Atomic-scale innovations in material sciences and microscopy are driving nanotechnology trends with applications across industries. Startups use nanomaterials to engineer a range of new structures, devices, and composite materials. Further, nanotechnology facilitates improvements in technologies such as additive manufacturing, quantum computing, and precision biotechnology.
The top nanotechnology trends range from advanced carbon and composite-based nanomaterials to nanoencapsulation. Read further to explore how these trends impact your business. This post was published in November 2022 and updated in August 2023.
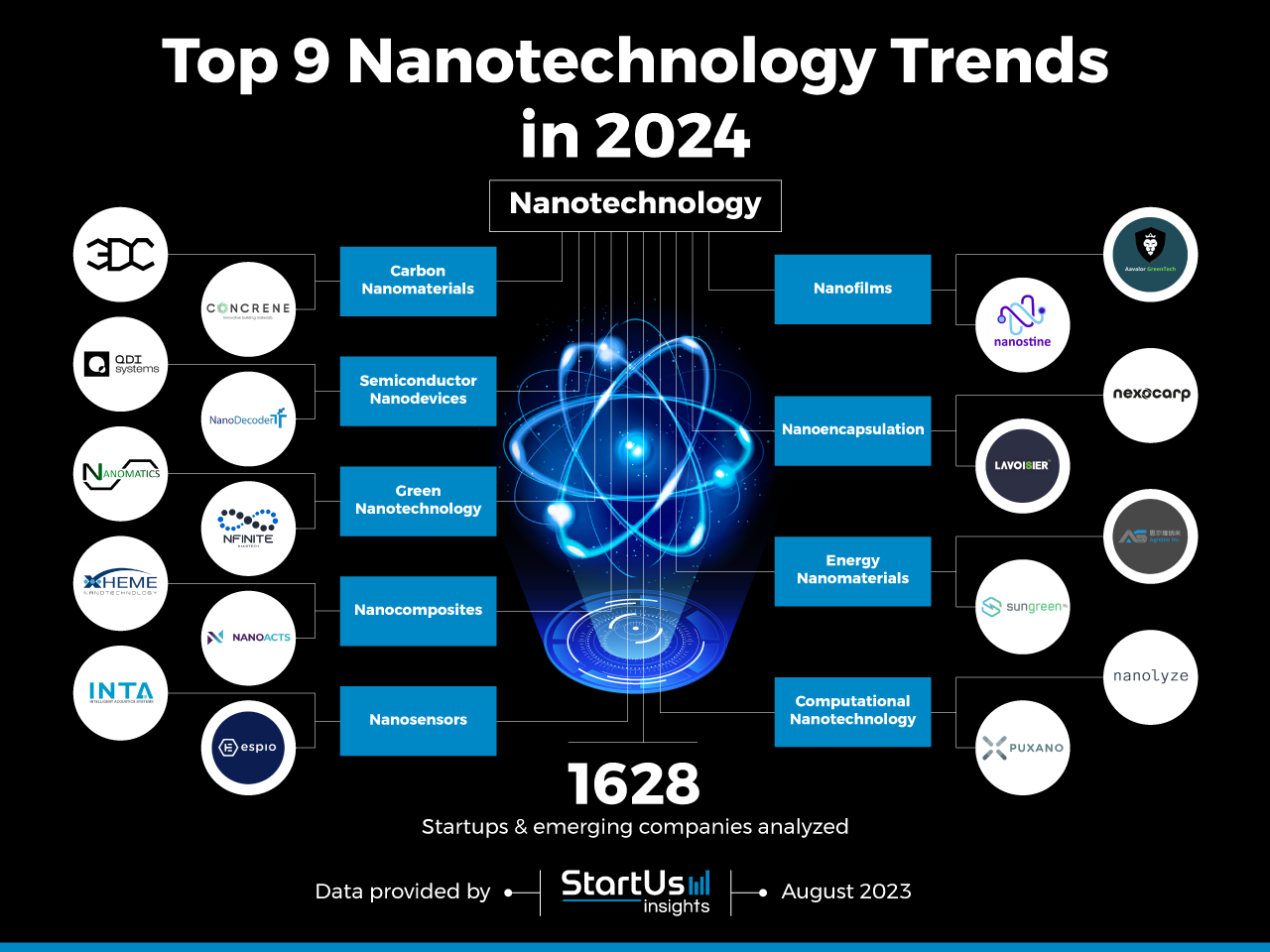
Innovation Map outlines the Top 9 Nanotechnology Trends & 18 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the top trends in nanotechnology and innovative startups, we analyzed a sample of 1628 global startups & scaleups. This data-driven research provides innovation intelligence that helps you improve strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies across numerous industries. In the Nanotechnology Innovation Map below, you get a comprehensive overview of the innovation trends & startups that impact your company.
