this transition by analyzing large volumes of network data. By 2027, global telecom data traffic is expected to exceed 300 exabytes per month. AI is able to process this data to predict congestion, enhance performance, and optimize resource allocation.
Besides, nearly 90% of telecom companies use AI. Of these, 48% are piloting solutions, while 41% have moved into active deployment.
Nokia is advancing AI adoption through its Autonomous Networks Fabric. In partnership with Google Cloud, it delivers telco-trained models that reach Level 4 automation under TM Forum’s framework.
Meanwhile, Gluware raised USD 43 million in growth funding led by Bain Capital to expand intelligent network automation for cloud-based environments.
The global AI in telecom market is growing rapidly. It is projected to reach USD 50.21 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 38.81% between 2025 and 2034.
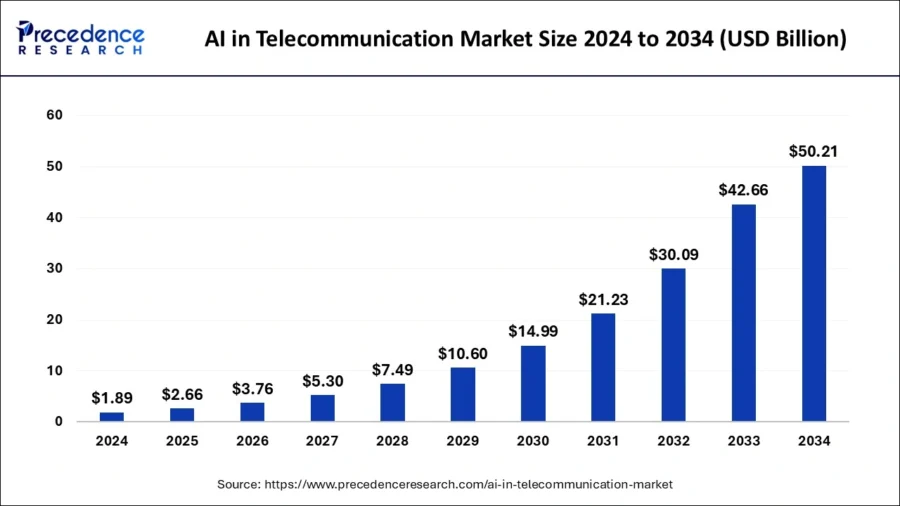
Credit: Precedence Research
NLPearl creates a Conversational AI Phone Agent
Israeli startup NLPearl develops an AI voice automation platform that manages customer phone interactions using human-like, multilingual voice agents. It applies natural language processing and domain-specific language models to convert user intents into executable workflows. This approach enables real-time responses and actions without human involvement.
Its platform includes a no-code interface that allows users to create conversation flows with simple prompts. It also integrates with tools like Slack, Salesforce, and Shopify through APIs.
The startup automates tasks such as call routing, appointment scheduling, data capture, and transactional messaging. It also provides transcripts, smart call tagging, and instant alerts to support performance tracking.
Infranomics enables AI-Powered Fibre Broadband Planning
UK-based startup Infranomics builds AI-driven tools for sales analytics, geospatial strategy, and network planning. These tools support business decisions across various industries.
The Hermes platform analyzes sales data with machine learning to predict customer behavior, refine targeting, and identify growth areas. Atlas provides detailed geospatial insights on demographics and wealth to allow companies to prioritize markets and plan network expansion.
Meanwhile, its Hercules applies proven AI models for scenario planning and fiber deployment. It enables users to reduce capital and operating expenses while adjusting to changing network needs.
2. Cybersecurity Innovations: Cybercrime to Cost USD 10.5 T Annually by 2025
The rising cyber threats are pushing innovation in telecom cybersecurity. The industry faces increasingly complex attacks, with global cybercrime costs expected to reach USD 10.5 trillion annually by this year.
Regulatory changes are also shaping security strategies. For example, India’s Telecommunications (Telecom Cyber Security) Rules 2024 require telecom entities to adopt detailed cybersecurity policies. These rules mandate the appointment of Chief Telecommunications Security Officers and the setup of 24/7 Security Operations Centers.
As telecom intersects with data-sensitive sectors like healthcare and finance, the need to secure data in transit has grown. These sectors rely on technologies such as NFVi, eSIM, and VoLTE, which demand encryption and protection protocols.
Telecom operators use cybersecurity to address data breaches, ransomware, man-in-the-middle attacks, and vulnerabilities in 5G infrastructure. They apply tools like network slicing, authentication protocols, and data encryption to strengthen defenses.
In addition, threat intelligence platforms allow for securing endpoints and connected devices. AI-driven threat detection and zero-trust architectures identify and neutralize advanced threats, including distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Darktrace offers Self-Learning AI that responds to cyber threats without human intervention. This solution supports lean security teams managing complex telecom environments.
The telecom cybersecurity market is projected to reach USD 83.79 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 16.9% from 2025 to 2034.
![Top 10 Telecom Industry Trends [2025 & Beyond] | StartUs Insights](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Telecom_Cyber_Security_Solution_Market_2025_Graph-900x675.webp)
Credit: The Business Research Company
BlackDice advances Telecom Cybersecurity
BlackDice, based in the UK provides enterprise-grade cybersecurity and data intelligence for small and medium-scale businesses. It uses AI-driven technology embedded within routers to protect broadband networks, devices, and IoT environments.
![Top 10 Telecom Industry Trends [2025 & Beyond] | StartUs Insights](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/BlackDice-solution-architecture-diagram-22-x-16.9-cm-2-900x691.webp)
The solution integrates machine learning and device-agnostic tools to identify and neutralize real-time threats such as advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware across entire cyber ecosystems.
Hiaware offers All-Network-based Cybersecurity & Encrypted Connections
Hiaware, based in Slovenia delivers all-network-based cybersecurity and encrypted connections for B2B, protecting various networks, including public Wi-Fi.
It uses a DNS-based system to filter malicious content and prevent malware attacks without requiring downloads, setups, or user maintenance. It also provides real-time threat detection and integration with existing systems.
3. IoT Integration: Cellular IoT Connections to Exceed USD 6.2 B by 2030
The rising demand for device connectivity is accelerating IoT integration in telecommunications. The global IoT connections are expected to reach 40 billion by 2030. Besides, cellular IoT connections surged a 24% in 2023 and are expected to exceed USD 6.2 billion by 2030.
Telecom providers are expanding infrastructure to support this growth. Wi-Fi leads with 31% of all IoT connections, followed by Bluetooth at 25% and cellular IoT at 21%. 5G RedCap technology supports download speeds up to 150 Mbps and latency under 100 milliseconds to enable faster and more responsive IoT applications. eSIM technology powers 33% of cellular IoT devices, which allows remote provisioning and improves security.
Several innovations are enhancing IoT performance. Network slicing creates virtual networks tailored to specific applications that improve reliability and efficiency. Edge computing processes data closer to devices, which reduces latency and improves responsiveness. LPWAN technologies such as NB-IoT and LoRaWAN support long-range, low-power connectivity, making them suitable for remote or battery-operated devices.
The cellular IoT connectivity market generated USD 15 billion in revenue in 2023. The analysts project an 18% CAGR through 2030. By then, 5G and 5G RedCap may contribute nearly half of the total IoT connectivity revenue. China accounts for 70% of global cellular IoT connections but only 36% of revenue, due to lower average revenue per user.
China Mobile leads in global cellular IoT connections and revenue. It benefits from low-cost IoT plans and widespread NB-IoT network deployment. The company plays a central role in China’s dominant share of global cellular IoT connections.
Looking ahead, the telecom IoT market is expected to reach USD 410.656 billion by 2033. This reflects a projected CAGR of 22.2% from 2023 to 2033.
JAG Industrials advances Decentralized Wireless Infrastructure
US-based startup JAG Industrials develops decentralized wireless infrastructure for peer-to-peer 5G and IoT networks. It uses the Helium Blockchain to support smart devices and connected environments.
The startup combines 5G CBRS and LoRaWAN protocols in its radios and hotspots. This setup provides long-range wireless coverage and enables data transfer across the Helium Network.
Its system relies on cryptographic authentication, distributed consensus, and dynamic mesh networking. These features support secure, scalable, and autonomous device communication.
Jag Industrials allows users to earn HNT, HMT, or IOT tokens. Users receive tokens for providing coverage and facilitating data transfer.
Moabits creates an IoT Connectivity Platform
German startup Moabits offers an IoT connectivity platform that automates device onboarding, diagnostics, and orchestration across multi-operator networks.
It uses Orion, an AI-powered management system, to monitor SIM activity and optimize network selection. Orion also enables easy switching across more than 500 mobile operators in over 190 countries.
The platform ensures secure connectivity through private APNs, VPN tunnels, and encrypted channels. It also provides automated billing and real-time consumption tracking to support cost control.