Top 9 Trends in Nanotechnology (2024)
- Carbon Nanomaterials
- Semiconductor Nanodevices
- Green Nanotechnology
- Nanocomposites
- Nanosensors
- Nanofilms
- Nanoencapsulation
- Energy Nanomaterials
- Computational Nanotechnology
These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, covering 3 790 000+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant technologies and industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
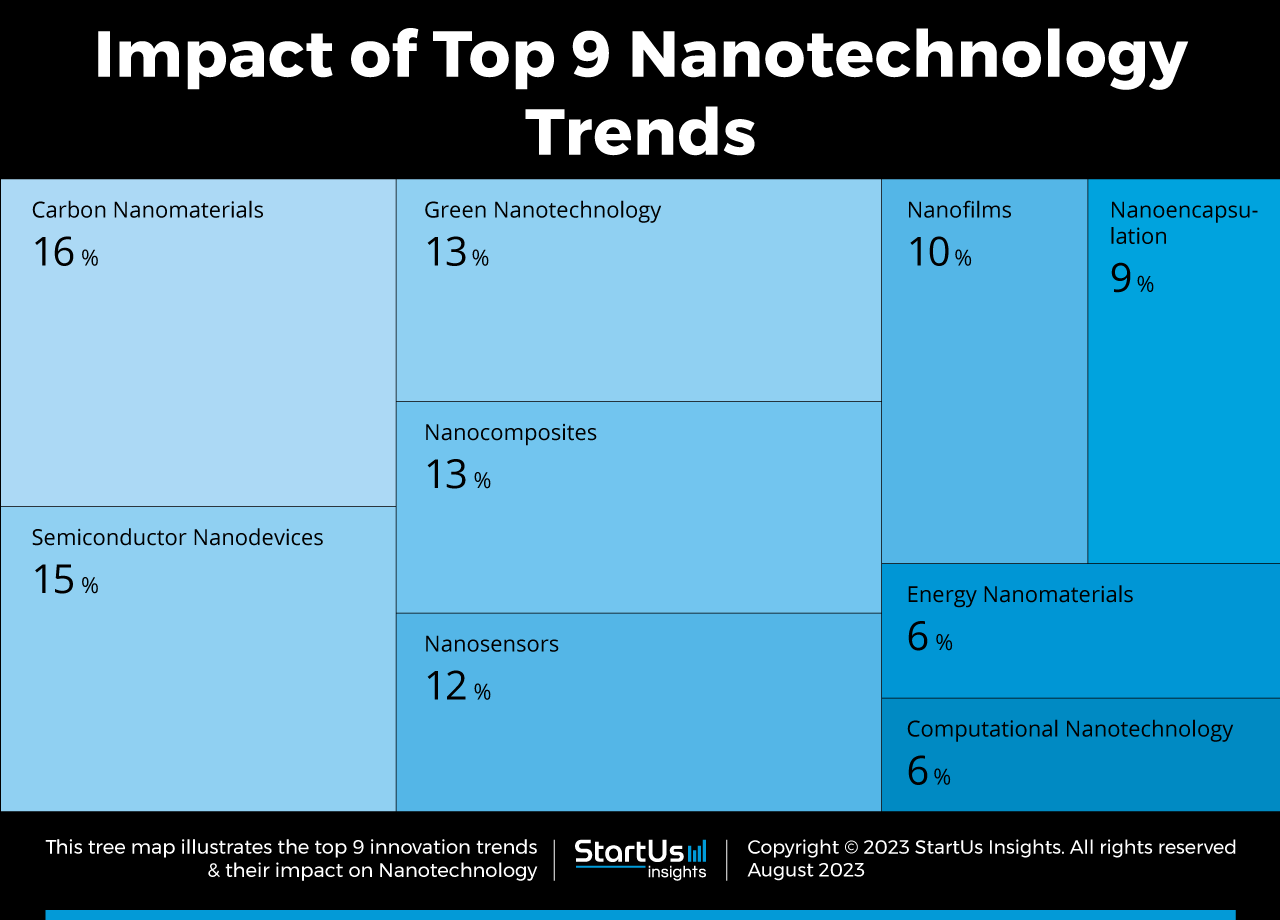
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 9 Nanotechnology Trends
Based on the Nanotechnology Innovation map, the Tree Map below illustrates the spread of the top 9 Nanotechnology trends in 2024. Startups and scaleups are developing carbon nanomaterials and nanocomposites with different complexity and features. Computational nanotechnology provides decision support for intelligent nanoparticle development.
Further, nanoparticle-based delivery systems, encapsulation, and nanosensors predominantly find use in precision medicine and drug development. Semiconductor nanodevices and nanobots are advancing device engineering capabilities. Similarly, startups are developing nanomembranes and nanofilms for versatile applications while green nanotechnology practices are enabling sustainable nanotech solutions.
Global Startup Heat Map covers 1628 Nanotechnology Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 1628 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that Europe has the highest density of nanotech startups.
Below, you get to meet 18 out of these 1628 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These nanotechnology startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, & more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Top 9 Nanotechnology Innovation Trends in 2024
1. Carbon Nanomaterials
Startups are continuously developing new methods and improving conventional methods such as carbon-vapor deposition (CVD) to synthesize carbon nanomaterials. This enables the development of carbon nanostructures with higher mechanical strength, chemical stability, durability, and flexibility compared to conventional materials. Graphene, carbon dots, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are some carbon nanomaterials that find use in electronics, tissue engineering, and textiles.