Moabits supports integration through REST APIs and offers multi-tenant access for partner-level visibility. This setup maintains administrative control while enabling collaboration.
4. 5G Expansion: 2.25 Billion 5G Connections as of April 2025
5G enhances telecommunications by improving speed, latency, capacity, and bandwidth. These features enable networks to manage usage spikes and unpredictable traffic more efficiently than previous generations.
Mobile data demand continues to rise. The global mobile data traffic reached 130 exabytes per month in 2023. Projections suggest it will triple to 403 exabytes per month by 2029. This growth highlights the need for 5G’s improved capacity and performance compared to 4G.
Government-led digital transformation initiatives are accelerating 5G infrastructure investment. India completed its nationwide 5G rollout by October 2024. Services now reach 779 out of 783 districts and are supported by 469 000 base stations.
Reliance Jio leads India’s 5G deployment. The company reports 68.8% 5G availability and uses standalone 5G technology. Its use of the 700MHz band enables deeper coverage and faster rollout, surpassing competitors.
Globally, 5G adoption continues to expand. As of April 2025, there are 2.25 billion 5G connections. This growth rate is four times faster than 4G during similar periods.
A total of 320 service providers have launched 5G networks, with 49 offering standalone 5G services.
Despite rapid deployment, telecom capital expenditure declined 10% year-over-year in the first half of 2024. The providers face challenges in monetizing 5G and managing excess network capacity.
The global 5G infrastructure market is expected to reach USD 95.88 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 22.9% from 2024 to 2030.
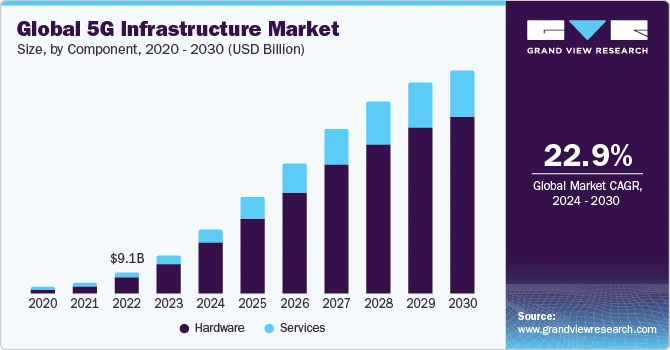
Credit: Grand View Research
Vaan Megam streamlines 5G Application Testing & Deploying
Vaan Megam is an Indian startup that provides a 5G lab-as-a-service platform that facilitates testing of protocols, performance, and latency.
The company uses real-world conditions through its realistic test bed and delivers accurate assessments for telecom operators, equipment manufacturers, and application developers.
It provides detailed reporting, test scheduling, monitoring, and value-added services like logging, resuming crashes, and rerunning on failure. This allows businesses to deploy high-quality 5G solutions without investing in expensive infrastructure.
Saviah Technologies provides 5G Core (5GC) Networks
Taiwanese startup Saviah Technologies provides 5GC in three variations: lightweight, industry-grade, and carrier-grade. These 5GC networks are used for various purposes, such as telecom technology centers and virtual reality. They also improve connectivity in industries like agriculture, manufacturing, healthcare, port, media, and entertainment.
Saviah Technologies’ 5GC complies with 3GPR R15/16 standards and covers end-to-end network functions like access and mobility management, session management, user plane, authentication server, and more. It also assists in network functions like slice selection, exposure, NF repository, and policy control.
5. Satellite Communication: Market to Reach USD 33.2 B by 2029
There is a global demand for reliable broadband, and the need to improve rural coverage. This brings satellite connectivity into mainstream telecom planning.
SpaceX’s Starlink expanded from 1 million subscribers in December 2022 to 6 million by August 2025. It roughly added one million users each quarter during 2024 and 2025.
Analysts estimate the US total-addressable market for LEO broadband ranges between USD 20.8 billion and USD 62.9 billion annually. This growth is supported by mass-produced micro-satellites, which measure as small as 11 centimeters and cost less than USD 7000 before launch. These compact satellites allow operators to scale fleets quickly and cost-effectively.
New technologies such as direct-to-device (D2D) and SAT-G also deliver satellite connectivity directly to standard mobile handsets and eliminate the need for specialized terminals. Multi-orbit networks that integrate LEO, MEO, and GEO satellites offer bandwidth-on-demand and improved resilience. For example, SES’s O3b mPOWER system delivers up to 1.5 Gbps per terminal.
Telstra is partnering with OneWeb to migrate remote mobile base stations to LEO networks. This move will extend coverage by an additional 100,000 square kilometers and support future rollouts in areas where satellite access is more practical.
The global satellite communication market is projected to reach USD 33.2 billion by 2029. This reflects a CAGR of 14.5% from 2024 to 2029.
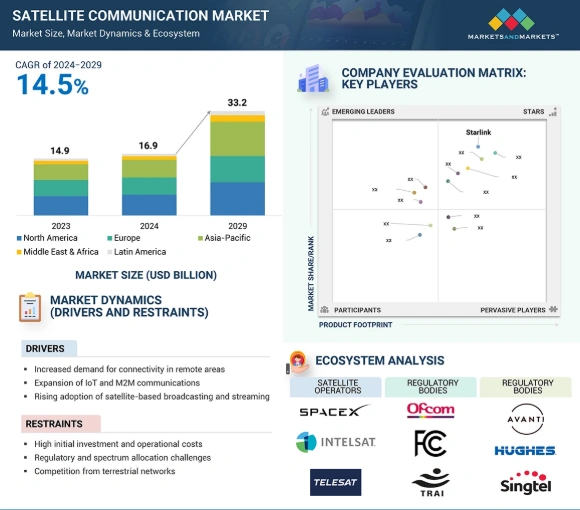
Credit: Markets and Markets
MinWave enables Satellite Optimization
Swiss startup MinWave designs metamaterial-based antennas and waveguide components for high-frequency communication in satellite, 5G, and IoT networks.
It uses low-loss metallic resonant metamaterials confined within sub-wavelength volumes. This method enables compact, lightweight devices that reduce size and improve efficiency compared to traditional hollow waveguides.
The startup develops passive RF components such as filters, diplexers, and filtering antennas. These components operate across 1 to 100 GHz and suit systems with strict volume and weight constraints.
MinWave fabricates monolithic RF parts through additive manufacturing and precision machining. It uses materials like aluminum, copper, and brass, and applies surface treatments such as silver plating to lower insertion loss and improve power handling.
It supports compact and cost-efficient RF solutions for space, defense, and emerging wireless systems.
Paradigma Technologies makes mmWave Solutions for Small Satellites
Slovenian startup Paradigma Technologies builds compact RF communication systems for satellites and aerospace platforms. These systems integrate phased array antennas with high-frequency transmitters, receivers, and transponders across Ka, K, and Q bands.
The startup uses electronically steered arrays and metamaterial-based designs. This approach enables beamforming, polarization control, and protocol compatibility while maintaining low size and weight.
Its product line includes radiation-tolerant Q Band transmitters, Ka Band transponders, and K Band transmitters. These devices support up to 250 MHz signal bandwidth and feature integrated modulators and digital gain controls.
Paradigma Technologies also offers Ka Band receivers with UHF transceivers. These units provide high-sensitivity signal capture, forward and return channels, and support for multi-standard modulation.
It combines miniaturized architecture with energy efficiency and EMI shielding to support scalable communication for LEO and GEO satellites, drones, and space-based IoT applications.

6. Digital Twins & Network Virtualization: Save 20% on Costs and Cut Energy Use by 15%
Telecom operators face growing pressure to reduce operating expenses, accelerate rollouts, and maintain quality of service across increasingly dense 5G networks.
Network digital twins (NDTs) offer predictive insights and safe environments for testing network changes. Nokia Bell Labs identified a potential 24.8% annual savings in network operations across 16 NDT use cases for mid-tier operators. Pilot projects have shown up to 20% cost savings and 15% lower energy consumption through improved planning and maintenance.
In parallel, network functions virtualization (NFV) separates software from proprietary hardware. NetCracker estimates that virtualization is able to reduce connectivity costs by more than 30% while enabling flexible, software-based service creation. Real-time, AI-powered digital twins mirror live KPIs, simulate what-if scenarios, and validate closed-loop automation before changes reach the production network.
The integration of edge computing, software-defined networking (SDN), and Kubernetes-native virtual network functions (VNFs) supports microservice agility and fine-grained scaling. According to ETSI, Tier-1 communication service providers run NFV in production or at scale-out stages.
Investment priorities are shifting from hardware upgrades to cloud automation. Telecom companies spend over USD 400 million annually on integration costs, which virtualization aims to reduce. In support of global standardization, India’s Department of Telecommunications is collaborating with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) to promote digital twin methodologies and host the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference in 2030.