Single and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs and MWCNTs) provide low resistance conductivity and therefore serve as nanofillers to develop electronic structures. Startups also use carbon-based nano additives like graphene-integrated catalysts, nanodiamonds, and carbon nanofibers to develop reinforced materials.
3DC develops Graphene Mesosponge
Japanese startup 3DC develops graphene mesosponge (GMS), a 3D carbon nanomaterial with a mesoporous framework made of single-layer graphene. 3D porosity provides GMS with a large surface area that increases durability, elasticity, and conductivity compared to other porous carbon materials. Moreover, 3DC’s proprietary template technique customizes carbon materials by controlling the pore structure at the nano-scale. The startup’s GMS material finds applications as an electrode active material and catalyst in capacitors, fuel cells, and next-generation battery technologies.
Concrene offers a Graphene-based Concrete Mix
UK-based startup Concrene makes a graphene-based concrete mix. The startup uses nanotechnology to integrate properties of graphite, like its mechanical strength and compatibility with composite materials, into concrete. Additionally, Concrene’s manufacturing process supports both graphite-derived and synthetic graphene. This enables construction companies to decarbonize and replace conventional concrete without compromising material quality.
2. Semiconductor Nanodevices
Advances in miniaturization are leading to the development of nanoscale semiconductor devices and nanorobotics. Startups utilize molecular nanotechnology (MNT) to manufacture devices and scientific instruments such as nanomanipulators and nanotransistors with high precision. Ultra-dense memory technologies, compact microprocessors, and chips in electronic circuitry enable high-performance computing in smaller form factors.
Additionally, nanodevices support performance requirements in earth observation satellites, consumer electronics, electronic sensing, and autonomous vehicles. Industrial use cases of nanobots include remote monitoring and servicing in hazardous environments.
QDI Systems fabricates Quantum Dots (QDs)
Dutch startup QDI Systems manufactures lead sulfite-based quantum dots. The startup’s semiconducting QD nanocrystals feature high attenuation rates, thus providing increased image resolution and contrast in X-ray imaging. Moreover, the QDI Systems’ technology enables the development of customized semiconductive QD films suited to manufacture a variety of optoelectronic devices. Medical device manufacturers use it to make high-resolution X-ray sensors and imaging devices at low radiation rates.
NanoDecoder develops Bioinspired Nanosystems
Swiss startup NanoDecoder engineers bioinspired nanosystems for product tracking and anti-counterfeiting. The startup’s complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) molecular electronic chips combine nanopore sensing and machine learning (ML) to verify product authenticity. The nanopores store digital information in DNA or synthetic molecules at ultra-high density. This provides a portable, faster, and cost-effective substitute for radiofrequency identification (RFID) tags and barcodes for logistics companies.
3. Green Nanotechnology
The nanotechnology sector is transitioning from combustion-based manufacturing processes to greener nanoparticle synthesis methods. Startups leverage biofabrication to develop analogous biomaterials from plants or other biobased raw materials. Circular economy measures also facilitate the development of biodegradable polymeric and metal nanomaterials from recycled metals, plastic, food, and agricultural waste. Beyond green synthesis, nanotechnology enables environment-friendly use cases as well. For instance, nanomaterials enable the bioremediation and biotransformation of soil, wastewater, oil spills, and other toxic pollutants.
Nanomatics makes Recycled Carbon Nanotubes
Singaporean startup Nanomatics creates recycled carbon nanotubes. The startup uses pyrolysis to decompose plastic waste into eco-friendly MWCNTs. Water-free techniques then remove metal impurities and functionalize these CNTs. Nanomatics’ CNTs possess low metal content and find use in energy storage, electronics, and as additives. Additionally, they reduce carbon emissions by eliminating the need for virgin materials and cutting down fossil resources, which reduces freshwater use.
Nfinite Nanotech manufactures Smart Nanocoatings
Canadian startup Nfinite Nanotech develops smart barrier nanocoatings for food packaging. The startup’s technology enables uniform ultrathin film deposition on existing biodegradable and recyclable packaging materials without altering their biodegradability. It provides plastic-like barrier properties against external conditions to compostable packaging and increases the shelf life of food. The technology integrates with existing production lines of food packaging manufacturers and works with different classes of packaging materials.
4. Nanocomposites
Nanocomposites like metal-organic framework (MOF) crystals, carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), and nano-ceramics increasingly find use in automotive and aerospace industries. Innovations in metal and polymer matrix nanocomposites are making their manufacturing easier with techniques like 3D printing. Further, nano-reinforcement alters the microscopic properties of standard materials.
This allows researchers to create nanocomposites with a higher surface-to-volume ratio as well as superior mechanical and optical characteristics. Startups leverage nanocomposites in various ways, including coatings, additives, catalysts, and structural components. Biotech startups are also developing polymer and organic nanocomposites for tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, drug delivery, and cellular therapies.
Xheme makes Polymeric Nanocomposites
US-based startup Xheme develops patented blood bags and tubing from a polymeric nanocomposite. The startup’s nanocomposite is free from plasticizers and provides barrier protection from additives seeping into the blood. Further, it prevents oxidation and increases the shelf life and functional health of whole blood and platelets. Xheme’s technology addresses blood degradation, shortage, and wastage in hospitals and blood banks.