The network function virtualization market is valued at USD 37.22 billion in 2025. It is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 28.8%, reaching USD 131.79 billion by 2030. This expansion is driven by cloud-native architecture adoption, rapid 5G deployment, and the shift from capital-intensive infrastructure to flexible operating models.
Deepwise creates a Geographical Digital Twin
Turkish startup Deepwise builds an AI-powered platform that creates large-scale geographical digital twins for energy, telecom, and government infrastructure. It integrates remote access and image-based asset monitoring to support centralized oversight.
The platform combines AI with advanced image processing to analyze visual data from distributed assets. It enables detailed mapping, anomaly detection, and condition tracking across smart cities, EV charging networks, and telecom sites.
The startup uses software-driven models to replicate field conditions. This approach reduces the need for imported devices and lowers infrastructure costs.
Its digital twin methodology enables organizations to manage and optimize performance remotely. The platform improves visibility and responsiveness that supports scalable digital transformation for public and industrial services that remain under-digitized.
AticaraTech provides a Software-based Network Traffic Simulator
Indian startup AticaraTech develops a software-based network traffic simulator to test SDN/NFV solutions, traditional hardware-based networks, and security products.
The virtual network function test uses a 1/10/25/40/50/100 Gbps traffic emulator to facilitate interaction with the network traffic and generate insights.
It is compatible with hypervisors like ESXI, KVM, OpenStack, and workstation virtualization software like VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox. The platform provides real-world traffic replay and malware testing capabilities.
7. Edge Computing & Ultra-Low Latency Applications: Market to Grow from USD 565B to USD 5.1T by 2034
The accelerated digital transformation is driving the adoption of edge computing. Global spending on edge computing is expected to rise. Enterprise interest continues to grow, with 73% of surveyed companies planning to improve edge investments over the next 12 months.
The rollout of 5G and demand for ultra-low latency are creating new requirements for edge deployment. 5G networks support latency as low as 1 millisecond through Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC). These capabilities enable mission-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and immersive AR/VR experiences.
Standardization of Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) by ETSI supports ultra-low latency and high bandwidth. MEC platforms provide real-time access to radio network data and allow flexible application deployment at cellular base stations. They also support multitenancy environments, making them suitable for diverse enterprise use cases.
5G features such as network slicing and URLLC ensure consistent Quality of Service. Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) delivers speeds up to 10 Gbps, while massive machine-type communications (mMTC) support millions of simultaneous device connections.
Edge-native AI integration enables real-time decision-making by processing data closer to endpoints. Edge computing acts as a bridge between connected devices and core IT systems. This setup reduces network congestion and accelerates response times for time-sensitive applications.
Verizon is advancing edge deployment through its partnership with AWS Wavelength. The company has launched 19 edge nodes across major US cities, each serving populations over 2 million. It focuses on 5G edge applications such as AR-based maintenance in manufacturing and real-time analytics.
The global edge computing market is projected to grow from USD 564.56 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 5.1 trillion by 2034, with a CAGR of 28% from 2025 onward.
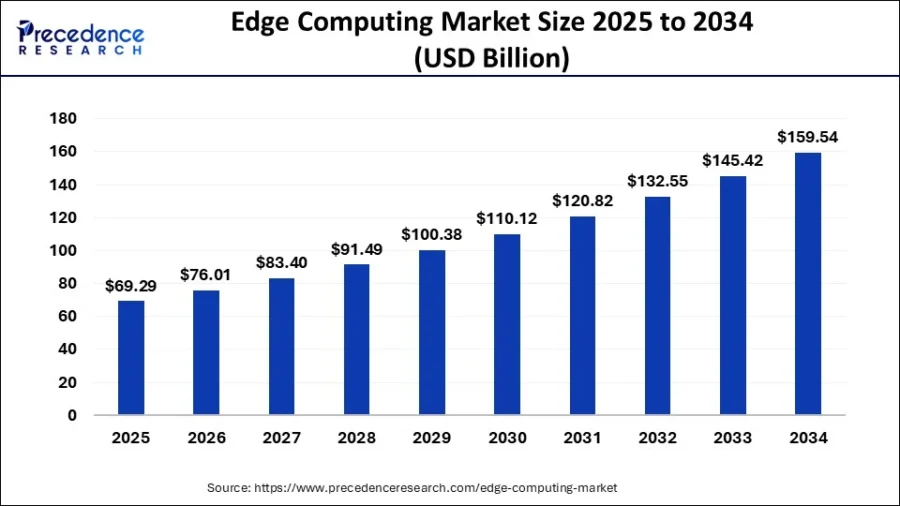
Credit: Precedence Research
SpectrEdge offers an AI-Powered 5G Network in a Box
US-based startup SpectrEdge builds AI-powered 5G edge computing solutions for secure, autonomous connectivity in tactical, expeditionary, and underserved environments. It integrates deep learning, network slicing, and multi-access edge computing into rugged, compact platforms.
Its platform PulsarEdge, is a 5G system that includes RAN, Core, and Wi-Fi 6 in a unit smaller than an iPad. It supports one-switch deployment in under two minutes and operates across multiple 5G spectrum bands. The system also includes built-in storage for hosting third-party machine learning models.
In addition, Spectrdge offers the Pulsar Cell Series, which features AI-SoC-based small cells with integrated baseband and spectrum monitoring. The Pulsar 5G AI Core Series provides AI-enabled RAN and Core optimization to support thousands of users.
It combines security standards, predictive analytics, and flexible backhaul options such as Starlink and MANET to deliver resilient wireless infrastructure for dynamic field operations.
Radian Arc provides Cloud Gaming & SDN Services
Radian Arc is an Australian startup that offers GPU computing, storage, and networking infrastructure for telecommunication service providers. The distributed GPU-based edge provides a low-latency network for improving value-added services, monetizing 5G investments, faster cloud gaming, and SDN services.
![Top 10 Telecom Industry Trends [2025 & Beyond] | StartUs Insights](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Radian-Arc-Chairman-900x435.webp)
The low-latency network also facilitates applications like AI and machine learning. The GPU edge solutions are also available as an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), a paid host of bare metal-as-a-service (BMaaS), and virtual machine-as-a-service (VMaaS).
8. 6G: Market to Reach USD 57.55 B by 2034
Emerging performance requirements for 6G include data rates reaching terabits per second, latency measured in microseconds, and highly reliable network operations. 6G will operate in the terahertz spectrum, using frequencies between 7-20 GHz for mobile coverage and W-band (75-110 GHz) and D-band (110-175 GHz) for access networks.
AI-native network architecture marks a major shift in telecom design. 6G is expected to embed AI directly into networking equipment. Machine learning systems will analyze traffic, identify patterns, allocate resources, and enhance security without manual intervention.
Terahertz communications support unprecedented speeds. Research has demonstrated data rates of 938 gigabits per second, which is far beyond current 5G capabilities. Samsung achieved indoor 6G speeds of 6 Gbps at 15 meters, 12 Gbps at 30 meters, and 2.3 Gbps at 120 meters.
Moreover, advanced network capabilities will support new use cases. AI-driven air interface design and network management will enable self-learning and self-training networks. Network slicing will allow dedicated virtual networks with customized performance. Zero-energy devices will harvest power from environmental sources, supporting sustainable deployments.
Telecom companies are investing in 6G development. Huawei, with USD 58.6 billion in revenue and a leading position in 5G patents, is focusing on AI integration and next-generation research. Ericsson, with USD 10.7 billion in revenue, is expanding its 6G research through global partnerships.
The global 6G market is projected to reach USD 57.55 billion by 2034. This growth reflects a compound annual rate of 24% from 2024 to 2034.
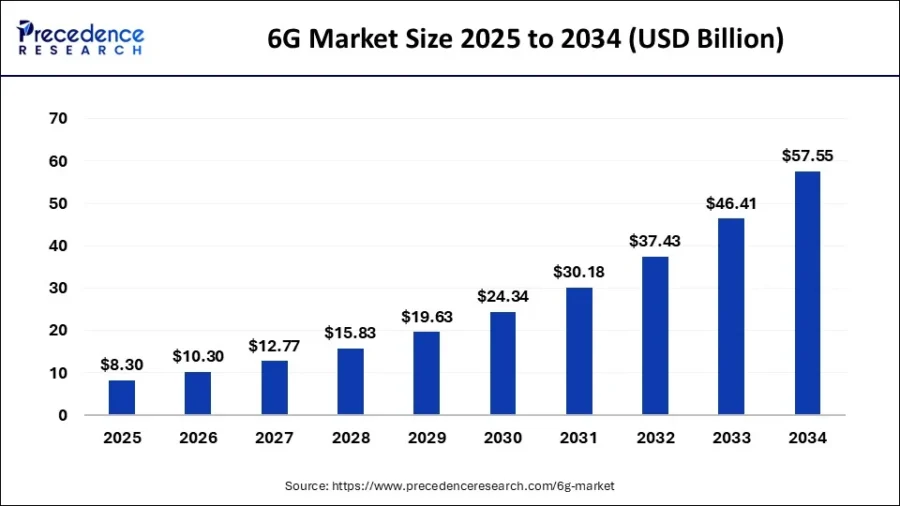
Credit: Precedence Research
TeraSi designs 6G-Compliant RF Products
TeraSi builds 6G-compliant RF components. It combines semiconductor construction, system-in-package (SiP) technology, ultra-low loss, and lightweight design to create high-performance RF systems. These components operate at frequencies beyond 100 GHz essential for next-generation wireless technologies.
The reduced size and weight assure convenient integration with semiconductor devices and passive components in telecoms, radar, and satellite applications.
Desire6g offers Programmable Distributed 6G Networks
Desire6g, based in North Holland integrates AI into a measurable and programmable data plane. This integration develops a zero-touch control, management, and orchestration platform to support extreme ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) applications.
The company enables automated management, better security, and high programmability, which contribute to the efficiency and reliability of 6G networks.
9. Fixed Wireless Access Growth: 78% of Global Providers Offer FWA
The demand for fast, deployable broadband is continuing to rise in underserved areas. Since mid-2022, FWA has accounted for all fixed-broadband subscriber growth in the US, adding 600 000 to 700 000 new users each quarter.
Operators are leveraging surplus 5G capacity to monetize spectrum. Currently, 78% of global service providers offer FWA. However, only 53% have adopted 5G-FWA, leaving room for further expansion.
FWA offers a cost advantage over fiber, especially in rural markets. Wireless internet service providers (WISPs) in the US need just 1-2% market share to break even, compared to 30-40% for fiber deployments.
Mid-band 5G FWA already reaches 30 million US homes through T-Mobile. Self-install customer premises equipment (CPE) and dynamic traffic management allow for maintaining mobile speeds as FWA usage increases.
In urban areas, mmWave phased-array antennas enable gigabit-class FWA while addressing range and penetration challenges. Meanwhile, RedCap (5G-A) CPE trials in Saudi Arabia are testing differentiated service tiers under the FWA 2.0 label.
In India, BSNL launched SIM-less Direct-to-Device 5G FWA in Hyderabad. This plug-and-play model eliminates the need for SIM cards and simplifies setup.
Moreover, the global FWA market is projected to reach USD 476.3 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual rate of 19.8% from 2024 to 2030.
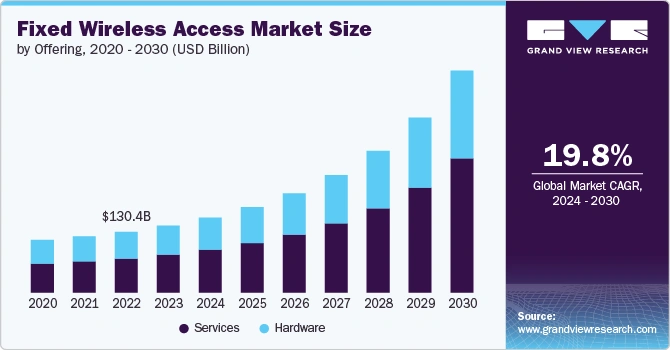
Credit: Grand View Research
Katalyst manufactures Carrier-Agnostic Fixed Wireless Routers
US-based startup Katalyst builds cellular-enabled hardware that provides internet access for businesses in remote, rural, and mobile settings. Its devices operate without traditional wiring or complex installation.
It offers plug-and-play 4G and 5G routers, including the SPARK K500A with a built-in battery and the KADET K300NB. These units run on standard cellular networks and activate through a simple onboarding process.
The startup’s product line also includes the SIREN outdoor omnidirectional antenna and the HAWK C401B solar-powered security camera. These devices support deployment in construction sites, retail locations, farms, and public safety operations.
Ambiflo makes the Digitized Development System
US-based startup Ambiflo creates digital and cellular connectivity tools that support telecom infrastructure projects. Its solutions combine interactive 3D lifecycle management with real-time wireless access.
The startup follows a dual approach. It provides plug-and-play 4G/5G routers for remote connectivity. It also offers a Digitized Development System (DDS) that transforms telecom network data into interactive 3D digital twins. Teams use these twins to plan, deploy, and maintain infrastructure more effectively.
The platform integrates geospatial data, AI, and game engine technology. This combination allows teams to visualize assets, simulate scenarios, and improve network operations.
Ambiflo’s hardware supports dual-SIM use, off-grid deployment, and secure communication in underserved areas. These features enhance flexibility and reliability in challenging environments.
10. Open RAN & Vendor Diversification: US Backs Development with USD 420 M for Trials and Tooling
Telecom operators aim to avoid single-vendor lock-in and strengthen supply chains. In response, governments are supporting Open RAN development. The US NTIA has allocated up to USD 420 million for trials and tooling. Besides, Japan’s MIC funded Rakuten’s test center in the UK.
Open RAN adoption is expanding. Ten countries already host commercial deployments. By 2029, operators are expected to roll out over 2 million Open RAN base stations.
Disaggregated radio, distributed, and centralized units (RU-DU-CU) with open fronthaul are active in trials by Rakuten, Dish, and Vodafone. Specifications from the O-RAN Alliance continue to mature.
The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) supports AI-driven network optimization. Orange demonstrated performance parity with traditional RAN systems during a pilot in Romania.
Rakuten Symphony offers cloud-native CU/DU software through subscription-based licensing. This model supports flexible deployment and ongoing updates.
Besides, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) brings together operators including AT&T, Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, and Telus. Their working group is refining open blueprints and continuous integration/testing frameworks.
The Open RAN market is projected to reach USD 20.9 billion by 2030. It is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 39.4% from 2024 to 2030.
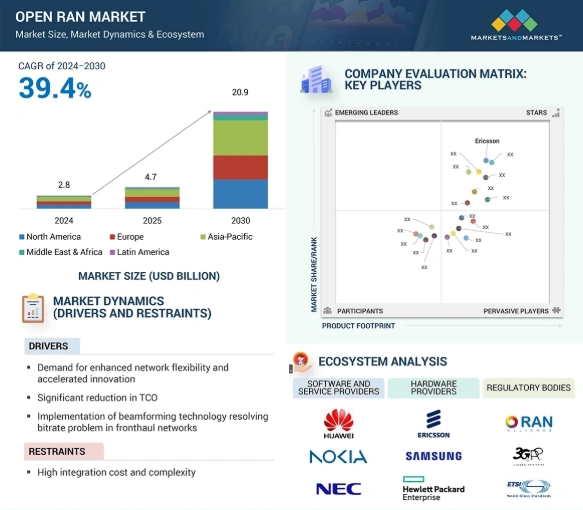
Credit: Markets and Markets
SliceFinity offers Network APIs, Slicing & Analytics
UK-based startup SliceFinity builds a cloud-native platform for Open RAN and 5G monetization. It allows telecom operators to virtualize radio access networks and offer programmable services.
The platform uses a modular design to deploy containerized baseband functions on commercial hardware. It also supports automation, orchestration, and AI-driven optimization across multivendor systems.
SliceFinity includes three core plugins. The Trusted Application Function (T-AF) connects 3GPP network APIs with enterprise and internal applications. The Service Differentiation module delivers time-bound, quality-assured user experiences. The Analytics engine consolidates data from the 5G Core, RAN intelligence, and external sources to support predictive reporting.
These tools enable operators to implement dynamic slicing, expose APIs, and monetize connectivity. They also simplify management of disaggregated infrastructure.
GENEViSiO develops 5G Open RAN inline PCIe DU
Taiwanese startup GENEViSiO builds open network infrastructure for telecom operators and private network providers. Its solutions combine disaggregated broadband systems with Open RAN technologies.
It offers a cloud-native broadband network gateway (BNG) operating system and specialized hardware. This includes an ASIC-based DU inline accelerator that offloads Layer 1 processing through PCIe cards using NXP’s Layerscape Access processors.
The accelerator lowers CPU load and latency. It supports multiple 25GbE eCPRI interfaces and connects with up to four 4T4R 100MHz radio units.
GENEViSiO also provides the NPN series of open fronthaul small cells. These support sub-6GHz to mmWave bands and allow DU+CU or DU-only configurations. They work in demanding environments such as manufacturing, railways, and agriculture.
Discover all Telecom Trends, Technologies & Startups
Quantum networking, AI-native orchestration, and energy-efficient infrastructure are advancing as performance and sustainability grow in importance. In parallel, programmable network APIs, terahertz communication, and space-based 5G/6G integration are taking shape. These technologies signal a shift toward connectivity that is intelligent, adaptive, and globally integrated.
The Telecom Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.



![10 Top AI Solutions for Telecom Operations [2025]](https://www.startus-insights.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/AI-Solutions-for-Telecom-Operations-SharedImg-StartUs-Insights-noresize-420x236.webp)