Nanoacts creates Nanogenerators
Bulgarian startup Nanoacts combines material science and artificial intelligence (AI) to create nanogenerators. The startup’s production method uses proprietary 2D or 3D bio-hybrid printing and hybrid nanocomposite coating deposition technologies. Its autonomous nanogenerators convert waste mechanical and chemical energy into electricity in real-time, thereby reducing dependence on fossil fuels. The technology finds use in autonomous devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), Internet of Body (IoB) networks, smart homes, and defense.
5. Nanosensors
Startups are creating nanometer-scale electrochemical and mechanical sensors for molecular-level detection and sensing. Nanolithography, molecular self-assembly, and bottom-up assembly are common techniques to produce these nanosensors. Nano-enhanced lab-on-a-chip solutions and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) are advancing DNA analysis, proteomics, atomic force microscopy, and disease detection.
Further, they find use in injectable biosensors and brain-computer interfaces for personalized treatments. Likewise, nano biosensors in wearables provide critical health data for workers and public safety. Smart nanosensors are also enabling contamination detection, environmental measurements, remote sensing, and communication.
INTA builds Lab-on-a-Chip
Italian startup INTA develops a lab-on-a-chip solution for biomolecular analysis. It uses nanoacoustics and a microfluidic channel on a piezoelectric chip to detect biomarkers of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in blood. Using AI, it then analyzes the difference in resonance frequency position of the biosensors after the immobilization of probe molecules. The technology enables rapid detection of several types of biological analytes with high accuracy for disease diagnosis, environmental monitoring, and food analysis.
Espio develops Graphene Nanosensors
Slovakian startup Espio produces ultra-thin nanosized graphene sensors for device temperature monitoring. The startup’s technology directly spray-coats the graphene-sensing nanolayer on a thin flexible foil. This improves the measurement reliability of the sensor and enables large-area temperature monitoring, including on curved surfaces. This way, the startup offers a low-cost and reliable solution for temperature sensing in battery technology, electronics, aerospace, and process industries.

6. Nanofilms
The porosity of natural and artificial nanofilms enables economical, atomic-level separation and filtration. This is why startups readily use graphene, MOFs, and other nanomembrane technologies for water purification, air filtration, and more. Startups are also developing nanoporous membranes for wastewater management, desalination, and demineralization. Nanofiltration has applications in the food, biotech, and oil and gas industries.
Further, nanofibers and bioinspired membranes enable technologies for biomass fuel production, microelectronics manufacturing, and nanomedicine. Color preserving and anti-bacterial food coating, hydrophobic nanocoatings in audiology, and hydrophilic antifouling coatings are some popular applications of nanocoatings.
Aavalor offers Nanofiltration Membranes
UK-based startup Aavalor develops nanofiltration technology for water purification. The startup’s scalable desalination technology uses graphene membranes to filter out heavy metals, contaminants, bacteria, and salt. The filter relies on the force of gravity instead of energy to provide clean water with low wastage. This solution empowers public and private stakeholders in the water and shipping industry to set up emission-free and affordable purifiers and desalinators.
Nanostine fabricates Nanostructured Coatings
Spanish startup Nanostine develops ultra-pure nanostructured coatings. The startup leverages ultra-high vacuum technology with magnetron sputtering to fabricate ligand-free nanoclusters and nanoparticles with high crystalline order. This technology controls the purity of the coatings for anti-multifactor and antimicrobial applications. For aerospace and space original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), the startup’s nanocoatings increase component durability and reduce performance wear and tear.
7. Nanoencapsulation
Nanoencapsulation has applications in targeted drug delivery, bioimaging, theragnosis, immunization as well as environmental use cases. Startups are advancing nanoencapsulation technologies that provide higher encapsulation efficiency, product yield, stability from degradation, and controlled release.
For instance, biopolymeric and organic nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, nanolaminates, and nanocapsules act as carrier platforms and replace microplastics. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems improve the solubility and bioavailability of drugs, nutraceuticals, and fertilizers, thus providing better results with smaller volumes and fewer doses.
nexocarp advances Sustainable Microencapsulation
Israeli startup nexocarp offers sustainable encapsulation technology for the agriculture, cosmetics, pharmaceutical, and food industries. It uses nanoshells made from natural materials such as lipids to encase core ingredients in a solid micro-encapsulated particle powder form. This enables the startup to create slow-release active ingredients with the potential for releasing both core and surface agents.
Lavoisier provides Nanencapsualted Drug Delivery
US-based startup Lavoisier creates a nanoencapsulation platform for drug delivery. It uses amphiphilic polyelectrolytes to encapsulate target biopharmaceuticals and produce formulations with desired properties. This increases the stability and in-vivo therapeutic effects of the encapsulated drug. The startup’s pipeline includes drugs for infectious diseases.
8. Energy Nanomaterials
Energy nanomaterials are increasing the efficiency and affordability of energy storage, conservation, and production systems. Nanotexturing of existing energy components results in increased durability and, hence, provides energy savings. Nanocoatings with anti-reflective, wear-resistant, thermal-resistant, and corrosion-protective properties improve the quality of electrodes and solar cells, among others. Nanoparticles find applications in supercapacitors and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. More recently, innovative nanocomposites, nanogels, and nanofoams have been useful in industrial and grid energy management.
Agnano fabricates Nanosilver Paste
Chinese startup Agnano produces a nanosilver paste for heterojunction technology (HJT) solar cells. It combines micro-nano silver powder, adhesive resin, solvents, and auxiliaries that protect the metalized electrodes of photovoltaic (PV) cells. The startup’s solution enables high printing efficiency and welding tension, low-temperature curing, as well as provides low resistivity. These properties allow solar PV module manufacturers to improve photovoltaic cell efficiency.
SunGreenH2 provides Nanostructured Components
Singaporean startup SunGreenH2 manufactures nanostructured components for electrolyzers. The startup’s platform technology and proprietary nanostructured materials reduce the need for expensive platinum group metals as catalysts. This enables the startup to develop low-carbon footprint electrolyzers and modular solar-to-hydrogen panels that accelerate green hydrogen production. This way, the startup is advancing the scalable adoption of zero-carbon hydrogen for energy storage, mobility, power-to-everything (P2X), and other industrial applications.
9. Computational Nanotechnology
Computational nanotechnology reduces time and costs in the design, modeling, and manufacturing of nanomaterials and nanomachines. Startups are leveraging computational methods to optimize production as well as advance the circular economy. Material startups employ genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization, and other techniques to create and analyze nanoparticle mega libraries. This speeds up the identification of nanostructures with desired properties.
Nanolyze aids Nanoparticle Characterization
Swedish startup Nanolyze develops tools for real-time nanoparticle characterization. The startup’s patented waveguide microscopy technology studies structural changes upon uptake at a single nanoparticle level. Further, it enables simultaneous fluorescent monitoring and nanoparticle sorting by analyzing particle size and localization. It then automates label-free particle analysis, which accelerates the development of next-generation delivery vehicles for pharmaceutical, diagnostic, and industrial applications.
PUXANO advances Protein Development
Belgian startup PUXANO combines nanotechnology and structural biology to further protein development. The startup’s proprietary platform facilitates high-throughput and high-resolution protein design, structural characterization, and data processing for purification and production. This allows pharmaceutical and biotech companies to generate structure and function-based insights on target proteins.
Discover all Nanotechnology Trends, Technologies & Startups
Nanotechnology will play a major role in advancing 3D and 4D printing of living tissues and smart materials. Startups are also beginning to use complex nanostructures for information encryption and decryption. While nanotechnology brings a host of benefits, nanotoxicity is a major concern that startups strive to solve. Sustainability and waste reduction also remain important goals for the sector.
The nanotechnology trends and startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation & startup scouting process. Identifying new opportunities & emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage.